Req or Req. may refer to:
- Required course
- Req (musician) (Ian Cassar; born 1966), English DJ and producer
- Esprit Requien, in botanist author citations (Req.)
Req or Req. may refer to:

In computing, a data warehouse, also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise. This is beneficial for companies as it enables them to interrogate and draw insights from their data and make decisions.
Modbus or MODBUS is a client/server data communications protocol in the application layer of the OSI model. It was originally published by Modicon in 1979 for use with its programmable logic controllers (PLCs). Modbus has become a de facto standard communication protocol for communication between industrial electronic devices in a wide range of buses and network.
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a protocol used to synchronize clocks throughout a computer network. On a local area network, it achieves clock accuracy in the sub-microsecond range, making it suitable for measurement and control systems. PTP is employed to synchronize financial transactions, mobile phone tower transmissions, sub-sea acoustic arrays, and networks that require precise timing but lack access to satellite navigation signals.

SystemVerilog, standardized as IEEE 1800, is a hardware description and hardware verification language used to model, design, simulate, test and implement electronic systems. SystemVerilog is based on Verilog and some extensions, and since 2008, Verilog is now part of the same IEEE standard. It is commonly used in the semiconductor and electronic design industry as an evolution of Verilog.

KOSI is a commercial radio station in Denver, Colorado. KOSI is owned by Salt Lake City–based Bonneville International and airs an adult contemporary music format, switching to Christmas music for much of November and December. Its studios and offices are on East Orchard Road in Greenwood Village, and the transmitter is on Mount Morrison in Genesee, above the Red Rocks Amphitheatre.

IEEE Standard 1355-1995, IEC 14575, or ISO 14575 is a data communications standard for Heterogeneous Interconnect (HIC).
A voltage ladder is a simple electronic circuit consisting of several resistors connected in series with a voltage placed across the entire resistor network, a generalisation of a two-resistor voltage divider. Connections to the nodes provide access to the voltages available. Voltage ladders are useful for providing a set of successive voltage references, for instance for a flash analog-to-digital converter.
Radoshitz, also spelled Radishitz, is the name of a Hasidic dynasty founded by Rebbe Yisochor Ber Baron (1765–1843) of Radoshitz, also known as the Saba Kadisha. He was a student of the Seer of Lublin and of the Maggid of Kozhnitz. He was particularly dedicated to the mitzvah of Kiddush HaChodesh, the sanctification of the month.

The United States Air Force's 291st Combat Communications Squadron is an Air National Guard combat communications unit located at Keaukaha Military Reservation in Hilo, Hawaii.
The DLM Forum is a European membership community of public archives and parties interested in archives, records and information management throughout the European Union. Membership is open to all. The Forum is known for its creation of the MoReq series of records management standards.
MoReq2 is short for “Model Requirements for the Management of Electronic Records”, second version. It consists of a formal requirements specification for a generic electronic records management system, accompanied by testing documentation and related information. Published in 2008 by the European Commission, it is intended for use across the European Union, but can be used elsewhere. MoReq2 is generally considered a de facto standard in Europe but it does not have any formal status as a standard.

RIF/ReqIF is an XML file format that can be used to exchange requirements, along with its associated metadata, between software tools from different vendors. The requirements exchange format also defines a workflow for transmitting the status of requirements between partners. Although developed in the automotive industry, ReqIF is suitable for lossless exchange of requirements in any industry.

Eclipse Vert.x is a polyglot event-driven application framework that runs on the Java Virtual Machine.
"The Crabfish" is a ribald humorous folk song of the English oral tradition. It dates back to the seventeenth century, appearing in Bishop Percy's Folio Manuscript as a song named "The Sea Crabb" based on an earlier tale. The moral of the story is that one should look in the chamber pot before using it.
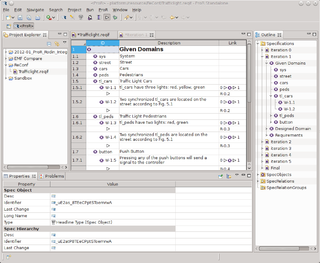
The Requirements Modeling Framework (RMF) is an open-source software framework for working with requirements based on the ReqIF standard. RMF consists of a core allowing reading, writing and manipulating ReqIF data, and a user interface allowing to inspect and edit request data.

Esprit Requien was a French naturalist, who made contributions in the fields of conchology, paleontology and especially botany.
Intercepting Filter is a JavaEE pattern which creates pluggable filters to process common services in a standard manner without requiring changes to core request processing code. The filters intercept incoming requests and outgoing responses, allowing preprocessing and post-processing, and these filters can be added or removed unobtrusively without changing existing code. This pattern applies reusable processing transparently before and after the actual request execution by the front and page controllers.

One is the debut studio album by English experimental electronic producer Req, recorded from September 1995 to 1996 and released on Skint Records in 1997. After releasing several EPs, Req decided to release an album to spread his sound. His conception for One was to create music that hints at a direction without ever arriving at one. Music critics had difficulty defining the album's style, and is seen as a "blunted take" on trip hop with downtempo ambience. The album was well received by critics, who praised its unique sound and production. Today, it is seen as a predecessor to the late 1990s' "intelligent big beat" of fellow Skint artists such as Lo-Fidelity Allstars, and in 2015, Fact named the album the 14th greatest trip hop album of all time.
Ian Cassar, better known as Req, is an English DJ, record producer, and graffiti artist.

Frequency Jams is the second studio album by English experimental electronic producer Req, released in 1998 on Skint Records. As with his debut album, One, Frequency Jams was recorded on a lo-fi 4-track recorder and featuries abstract arrangements that incorporate esoteric, fractured beats, while also introducing new, eclectic influences such as jazz-funk and avant-rock into Req's music. Some felt the album pushed Req closer to the avant-garde, with stronger usage of noise. The album has received critical acclaim for its bleak, dark tone and atypical production. It was named the year's 47th best album by The Wire.