Operation or Operations may refer to:

In calculus, Taylor's theorem gives an approximation of a k-times differentiable function around a given point by a polynomial of degree k, called the kth-order Taylor polynomial. For a smooth function, the Taylor polynomial is the truncation at the order k of the Taylor series of the function. The first-order Taylor polynomial is the linear approximation of the function, and the second-order Taylor polynomial is often referred to as the quadratic approximation. There are several versions of Taylor's theorem, some giving explicit estimates of the approximation error of the function by its Taylor polynomial.

Perry Mason is a fictional character, an American criminal defense lawyer who is the main character in works of detective fiction written by Erle Stanley Gardner. Perry Mason features in 82 novels and 4 short stories, all of which involve a client being charged with murder, usually involving a preliminary hearing or jury trial. Typically, Mason establishes his client's innocence by finding the real murderer. The character was inspired by famed Los Angeles criminal defense attorney Earl Rogers.

A charitable trust is an irrevocable trust established for charitable purposes and, in some jurisdictions, a more specific term than "charitable organization". A charitable trust enjoys a varying degree of tax benefits in most countries. It also generates good will. Some important terminology in charitable trusts is the term "corpus", which refers to the assets with which the trust is funded, and the term "donor", which is the person donating assets to a charity.
Exposure or Exposures may refer to:
Run(s) or RUN may refer to:
Endgame, Endgames, End Game, End Games, or similar variations may refer to:
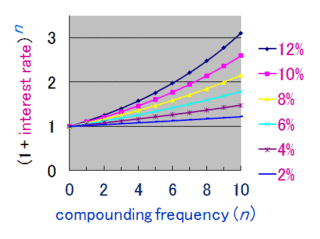
Compound interest is the addition of interest to the principal sum of a loan or deposit, or in other words, interest on interest. It is the result of reinvesting interest, rather than paying it out, so that interest in the next period is then earned on the principal sum plus previously accumulated interest. Compound interest is standard in finance and economics.
Watchman or Watchmen may refer to:
An assassin is a person who commits targeted murder.

In mathematics, a linear approximation is an approximation of a general function using a linear function. They are widely used in the method of finite differences to produce first order methods for solving or approximating solutions to equations.
A tribe in anthropology is a human social group.

Iriññāttappiḷḷi Mādhavan Nampūtiri known as Mādhava of Sangamagrāma was a mathematician and astronomer from the town believed to be present-day Kallettumkara, Aloor Panchayath, Irinjalakuda in Thrissur District, Kerala, India. He is considered the founder of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics. One of the greatest mathematician-astronomers of the Middle Ages, Madhava made pioneering contributions to the study of infinite series, calculus, trigonometry, geometry, and algebra. He was the first to use infinite series approximations for a range of trigonometric functions, which has been called the "decisive step onward from the finite procedures of ancient mathematics to treat their limit-passage to infinity".
Acceptance is the experience of a situation without an intention to change that situation.
Yuktibhāṣā, also known as Gaṇitanyāyasaṅgraha, is a major treatise on mathematics and astronomy, written by the Indian astronomer Jyesthadeva of the Kerala school of mathematics around 1530. The treatise, written in Malayalam, is a consolidation of the discoveries by Madhava of Sangamagrama, Nilakantha Somayaji, Parameshvara, Jyeshtadeva, Achyuta Pisharati, and other astronomer-mathematicians of the Kerala school.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.





