
Mexico City, or the City of Mexico, is the capital of Mexico and the most populous city in North America. Mexico City is one of the most important cultural and financial centres in the Americas. It is located in the Valley of Mexico, a large valley in the high plateaus in the center of Mexico, at an altitude of 2,240 meters (7,350 ft). The city has 16 boroughs.

Mexican cuisine began about 9,000 years ago, when agricultural communities such as the Maya formed, domesticating maize, creating the standard process of corn nixtamalization, and establishing their foodways. Successive waves of other Mesoamerican groups brought with them their own cooking methods. These included the Olmec, Teotihuacanos, Toltec, Huastec, Zapotec, Mixtec, Otomi, Purépecha, Totonac, Mazatec, and Mazahua.

North America is a continent entirely within the Northern Hemisphere and almost all within the Western Hemisphere; it is also considered by some to be a northern subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean, and to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea.

New Mexico is a state in the Southwestern region of the United States of America; its capital and cultural center is Santa Fe, which was founded in 1610 as capital of Nuevo México, while its largest city is Albuquerque with its accompanying metropolitan area. It is one of the Mountain States and shares the Four Corners region with Utah, Colorado, and Arizona; its other neighboring states are Oklahoma to the northeast, Texas to the east-southeast, and the Mexican states of Chihuahua to the south and Sonora to the southwest. With a population around two million, New Mexico is the 36th state by population. With a total area of 121,592 sq mi (314,920 km2), it is the fifth-largest and sixth-least densely populated of the 50 states. Due to their geographic locations, northern and eastern New Mexico exhibit a colder, alpine climate, while western and southern New Mexico exhibit a warmer, arid climate.

The North American Free Trade Agreement is an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994, and superseded the 1988 Canada–United States Free Trade Agreement between the United States and Canada. The NAFTA trade bloc is one of the largest trade blocs in the world by gross domestic product.

The Day of the Dead is a Mexican holiday celebrated throughout Mexico, in particular the Central and South regions, and by people of Mexican heritage elsewhere. The multi-day holiday involves family and friends gathering to pray for and remember friends and family members who have died, and helping support their spiritual journey. In Mexican culture, death is viewed as a natural part of the human cycle. Mexicans view it not as a day of sadness but as a day of celebration because their loved ones awake and celebrate with them. In 2008, the tradition was inscribed in the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity by UNESCO.

The Aztecs were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec peoples included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (altepetl), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427, Tenochtitlan, city-state of the Mexica or Tenochca; Texcoco; and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521–1821). The definitions of Aztec and Aztecs have long been the topic of scholarly discussion, ever since German scientist Alexander von Humboldt established its common usage in the early nineteenth century.

The Mexican Revolution, also known as the Mexican Civil War, was a major armed struggle, lasting roughly from 1910 to 1920, that radically transformed Mexican culture and government. Although recent research has focused on local and regional aspects of the Revolution, it was a genuinely national revolution. Its outbreak in 1910 resulted from the failure of the 35-year-long regime of Porfirio Díaz to find a managed solution to the presidential succession. This meant there was a political crisis among competing elites and the opportunity for agrarian insurrection. Wealthy landowner Francisco I. Madero challenged Díaz in the 1910 presidential election, and following the rigged results, revolted under the Plan of San Luis Potosí. Armed conflict ousted Díaz from power; a new election was held in 1911, bringing Madero to the presidency.

Mexican Americans are Americans of full or partial Mexican descent. As of July 2016, Mexican Americans made up 11.2% of the United States' population, as 36.3 million U.S. residents identified as being of full or partial Mexican ancestry. As of July 2016, Mexican Americans comprised 63.2% of all Latinos in Americans in the United States. Many Mexican Americans reside in the American Southwest; over 60% of all Mexican Americans reside in the states of California and Texas. As of 2016, Mexicans make up 53% of total percent population of Latin foreign-born. Mexicans are also the largest foreign-born population, accounting for 25% of the total foreign-born population, as of 2017.

