
Plumbing is any system that conveys fluids for a wide range of applications. Plumbing uses pipes, valves, plumbing fixtures, tanks, and other apparatuses to convey fluids. Heating and cooling (HVAC), waste removal, and potable water delivery are among the most common uses for plumbing, but it is not limited to these applications. The word derives from the Latin for lead, plumbum, as the first effective pipes used in the Roman era were lead pipes.

A latrine is a toilet or an even simpler facility that is used as a toilet within a sanitation system. For example, it can be a communal trench in the earth in a camp to be used as emergency sanitation, a hole in the ground, or more advanced designs, including pour-flush systems.

An outhouse is a small structure, separate from a main building, which covers a toilet. This is typically either a pit latrine or a bucket toilet, but other forms of dry (non-flushing) toilets may be encountered. The term may also be used to denote the toilet itself, not just the structure.

A drain-waste-vent system is the combination of pipes and plumbing fittings that captures sewage and greywater within a structure and routes it toward a water treatment system. It includes venting to the exterior environment to prevent a vacuum from forming and impeding fixtures such as sinks, showers, and toilets from draining freely, and employs water-filled traps to block dangerous sewer gasses from entering a plumbed structure.

A composting toilet is a type of dry toilet that treats human waste by a biological process called composting. This process leads to the decomposition of organic matter and turns human waste into compost-like material. Composting is carried out by microorganisms under controlled aerobic conditions. Most composting toilets use no water for flushing and are therefore called "dry toilets".

A pit latrine, also known as pit toilet, is a type of toilet that collects human waste in a hole in the ground. Urine and feces enter the pit through a drop hole in the floor, which might be connected to a toilet seat or squatting pan for user comfort. Pit latrines can be built to function without water or they can have a water seal. When properly built and maintained, pit latrines can decrease the spread of disease by reducing the amount of human feces in the environment from open defecation. This decreases the transfer of pathogens between feces and food by flies. These pathogens are major causes of infectious diarrhea and intestinal worm infections. Infectious diarrhea resulted in about 700,000 deaths in children under five years old in 2011 and 250 million lost school days. Pit latrines are a low-cost method of separating feces from people.

A chemical toilet collects human excreta in a holding tank and uses chemicals to minimize odors. They do not require a connection to a water supply and are used in a variety of situations. These toilets are usually, but not always, self-contained and movable. A chemical toilet is structured around a relatively small tank, which requires frequent emptying. It is not connected to a hole in the ground, nor to a septic tank, nor is it plumbed into a municipal system leading to a sewage treatment plant. When the tank is emptied, the contents are usually pumped into a sanitary sewer or directly to a treatment plant.

A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipe is far stiffer per unit weight than solid members.
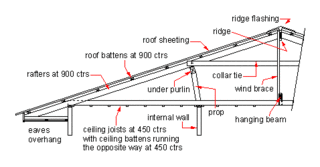
Domestic roof construction is the framing and roof covering which is found on most detached houses in cold and temperate climates. Such roofs are built with mostly timber, take a number of different shapes, and are covered with a variety of materials.

A fitting or adapter is used in pipe systems to connect sections of pipe or tube, adapt to different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing to manipulate the conveyance of fluids such as water for potatory, irrigational, sanitary, and refrigerative purposes, gas, petroleum, liquid waste, or any other liquid or gaseous substances required in domestic or commercial environments, within a system of pipes or tubes, connected by various methods, as dictated by the material of which these are made, the material being conveyed, and the particular environmental context in which they will be used, such as soldering, mortaring, caulking, Plastic welding, welding, friction fittings, threaded fittings, and compression fittings.
Cold water pitting of copper tube occurs in only a minority of installations. Copper water tubes are usually guaranteed by the manufacturer against manufacturing defects for a period of 50 years. The vast majority of copper systems far exceed this time period but a small minority may fail after a comparatively short time.
Erosion corrosion, also known as impingement damage, is the combined effect of corrosion and erosion caused by rapid flowing turbulent water. It is probably the second most common cause of copper tube failures behind Type 1 pitting which is also known as Cold Water Pitting of Copper Tube.
Biogenic sulfide corrosion is a bacterially mediated process of forming hydrogen sulfide gas and the subsequent conversion to sulfuric acid that attacks concrete and steel within wastewater environments. The hydrogen sulfide gas is biochemically oxidized in the presence of moisture to form sulfuric acid. The effect of sulfuric acid on concrete and steel surfaces exposed to severe wastewater environments can be devastating. In the USA alone, corrosion causes sewer asset losses estimated at $14 billion per year. This cost is expected to increase as the aging infrastructure continues to fail.

Sustainable sanitation is a sanitation system designed to meet certain criteria and to work well over the long-term. Sustainable sanitation systems consider the entire "sanitation value chain", from the experience of the user, excreta and wastewater collection methods, transportation or conveyance of waste, treatment, and reuse or disposal. The Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) includes five features in its definition of "sustainable sanitation": Systems need to be economically and socially acceptable, technically and institutionally appropriate and protect the environment and natural resources.

Plastic pipe is a tubular section, or hollow cylinder, made of plastic. It is usually, but not necessarily, of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow—liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipes are far stiffer per unit weight than solid members.

A toilet is a piece of sanitary hardware that collects human urine and feces, and sometimes toilet paper, usually for disposal. Flush toilets use water, while dry or non-flush toilets do not. They can be designed for a sitting position popular in Europe and North America with a toilet seat, with additional considerations for those with disabilities, or for a squatting posture more popular in Asia, known as a squat toilet. In urban areas, flush toilets are usually connected to a sewer system; in isolated areas, to a septic tank. The waste is known as blackwater and the combined effluent, including other sources, is sewage. Dry toilets are connected to a pit, removable container, composting chamber, or other storage and treatment device, including urine diversion with a urine-diverting toilet.

An arborloo is a simple type of composting toilet in which feces are collected in a shallow pit and a fruit tree is later planted in the fertile soil of the full pit. Arborloos have: a pit like a pit latrine but less deep; a concrete, ferrocement or other strong floor; a superstructure to provide privacy; and possibly a ring beam to protect the pit from collapsing. The pit should remain well above the water table in the soil, so as to not contaminate groundwater.

Ductile iron pipe is pipe made of ductile cast iron commonly used for potable water transmission and distribution. This type of pipe is a direct development of earlier cast iron pipe, which it has superseded.

Copper tubing is available in two basic types of tube—plumbing tube and air conditioning/refrigeration (ACR) tube, and in both drawn (hard) and annealed (soft) tempers. Because of its high level of corrosion resistance, it is used for water distribution systems, oil fuel transfer lines, non-flammable medical-gas systems, and as a refrigerant line in HVAC systems. Copper tubing is joined using flare connection, compression connection, pressed connection, or solder.

A urine-diverting dry toilet (UDDT) is a type of dry toilet with urine diversion that can be used to provide safe, affordable sanitation in a variety of contexts worldwide. The separate collection of feces and urine without any flush water has many advantages, such as odor-free operation and pathogen reduction by drying. While dried feces and urine harvested from UDDTs can be and routinely are used in agriculture, many UDDT installations do not apply any sort of recovery scheme. The UDDT is an example of a technology that can be used to achieve a sustainable sanitation system. This dry excreta management system is an alternative to pit latrines and flush toilets, especially where water is scarce, a connection to a sewer system and centralized wastewater treatment plant is not feasible or desired, fertilizer and soil conditioner are needed for agriculture, or groundwater pollution should be minimized.
















