Quinolone may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Quinolone may refer to:
| This set index page lists chemical compounds articles associated with the same name. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
DNA gyrase, or simply gyrase, is an enzyme within the class of topoisomerase and is a subclass of Type II topoisomerases that reduces topological strain in an ATP dependent manner while double-stranded DNA is being unwound by elongating RNA-polymerase or by helicase in front of the progressing replication fork. The enzyme causes negative supercoiling of the DNA or relaxes positive supercoils. It does so by looping the template so as to form a crossing, then cutting one of the double helices and passing the other through it before releasing the break, changing the linking number by two in each enzymatic step. This process occurs in prokaryotes, whose single circular DNA is cut by DNA gyrase and the two ends are then twisted around each other to form supercoils. Gyrase has been found in the apicoplast of the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum, a unicellular eukaryote and in chloroplasts of several plants. Bacterial DNA gyrase is the target of many antibiotics, including nalidixic acid, novobiocin, and ciprofloxacin.

Nalidixic acid is the first of the synthetic quinolone antibiotics.

Norfloxacin, sold under the brand name Noroxin among others, is an antibiotic that belongs to the class of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. It is used to treat urinary tract infections, gynecological infections, inflammation of the prostate gland, gonorrhea and bladder infection. Eye drops were approved for use in children older than one year of age.
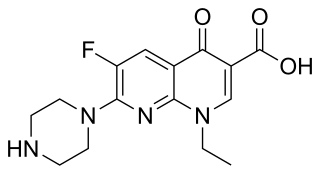
Enoxacin is an oral broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent used in the treatment of urinary tract infections and gonorrhea. Insomnia is a common adverse effect. It is no longer available in the United States.

Pefloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. Pefloxacin has not been approved for use in the United States.

Cinoxacin is a quinolone antibiotic that has been discontinued in the U.K. as well the United States, both as a branded drug or a generic.
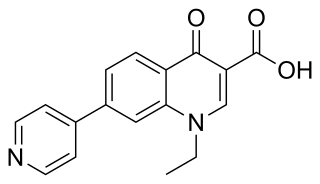
Rosoxacin is a quinolone antibiotic indicated for the treatment of urinary tract infections and certain sexually transmitted diseases. Rosoxacin is not available in the United States.
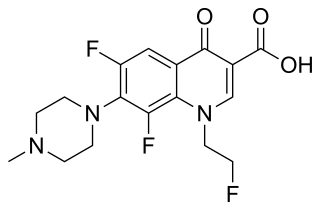
Fleroxacin is a quinolone antibiotic. It is sold under the brand names Quinodis and Megalocin.

Flumequine is a synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. It is a first-generation fluoroquinolone antibacterial that has been removed from clinical use and is no longer being marketed. It kills bacteria by interfering with the enzymes that cause DNA to unwind and duplicate. Flumequine was used in veterinarian medicine for the treatment of enteric infections, as well as to treat cattle, swine, chickens, and fish, but only in a limited number of countries. It was occasionally used in France to treat urinary tract infections under the trade name Apurone. However this was a limited indication because only minimal serum levels were achieved.

Rufloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic. It is sold under the brand names, Ruflox, Monos, Qari, Tebraxin, Uroflox, Uroclar.

Prulifloxacin is an older synthetic antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone class undergoing clinical trials prior to a possible NDA submission to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is a prodrug which is metabolized in the body to the active compound ulifloxacin. It was developed over two decades ago by Nippon Shinyaku Co. and was patented in Japan in 1987 and in the United States in 1989.
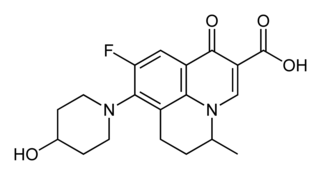
Nadifloxacin is a topical fluoroquinolone antibiotic for the treatment of acne vulgaris. It is also used to treat bacterial skin infections.

Tosufloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. It has a controversial safety profile in relation to other fluoroquinolones. It is associated with severe thrombocytopenia and nephritis, and hepatotoxicity. It is sold in Japan under the brand name Ozex.

Orbifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic which is approved for use in dogs, marketed by Schering-Plough Animal Health.

Pazufloxacin (INN) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. It is sold in Japan under the brand names Pasil and Pazucross.
Sarafloxacin (INN) is a quinolone antibiotic drug, which was removed from clinical use by its manufacturer Abbott Laboratories from April 30, 2001.

SER-601 (COR-167) is a drug which acts as a potent and selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonist, based on a quinolone-3-carboxylic acid core structure, with 190x selectivity for CB2 over the related CB1 receptor. It has analgesic effects in animal studies, as well as neuroprotective effects, but without a "cannabis high" due to it's low affinity for CB1. A number of related compounds are known, almost all of which have high selectivity for CB2.

A quinolone antibiotic is a member of a large group of broad-spectrum bactericides that share a bicyclic core structure related to the compound 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well as in animal husbandry.

Nemonoxacin is a non-fluorinated quinolone antibiotic undergoing clinical trials. It has the same mechanism of action as fluouroquinolones; it inhibits DNA gyrase, preventing DNA synthesis, gene duplication, and cell division. At the end of 2016, it had reached market in Taiwan, Russia, the Commonwealth Independent States, Turkey, mainland China, and Latin America under the brand name Taigexyn. Nemonoxacin has completed phase 2 trials in the USA and has moved on to phase 3 trials. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted nemonoxacin qualified infectious disease product (QIDP) and fast track designations for community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CAP) and acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections (ABSSSI).

4-Quinolone is an organic compound derived from quinoline. It and 2-quinolone are the two most important parent quinolones. 4-Quinolone exists in equilibrium with a minor tautomer, 4-hydroxyquinoline (CAS#611-36-9). Aside from pedagogical interest, 4-Quinolone is of little intrinsic value but its derivatives, the 4-quinolone antibiotics represent a large class of important drugs.