The Battle of the Alamo was a pivotal event in the Texas Revolution. Following a 13-day siege, Mexican troops under President General Antonio López de Santa Anna reclaimed the Alamo Mission near San Antonio de Béxar, killing the Texian and immigrant occupiers. Santa Anna's cruelty during the battle inspired many Texians, both legal Texas settlers and illegal immigrants from the United States, to join the Texian Army. Buoyed by a desire for revenge, the Texians defeated the Mexican Army at the Battle of San Jacinto, on April 21, 1836, ending the rebellion.

Carlos Slim Helú is a Mexican business magnate, engineer, investor and philanthropist. From 2010 to 2013, Slim was ranked as the richest person in the world by the Forbes business magazine. He derived his fortune from his extensive holdings in a considerable number of Mexican companies through his conglomerate, Grupo Carso. As of April 2019, he is the fifth-richest person in the world according to Forbes' listing of The World's Billionaires, with him and his family having a net worth estimated at $63.1 billion. He is the richest man in Mexico and Latin America.

Mexicans are the people of the United Mexican States, a multiethnic country in North America.

The Mexico national football team represents Mexico in international football and is governed by the Mexican Football Federation. It competes as a member of CONCACAF, which encompasses the countries of North and Central America, and the Caribbean. The team plays its home games at the Estadio Azteca.
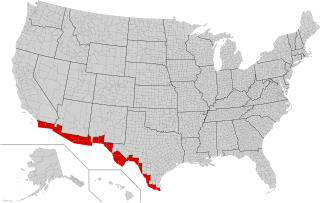
The Mexico–United States border is an international border separating Mexico and the United States, extending from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border traverses a variety of terrains, ranging from urban areas to deserts. The Mexico–US border is the most frequently crossed border in the world, with approximately 350 million documented crossings annually.

Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Covering almost 2,000,000 square kilometres (770,000 sq mi), the nation is the fifth largest country in the Americas by total area and the 13th largest independent state in the world. With an estimated population of over 120 million people, the country is the tenth most populous state and the most populous Spanish-speaking state in the world, while being the second most populous nation in Latin America after Brazil. Mexico is a federation comprising 31 states and Mexico City, a special federal entity that is also the capital city and its most populous city. Other metropolises in the state include Guadalajara, Monterrey, Puebla, Toluca, Tijuana and León.

Joaquín Archivaldo Guzmán Loera is a Mexican drug lord and former leader of the Sinaloa Cartel, an international crime syndicate. Known as "El Chapo" because of his 168 cm stature, Guzmán is considered to have been the most powerful drug trafficker in the world.
The Mexican Drug War is an ongoing asymmetric low-intensity conflict between the Mexican government and various drug trafficking syndicates. In 2006 when the Mexican military began to intervene, the government's principal goal was to reduce drug-related violence. The Mexican government has asserted that their primary focus is on dismantling the powerful drug cartels, rather than on preventing drug trafficking and demand, which is left to U.S. functionaries.

The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the Intervención estadounidense en México, was an armed conflict between the United States of America and the Second Federal Republic of Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed in the wake of the 1845 American annexation of the Republic of Texas, not formally recognized by the Mexican government, disputing the Treaties of Velasco signed by the unstable Mexican caudillo President/General Antonio López de Santa Anna after the Texas Revolution a decade earlier. In 1845, newly elected U.S. President James K. Polk, who saw the annexation of Texas as the first step towards a further expansion of the United States, sent troops to the disputed area and a diplomatic mission to Mexico. After Mexican forces attacked American forces, Polk cited this in his request that Congress declare war.

Cinco de Mayo is an annual celebration held on May 5. The date is observed to commemorate the Mexican Army's victory over the French Empire at the Battle of Puebla, on May 5, 1862, under the leadership of General Ignacio Zaragoza. The victory of the smaller Mexican force against a larger French force was a boost to morale for the Mexicans. A year after the battle, a larger French force defeated Zaragoza at the Second Battle of Puebla, and Mexico City soon fell to the invaders.


















