Related Research Articles
Financial capital is any economic resource measured in terms of money used by entrepreneurs and businesses to buy what they need to make their products or to provide their services to the sector of the economy upon which their operation is based, i.e. retail, corporate, investment banking, etc. In other words, financial capital is internal retained earnings generated by the entity or funds provided by lenders to businesses in order to purchase real capital equipment or services for producing new goods and/or services.
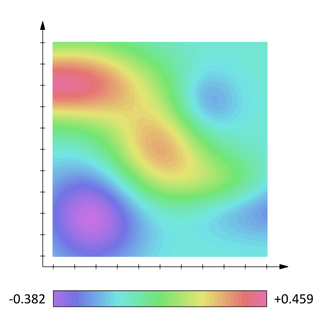
In mathematics and physics, a scalar field or scalar-valued function associates a scalar value to every point in a space – possibly physical space. The scalar may either be a (dimensionless) mathematical number or a physical quantity. In a physical context, scalar fields are required to be independent of the choice of reference frame, meaning that any two observers using the same units will agree on the value of the scalar field at the same absolute point in space regardless of their respective points of origin. Examples used in physics include the temperature distribution throughout space, the pressure distribution in a fluid, and spin-zero quantum fields, such as the Higgs field. These fields are the subject of scalar field theory.
Jealousy generally refers to the thoughts or feelings of insecurity, fear, and concern over a relative lack of possessions or safety.
In economics, capital consists of human-created assets that can enhance one's power to perform economically useful work. For example, a stone arrowhead is capital for a hunter-gatherer who can use it as a hunting instrument; similarly, roads are capital for inhabitants of a city. Capital is distinct from land and other non-renewable resources in that it can be increased by human labor, and does not include certain durable goods like homes and personal automobiles that are not used in the production of saleable goods and services. Adam Smith defined capital as "that part of man's stock which he expects to afford him revenue". In economic models, capital is an input in the production function.

Friedrich Freiherr von Wieser was an early economist of the Austrian School of economics. Born in Vienna, the son of Privy Councillor Leopold von Wieser, a high official in the war ministry, he first trained in sociology and law. In 1872, the year he took his degree, he encountered Austrian-school founder Carl Menger's Grundsätze and switched his interest to economic theory. Wieser held posts at the universities of Vienna and Prague until succeeding Menger in Vienna in 1903, where along with his brother-in-law Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk he shaped the next generation of Austrian economists including Ludwig von Mises, Friedrich Hayek and Joseph Schumpeter in the late 1890s and early 20th century. He was the Austrian Minister of Commerce from August 30, 1917 to November 11, 1918.
In particle physics, the Peccei–Quinn theory is a well-known, long-standing proposal for the resolution of the strong CP problem. It was formulated by Roberto Peccei and Helen Quinn in 1977. The theory proposes that the QCD Lagrangian be extended with a CP-violating term known as “the θ term”. Because experiments have never measured a value for θ, its value must be very nearly zero.

Raas or Dandiya Raas is the socio-religious folk dance originating from Indian state of Gujarat and popularly performed in the festival of Navaratri. The dance is performed in the Marwar region of Rajasthan too.The etymology of Dandiya-Raas is in Sanskrit. Dandiya-raas exists in the different forms, including the collegiate competitive form. The dance style is now in a competitive format and a traditional format.

Collapse: How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed is a 2005 book by academic and popular science author Jared Diamond, in which the author first defines collapse: "a drastic decrease in human population size and/or political/economic/social complexity, over a considerable area, for an extended time." He then reviews the causes of historical and pre-historical instances of societal collapse—particularly those involving significant influences from environmental changes, the effects of climate change, hostile neighbors, trade partners, and the society's response to the foregoing four challenges—and considers the success or failure different societies have had in coping with such threats.

Elections in Nicaragua gives information on elections and election results in Nicaragua.
In management, business value is an informal term that includes all forms of value that determine the health and well-being of the firm in the long run. Business value expands concept of value of the firm beyond economic value to include other forms of value such as employee value, customer value, supplier value, channel partner value, alliance partner value, managerial value, and societal value. Many of these forms of value are not directly measured in monetary terms.
In quantum electrodynamics, the anomalous magnetic moment of a particle is a contribution of effects of quantum mechanics, expressed by Feynman diagrams with loops, to the magnetic moment of that particle.
Reproductive value (RV) is a term used in social psychology to describe the level of attractiveness of women. The reproduction value theory introduces a mechanism that men unintentionally use when "searching" for a partner. The level of the RV is decided by several things, including:
Fleetwood RV, Inc. is a producer of recreational vehicles (RVs). Founded in 1950, Fleetwood RV is part of the REV Group. Rev's recreation division includes Fleetwood RV, American Coach, Monaco, Holiday Rambler, Renegade RV, Midwest Automotive Designs, and Lance Campers.
Age disparity in sexual relationships is the difference in ages of individuals in sexual relationships. Concepts of these relationships, including what defines an age disparity, have developed over time and vary among societies. Differences in age preferences for mates can stem from evolutionary mating strategies and age preferences in sexual partners may vary cross-culturally. There are also social theories for age differences in relationships as well as suggested reasons for 'alternative' age-hypogamous relationships. Age-disparity relationships have been documented for most of recorded history and have been regarded with a wide range of attitudes dependent on sociocultural norms and legal systems.
Return on investment (ROI) or return on costs (ROC) is a ratio between net income and investment. A high ROI means the investment's gains compare favourably to its cost. As a performance measure, ROI is used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or to compare the efficiencies of several different investments. In economic terms, it is one way of relating profits to capital invested.
The friendship paradox is the phenomenon first observed by the sociologist Scott L. Feld in 1991 that most people have fewer friends than their friends have, on average. It can be explained as a form of sampling bias in which people with more friends are more likely to be in one's own friend group. Or, said another way, one is less likely to be friends with someone who has very few friends. In contradiction to this, most people believe that they have more friends than their friends have.
Recovery as a service (RaaS), sometimes referred to as disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS), is a category of cloud computing used for protecting an application or data from a natural or human disaster or service disruption at one location by enabling a full recovery in the cloud. RaaS differs from cloud-based backup services by protecting data and providing standby computing capacity on demand to facilitate more rapid application recovery. RaaS capacity is delivered in a cloud-computing model so recovery resources are only paid for when they are used, making it more efficient than a traditional disaster recovery warm site or hot site where the recovery resources must be running at all times.

In evolutionary psychology and behavioral ecology, human mating strategies are a set of behaviors used by individuals to select, attract, and retain mates. Mating strategies overlap with reproductive strategies, which encompass a broader set of behaviors involving the timing of reproduction and the trade-off between quantity and quality of offspring.
Events from the year 1907 in Sweden
Mate value is derived from Charles Darwin's theory of evolution and sexual selection, as well as the social exchange theory of relationships. Mate value is defined as the sum of traits that are perceived as desirable, representing genetic quality and/or fitness (biology), an indication of a potential mate's reproductive success. Based on mate desirability and mate preference, mate value underpins mate selection and the formation of romantic relationships.
References
- Stewart, Stinnett and Rosenfeld. "Sex Differences in Desired Characteristics of Short-Term and Long-Term Relationship Partners"