
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines to applied disciplines.
In software engineering and computer science, abstraction is the process of generalizing concrete details, such as attributes, away from the study of objects and systems to focus attention on details of greater importance. Abstraction is a fundamental concept in computer science and software engineering, especially within the object-oriented programming paradigm. Examples of this include:
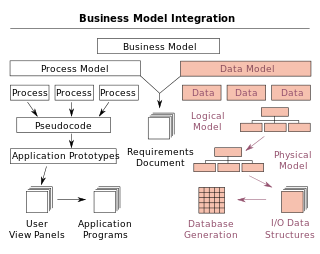
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner.
Computer science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and their implementation and application in computer systems. One well known subject classification system for computer science is the ACM Computing Classification System devised by the Association for Computing Machinery.
NetKernel is a British software company and software platform by the same name that is used for High Performance Computing, Enterprise Application Integration, and Energy Efficient Computation.
A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express data, information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in the structure of a programming language.

Solid modeling is a consistent set of principles for mathematical and computer modeling of three-dimensional shapes (solids). Solid modeling is distinguished within the broader related areas of geometric modeling and computer graphics, such as 3D modeling, by its emphasis on physical fidelity. Together, the principles of geometric and solid modeling form the foundation of 3D-computer-aided design, and in general, support the creation, exchange, visualization, animation, interrogation, and annotation of digital models of physical objects.

An entity–relationship model describes interrelated things of interest in a specific domain of knowledge. A basic ER model is composed of entity types and specifies relationships that can exist between entities.

Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying certain formal techniques. It may be applied as part of broader Model-driven engineering (MDE) concept.

The Zachman Framework is an enterprise ontology and is a fundamental structure for enterprise architecture which provides a formal and structured way of viewing and defining an enterprise. The ontology is a two dimensional classification schema that reflects the intersection between two historical classifications. The first are primitive interrogatives: What, How, When, Who, Where, and Why. The second is derived from the philosophical concept of reification, the transformation of an abstract idea into an instantiation. The Zachman Framework reification transformations are: identification, definition, representation, specification, configuration and instantiation.
REST is a software architectural style that was created to guide the design and development of the architecture for the World Wide Web. REST defines a set of constraints for how the architecture of a distributed, Internet-scale hypermedia system, such as the Web, should behave. The REST architectural style emphasises uniform interfaces, independent deployment of components, the scalability of interactions between them, and creating a layered architecture to promote caching to reduce user-perceived latency, enforce security, and encapsulate legacy systems.
A logical data model or logical schema is a data model of a specific problem domain expressed independently of a particular database management product or storage technology but in terms of data structures such as relational tables and columns, object-oriented classes, or XML tags. This is as opposed to a conceptual data model, which describes the semantics of an organization without reference to technology.

Logic in computer science covers the overlap between the field of logic and that of computer science. The topic can essentially be divided into three main areas:
Concurrent computing is a form of computing in which several computations are executed concurrently—during overlapping time periods—instead of sequentially—with one completing before the next starts.
A web resource is any identifiable resource present on or connected to the World Wide Web. Resources are identified using Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs). In the Semantic Web, web resources and their semantic properties are described using the Resource Description Framework (RDF).

Integration DEFinition for information modeling (IDEF1X) is a data modeling language for the development of semantic data models. IDEF1X is used to produce a graphical information model which represents the structure and semantics of information within an environment or system.

Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.

A semantic data model (SDM) is a high-level semantics-based database description and structuring formalism for databases. This database model is designed to capture more of the meaning of an application environment than is possible with contemporary database models. An SDM specification describes a database in terms of the kinds of entities that exist in the application environment, the classifications and groupings of those entities, and the structural interconnections among them. SDM provides a collection of high-level modeling primitives to capture the semantics of an application environment. By accommodating derived information in a database structural specification, SDM allows the same information to be viewed in several ways; this makes it possible to directly accommodate the variety of needs and processing requirements typically present in database applications. The design of the present SDM is based on our experience in using a preliminary version of it. SDM is designed to enhance the effectiveness and usability of database systems. An SDM database description can serve as a formal specification and documentation tool for a database; it can provide a basis for supporting a variety of powerful user interface facilities, it can serve as a conceptual database model in the database design process; and, it can be used as the database model for a new kind of database management system.

Praxeme is a methodology for enterprise architecture which provides a structured approach to the design and implementation of an enterprise information architecture.
This glossary of computer science is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in computer science, its sub-disciplines, and related fields, including terms relevant to software, data science, and computer programming.










