Related Research Articles

Assam is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of 78,438 km2 (30,285 sq mi). The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a 22 kilometres (14 mi) wide strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese is the official and most commonly spoken language of the state, followed by Bengali, which is official in the Barak Valley and Bodo, which is co-official in Assam and official in Bodoland Territorial Region.

Cachar is an administrative district in the state of Assam in India. After independence the undivided Cachar district was split into four districts in Assam: Dima Hasao district, Cachar district alongside Hailakandi and Karimganj.

Karimganj district is one of the 34 districts of the Indian state of Assam. Karimganj town is both the administrative headquarters district and the biggest town of this district. It is located in southern Assam and borders Tripura and the Sylhet Division of Bangladesh. It makes up the Barak Valley alongside Hailakandi and Cachar. Karimganj was previously part of the Sylhet District before the Partition of India. It became a district in 1983.

The Barak River flows 900 kilometres (560 mi) through the states of Manipur, Nagaland, Mizoram and Assam in India. Further it enters Bangladesh where it is known by the name of the Surma and the Kushiyara and later called the Meghna before receiving the combined flow of the Ganga and the Brahmaputra. It flows into the Bay of Bengal via Bangladesh. Of its length 524 km (326 mi) is in India, 31 km (19 mi) on the Indo–Bangladesh border and the rest is in Bangladesh. The upper part of its navigable part is in India — 121 km (75 mi) between Lakhipur and Bhanga, declared as National Waterway 6, (NW-6) since the year 2016. It drains a basin of 52,000 km2 (20,000 sq mi), of which 41,723 km2 (16,109 sq mi) lies in India, 1.38% (rounded) of the country. The water and banks host or are visited by a wide variety of flora and fauna.

Goalpariya is a group of Indo-Aryan dialects also called Rangpuri Language same language divided in two countries that's why the dialects names in two districts Rangpur, Bangladesh and Goalpara instead. Spoken in the Goalpara region of Assam, India and Rangpur District of Bangladesh Along with Kamrupi, they form the western group of Assamese and Bengali language dialects. The North Bengali dialect is situated to its west, amidst a number of Tibeto-Burman speech communities. The basic characteristic of the Goalpariya is that it is a composite one into which words of different concerns and regions have been amalgamated. Deshi people speak this language and there are around 20 lakhs people.

The Brahmaputra Valley is a region situated between hill ranges of the eastern and northeastern Himalayan range in Eastern India.
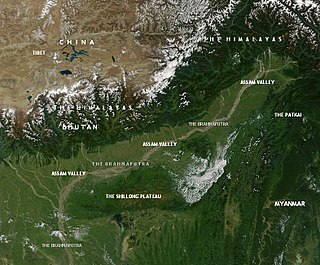
This article discusses the geological origin, geomorphic characteristics, and climate of the northeastern Indian state of Assam. Extending from 89° 42′ E to 96°2, similar to that of Ireland or Austria.

The Barak Valley is located in the southern region of the Indian state of Assam. The main city of the valley is Silchar. The region is named after the Barak river. The Barak valley mainly consists of three administrative districts of Assam - namely Cachar, Karimganj, and Hailakandi.

Upper – Assam is an administrative division of the state of Assam comprising the undivided Lakhimpur and Sivasagar districts, of the upper reaches of the Brahmaputra valley. The other divisions are: Lower – Assam, North Assam and Hills and Barak Valley. The division is under the jurisdiction of a Commissioner, stationed at Jorhat.

Lower Assam is a region situated in Western Brahmaputra Valley encompassing undivided Kamrup and Goalpara regions. Soon after the formal creation of the British districts in 1833, Lower Assam denoted one of the five initial districts that were created west of the Dhansiri river, which, along with the six paraganas, became a single district of Kamrup in 1836. It was home to the kingdom of Kamarupa, ruled by Varman's and Pala's from their capital's Pragjyotishpura (Guwahati) and Durjaya. Today Guwahati is the largest city of North-East India while Dispur, the capital of Assam, is within the town.

Kamrup is the modern region situated between two rivers, the Manas and the Barnadi in Western Assam, with the same territorial extent as the Colonial and post-Colonial "Undivided Kamrup district". It was the capital region of two of the three dynasties of Kamarupa and Guwahati, the current political center of Assam, is situated here. It is characterized by its cultural artifacts.

Undivided Kamrup district is a former administrative district located in Western Assam from which Kamrup Rural (2003), Kamrup Metropolitan (2003), Barpeta (1983), Nalbari (1985) and Baksa (2004) districts were formed. It was announced in January 2020 that the Bajali sub-division of Barpeta district will be upgraded to a full district.

Kamarupa Pithas or Kamrup Piths are ancient pithas or geographical divisions of Kamarupa. The division of the Pithas are not consistent in different sources, though the number of pithas are usually four. Since these pithas are not mentioned in the Kamarupa inscriptions, and are found mentioned only in later medieval texts some authors have suggested that these divisions are possible later fabrications. The Yogini Tantra, mentions the Kamarupa Pithas, the same work which gives boundaries of ancient Kamrup kingdom as well.
Goalpara region, largely congruous to the historical undivided Goalpara district, is a region that is associated with the people and culture of Goalpara. It is bounded on the north by Bhutan, on the east by the Kamrup region, in the south by Meghalaya and in the west by Cooch Behar and Jalpaiguri in West Bengal and Rangpur in Bangladesh. The natural landmarks are: Sankosh and Brahmaputra rivers on the west, the Manas river on the east in the north bank, and a corresponding region in the south bank; the Garo Hills in the south and Bhutan Hills in the north.

The Undivided Goalpara district is an erstwhile district of Assam, India, first constituted by the British rulers of Colonial Assam.

Kamapitha is one of the four Kamarupa Pithas, the geographical divisions of ancient Kamarupa. Dineshchandra Sircar points out that these divisions are not found in the Kamarupa inscriptions and that they might be fabrications from late medieval sources, such as 16th-century work Yogini Tantra gives the boundaries of Kamapitha and other three pithas, the same work which gives boundaries of ancient Kamrup kingdom as well. The eastern border of Kamarupa was the temple of the goddess Tamreshvari near present-day Sadiya

Islam is the second largest religion in Assam. The Muslim population was approximately 14.61 million, constituting over 40.03% of the total population of the state as of 2021 year estimation, making Assam the second-largest Muslim-populated state in the country after Kashmir. Reaching the region in the 13th century, Islam is the fastest-growing religion in Assam. Muslims are a majority in almost thirteen districts of Assam and highly concentrated in four districts.
Assam – 16th largest, 15th most populous and 26th most literate state of the 29 states of the democratic Republic of India. Assam is at 14th position in life expectancy and 8th in female-to-male sex ratio. Assam is the 21st most media exposed states in India. The Economy of Assam is largely agriculture based with 69% of the population engaged in it. Growth rate of Assam's income has not kept pace with that of India's during the Post-British Era; differences increased rapidly since the 1970s. While the Indian economy grew at 6 percent per annum over the period of 1981 to 2000, the same of Assam's grew only by 3.3 percent.
References
- Dutta, Birendranath (1995). A Study of the Folk Culture of the Goalpara Region of Assam. Guwahati, Assam: University Publication Department, Gauhati University.
- Tunga, S. S. (1995). Bengali and Other Related Dialects of South Assam. Delhi: Mittal Publications. ISBN 9788170995883 . Retrieved 19 February 2013.