Background radiation is a measure of the level of ionizing radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources.

A Geiger counter is an instrument used for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation. Also known as a Geiger–Mueller counter, it is widely used in applications such as radiation dosimetry, radiological protection, experimental physics, and the nuclear industry.
Particle radiation is the radiation of energy by means of fast-moving subatomic particles. Particle radiation is referred to as a particle beam if the particles are all moving in the same direction, similar to a light beam.

In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:

A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation, is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and β+ decay, which produce electrons and positrons respectively.

A scintillation counter is an instrument for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation by using the excitation effect of incident radiation on a scintillating material, and detecting the resultant light pulses.
Radiation dosimetry in the fields of health physics and radiation protection is the measurement, calculation and assessment of the ionizing radiation dose absorbed by an object, usually the human body. This applies both internally, due to ingested or inhaled radioactive substances, or externally due to irradiation by sources of radiation.
Radiation protection, also known as radiological protection, is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The protection of people from harmful effects of exposure to ionizing radiation, and the means for achieving this". The IAEA also states "The accepted understanding of the term radiation protection is restricted to protection of people. Suggestions to extend the definition to include the protection of non-human species or the protection of the environment are controversial". Exposure can be from a radiation source external to the human body or due to the bodily intake of a radioactive material.

A lower gastrointestinal series is a medical procedure used to examine and diagnose problems with the human colon. Radiographs are taken while barium sulfate, a radiocontrast agent, fills the colon via an enema through the rectum.

Health physics is the applied physics of radiation protection for health and health care purposes. It is the science concerned with the recognition, evaluation, and control of health hazards to permit the safe use and application of ionizing radiation. Health physics professionals promote excellence in the science and practice of radiation protection and safety. Health physicists principally work at facilities where radionuclides or other sources of ionizing radiation are used or produced; these include hospitals, government laboratories, academic and research institutions, nuclear power plants, regulatory agencies, and manufacturing plants.
The ionization chamber is the simplest of all gas-filled radiation detectors, and is widely used for the detection and measurement of certain types of ionizing radiation; X-rays, gamma rays, and beta particles. Conventionally, the term "ionization chamber" is used exclusively to describe those detectors which collect all the charges created by direct ionization within the gas through the application of an electric field. It only uses the discrete charges created by each interaction between the incident radiation and the gas, and does not involve the gas multiplication mechanisms used by other radiation instruments, such as the Geiger counter or the proportional counter.
The film badge dosimeter or film badge is a personal dosimeter used for monitoring cumulative radiation dose due to ionizing radiation.
Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials (NORM) and Technologically Enhanced Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials (TENORM) consist of materials, usually industrial wastes or by-products enriched with radioactive elements found in the environment, such as uranium, thorium and potassium and any of their decay products, such as radium and radon.
Radiobiology is a field of clinical and basic medical sciences that involves the study of the action of ionizing radiation on living things, especially health effects of radiation. Ionizing radiation is generally harmful and potentially lethal to living things but can have health benefits in radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer and thyrotoxicosis. Its most common impact is the induction of cancer with a latent period of years or decades after exposure. High doses can cause visually dramatic radiation burns, and/or rapid fatality through acute radiation syndrome. Controlled doses are used for medical imaging and radiotherapy.
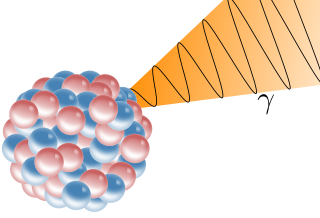
A gamma ray or gamma radiation, is a penetrating electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves and so imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation gamma rays based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; he had previously discovered two less penetrating types of decay radiation, which he named alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power.

Radiation monitoring involves the measurement of radiation dose or radionuclide contamination for reasons related to the assessment or control of exposure to radiation or radioactive substances, and the interpretation of the results.
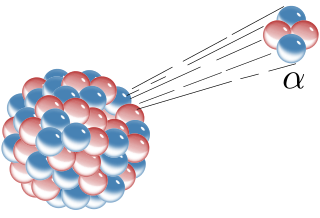
Alpha particles, also called alpha ray or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produced in other ways. Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α. The symbol for the alpha particle is α or α2+. Because they are identical to helium nuclei, they are also sometimes written as He2+
or 4
2He2+
indicating a helium ion with a +2 charge. If the ion gains electrons from its environment, the alpha particle becomes a normal helium atom 4
2He.
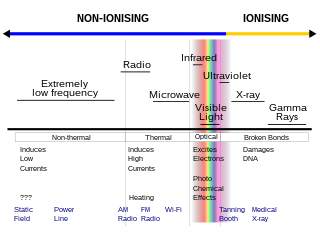
Non-ionizing radiation refers to any type of electromagnetic radiation that does not carry enough energy per quantum to ionize atoms or molecules—that is, to completely remove an electron from an atom or molecule. Instead of producing charged
ions when passing through matter, non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation has sufficient energy only for excitation, the movement of an electron to a higher energy state. Ionizing radiation which has a higher frequency and shorter wavelength than nonionizing radiation, has many uses but can be a health hazard; exposure to it can cause burns, radiation sickness, cancer, and genetic damage. Using ionizing radiation requires elaborate radiological protection measures which in general are not required with nonionizing radiation.











