A Vietnam veteran is a person who served in the armed forces of participating countries during the Vietnam War.
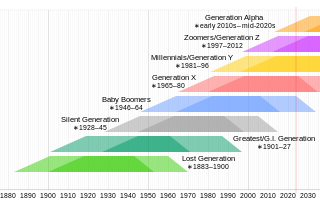
The Greatest Generation, also known as the G.I. Generation and the World War II generation, is the demographic cohort following the Lost Generation and preceding the Silent Generation. The generation is generally defined as people born from 1901 to 1927. They were shaped by the Great Depression and were the primary generation composing the enlisted forces in World War II.
During the weekend of July 4, 1999, white supremacist Benjamin Smith targeted Orthodox Jews and members of racial and ethnic minorities in 3-day drive-by shooting rampage in Illinois and Indiana, after which he committed suicide. Smith was member of the neo-Nazi World Church of the Creator.

The Philippine–American War or the Filipino–American War, previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an armed conflict between the First Philippine Republic and the United States that started on February 4, 1899, and ended on July 2, 1902. The conflict arose in 1898 when the United States, rather than acknowledging the Philippines' declaration of independence, annexed the Philippines under the Treaty of Paris at the conclusion of the Spanish–American War. The war can be seen as a continuation of the Philippine struggle for independence that began in 1896 with the Philippine Revolution against Spanish rule.

The United Service Organizations Inc. (USO) is an American nonprofit-charitable corporation that provides live entertainment, such as comedians, actors and musicians, social facilities, and other programs to members of the United States Armed Forces and their families. Since 1941, it has worked in partnership with the Department of War, and later with the Department of Defense (DoD), relying heavily on private contributions and on funds, goods, and services from various corporate and individual donors. Although it is congressionally chartered, it is not a government agency.

The Wounded Knee Massacre, also known as the Battle of Wounded Knee, was a massacre of nearly three hundred Lakota people by soldiers of the United States Army. It occurred on December 29, 1890, near Wounded Knee Creek on the Lakota Pine Ridge Indian Reservation in South Dakota, following a botched attempt to disarm the Lakota camp. The previous day, a detachment of the U.S. 7th Cavalry Regiment commanded by Major Samuel M. Whitside approached Spotted Elk's band of Miniconjou Lakota and 38 Hunkpapa Lakota near Porcupine Butte and escorted them five miles westward to Wounded Knee Creek, where they made camp. The remainder of the 7th Cavalry Regiment, led by Colonel James W. Forsyth, arrived and surrounded the encampment. The regiment was supported by a battery of four Hotchkiss mountain guns. They were responding to concerns of the settlers who were worried the Ghost Dance might be a prelude to an armed attack.

Charles Joseph Watters was a chaplain (major) in the United States Army and Roman Catholic priest. He was posthumously awarded the Medal of Honor for bravery exhibited while rescuing wounded men in the Vietnam War's Battle of Dak To.

Der Fuehrer's Face is a 1943 American animated anti-Nazi propaganda short film produced by Walt Disney Productions, created in 1942 and released on January 1, 1943 by RKO Radio Pictures. The cartoon, which features Donald Duck in a nightmare setting working at a factory in Nazi Germany, was made in an effort to sell war bonds and is an example of American propaganda during World War II. The film was directed by Jack Kinney and written by Joe Grant and Dick Huemer. Spike Jones released a version of Oliver Wallace's theme for the short before the film was released.

The Belgian Shepherd is a breed of medium-sized herding dog from Belgium. While predominantly considered a single breed, it is bred in four distinct varieties based on coat type and colour; the long-haired black Groenendael, the rough-haired fawn Laekenois, the short-haired fawn Malinois, and the long-haired fawn Tervuren; in the United States the American Kennel Club considers the four varieties to be separate breeds.

The "Day of Infamy" speech, sometimes referred to as just "The Infamy speech", was delivered by Franklin D. Roosevelt, the 32nd president of the United States, to a joint session of Congress on December 8, 1941. The previous day, the Empire of Japan attacked the United States military bases at the Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, and the Philippines, and declared war on the United States and the British Empire. The speech is known for its first line: "Yesterday, December 7, 1941—a date which will live in infamy..."

Desmond Thomas Doss was a United States Army corporal who served as a combat medic with an infantry company in World War II. He was twice awarded the Bronze Star Medal for actions on Guam and in the Philippines. Doss further distinguished himself in the Battle of Okinawa by saving 75 men, becoming the only conscientious objector to receive the Medal of Honor for his actions during the war. His life has been the subject of books, the 2004 documentary The Conscientious Objector, and the 2016 Oscar nominated film Hacksaw Ridge, where he was portrayed by Andrew Garfield.

Arthur Housman was an American actor in films during both the silent film era and the Golden Age of Hollywood.

Freedom Comes High is a 1944 dramatic short film commissioned by the United States Government during World War II and directed by Lewis Allen.
Between 1941 and 1945, during World War II, Walt Disney was involved in the production of propaganda films for the U.S. government. The widespread familiarity of Disney's productions benefited the U.S. government in producing pro-American war propaganda in an effort to increase support for the war.

Timothy Alistair Telemachus Hetherington was a British photojournalist. He produced books, films and other work that "ranged from multi-screen installations, to fly-poster exhibitions, to handheld device downloads" and was a regular contributor to Vanity Fair.

The Days of Remembrance of the Victims of the Holocaust (DRVH) is an annual eight-day period designated by the United States Congress for civic commemorations and special educational programs that help citizens remember and draw lessons from the Holocaust. The annual DRVH period normally begins on the Sunday before the Israeli observance of Yom HaShoah, Holocaust Memorial Day, and continues through the following Sunday, usually in April or May. A National Civic Commemoration is held in Washington, D.C., with state, city, and local ceremonies and programs held in most of the fifty states, and on U.S. military ships and stations around the world. The United States Holocaust Memorial Museum designates a theme for each year's programs, and provides materials to help support remembrance efforts.

The United States Army Nurse Corps (USANC) was formally established by the U.S. Congress in 1901. It is one of the six medical special branches of officers which – along with medical enlisted soldiers – comprise the Army Medical Department (AMEDD). The ANC is the nursing service for the U.S. Army and provides nursing staff in support of the Department of Defense medical plans. The ANC is composed entirely of Registered Nurses (RNs).
World War II changed the possibilities for animation. Prior to the war, animation was mostly seen as a form of family entertainment. The attack on Pearl Harbor was a turning point in its utility. On December 8, 1941, the United States Army began working with Walt Disney at his studio, stationing Military personnel there for the duration of the war. The Army and Disney set about making various types of films for several different audiences. Most films meant for the public included some type of propaganda, while films for the troops included training and education about a given topic.

The term "people's princess" is a sobriquet used on 31 August 1997 by the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Tony Blair to describe Diana, Princess of Wales, following her death earlier that day. The term had first been applied to Diana in a 1992 article by Julie Burchill in the Modern Review, when she described Diana as "the one and only People's – and Pop's – Princess".















