Related Research Articles

The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993.
In molecular biology, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is a technique that exploits variations in homologous DNA sequences, known as polymorphisms, in order to distinguish individuals, populations, or species or to pinpoint the locations of genes within a sequence. The term may refer to a polymorphism itself, as detected through the differing locations of restriction enzyme sites, or to a related laboratory technique by which such differences can be illustrated. In RFLP analysis, a DNA sample is digested into fragments by one or more restriction enzymes, and the resulting restriction fragments are then separated by gel electrophoresis according to their size.
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.
Protein engineering is the process of developing useful or valuable proteins. It is a young discipline, with much research taking place into the understanding of protein folding and recognition for protein design principles. It has been used to improve the function of many enzymes for industrial catalysis. It is also a product and services market, with an estimated value of $168 billion by 2017.

Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It is primarily used to measure the amount of a specific RNA. This is achieved by monitoring the amplification reaction using fluorescence, a technique called real-time PCR or quantitative PCR (qPCR). Combined RT-PCR and qPCR are routinely used for analysis of gene expression and quantification of viral RNA in research and clinical settings.
Genetic linkage is the tendency of DNA sequences that are close together on a chromosome to be inherited together during the meiosis phase of sexual reproduction. Two genetic markers that are physically near to each other are unlikely to be separated onto different chromatids during chromosomal crossover, and are therefore said to be more linked than markers that are far apart. In other words, the nearer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the chance of recombination between them, and the more likely they are to be inherited together. Markers on different chromosomes are perfectly unlinked, although the penetrance of potentially deleterious alleles may be influenced by the presence of other alleles, and these other alleles may be located on other chromosomes than that on which a particular potentially deleterious allele is located.
In molecular biology, an amplicon is a piece of DNA or RNA that is the source and/or product of amplification or replication events. It can be formed artificially, using various methods including polymerase chain reactions (PCR) or ligase chain reactions (LCR), or naturally through gene duplication. In this context, amplification refers to the production of one or more copies of a genetic fragment or target sequence, specifically the amplicon. As it refers to the product of an amplification reaction, amplicon is used interchangeably with common laboratory terms, such as "PCR product."
The first isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was done in 1869 by Friedrich Miescher. Currently, it is a routine procedure in molecular biology or forensic analyses. For the chemical method, many different kits are used for extraction, and selecting the correct one will save time on kit optimization and extraction procedures. PCR sensitivity detection is considered to show the variation between the commercial kits.
Genetics, a discipline of biology, is the science of heredity and variation in living organisms.

AFLP-PCR or just AFLP is a PCR-based tool used in genetics research, DNA fingerprinting, and in the practice of genetic engineering. Developed in the early 1990s by KeyGene, AFLP uses restriction enzymes to digest genomic DNA, followed by ligation of adaptors to the sticky ends of the restriction fragments. A subset of the restriction fragments is then selected to be amplified. This selection is achieved by using primers complementary to the adaptor sequence, the restriction site sequence and a few nucleotides inside the restriction site fragments. The amplified fragments are separated and visualized on denaturing on agarose gel electrophoresis, either through autoradiography or fluorescence methodologies, or via automated capillary sequencing instruments.
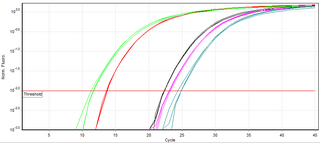
A real-time polymerase chain reaction is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR, not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively and semi-quantitatively.
Gene maps help describe the spatial arrangement of genes on a chromosome. Genes are designated to a specific location on a chromosome known as the locus and can be used as molecular markers to find the distance between other genes on a chromosome. Maps provide researchers with the opportunity to predict the inheritance patterns of specific traits, which can eventually lead to a better understanding of disease-linked traits.

Genetic analysis is the overall process of studying and researching in fields of science that involve genetics and molecular biology. There are a number of applications that are developed from this research, and these are also considered parts of the process. The base system of analysis revolves around general genetics. Basic studies include identification of genes and inherited disorders. This research has been conducted for centuries on both a large-scale physical observation basis and on a more microscopic scale. Genetic analysis can be used generally to describe methods both used in and resulting from the sciences of genetics and molecular biology, or to applications resulting from this research.
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) is a variation of the multiplex polymerase chain reaction that permits amplification of multiple targets with only a single primer pair. It detects copy number changes at the molecular level, and software programs are used for analysis. Identification of deletions or duplications can indicate pathogenic mutations, thus MLPA is an important diagnostic tool used in clinical pathology laboratories worldwide.
Delitto perfetto is a genetic technique for in vivo site-directed mutagenesis in yeast. This name is the Italian term for "perfect murder", and it refers to the ability of the technique to create desired genetic changes without leaving any foreign DNA in the genome.
Microfluidic whole genome haplotyping is a technique for the physical separation of individual chromosomes from a metaphase cell followed by direct resolution of the haplotype for each allele.
A sequence related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) is a molecular technique, developed by G. Li and C. F. Quiros in 2001, for detecting genetic variation in the open reading frames (ORFs) of genomes of plants and related organisms.

Genetic engineering techniques allow the modification of animal and plant genomes. Techniques have been devised to insert, delete, and modify DNA at multiple levels, ranging from a specific base pair in a specific gene to entire genes. There are a number of steps that are followed before a genetically modified organism (GMO) is created. Genetic engineers must first choose what gene they wish to insert, modify, or delete. The gene must then be isolated and incorporated, along with other genetic elements, into a suitable vector. This vector is then used to insert the gene into the host genome, creating a transgenic or edited organism.
Bulked segregant analysis (BSA) is a technique used to identify genetic markers associated with a mutant phenotype. This allows geneticists to discover genes conferring certain traits of interest, such as disease resistance or susceptibility.
Physical map is a technique used in molecular biology to find the order and physical distance between DNA base pairs by DNA markers. It is one of the gene mapping techniques which can determine the sequence of DNA base pairs with high accuracy. Genetic mapping, another approach of gene mapping, can provide markers needed for the physical mapping. However, as the former deduces the relative gene position by recombination frequencies, it is less accurate than the latter.
References
- Masters, John R. W. (2000). "Irradiation fusion gene transfer". Animal Cell Culture: A Practical Approach. Oxford University Press. pp. 252–255. ISBN 0-19-963796-2.