
A blimp, or non-rigid airship, is an airship (dirigible) without an internal structural framework or a keel. Unlike semi-rigid and rigid airships, blimps rely on the pressure of the lifting gas inside the envelope and the strength of the envelope itself to maintain their shape.

The United Provinces of the Netherlands, officially the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands, and commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands. The republic was established after seven Dutch provinces in the Spanish Netherlands revolted against Spanish rule, forming a mutual alliance against Spain in 1579 and declaring their independence in 1581. It comprised Groningen, Frisia, Overijssel, Guelders, Utrecht, Holland and Zeeland.
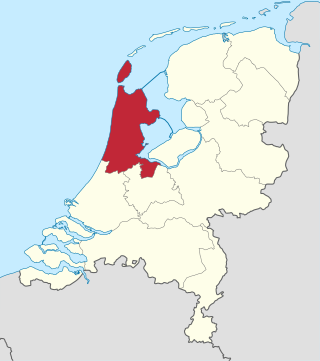
North Holland is a province of the Netherlands in the northwestern part of the country. It is located on the North Sea, north of South Holland and Utrecht, and west of Friesland and Flevoland. In November 2019, it had a population of 2,877,909 and a total area of 4,092 km2 (1,580 sq mi), of which 1,430 km2 (550 sq mi) is water.

An airship or dirigible balloon is a type of aerostat or lighter-than-air aircraft that can navigate through the air under its own power. Aerostats gain their lift from a lifting gas that is less dense than the surrounding air.

Rabobank is a Dutch multinational banking and financial services company headquartered in Utrecht, Netherlands. The group comprises 89 local Dutch Rabobanks (2019), a central organisation, and many specialised international offices and subsidiaries. Food and agribusiness constitute the primary international focus of the Rabobank Group. Rabobank is the second-largest bank in the Netherlands in terms of total assets.

Nederlandse Organisatie voor Toegepast Natuurwetenschappelijk Onderzoek is an independent research organization in the Netherlands that focuses on applied science.

The Zeppelin NT is a class of helium-filled airships being manufactured since the 1990s by the German company Zeppelin Luftschifftechnik GmbH (ZLT) in Friedrichshafen. The initial model is the N07. The company considers itself the successor of the companies founded by Ferdinand von Zeppelin which constructed and operated the very successful Zeppelin airships in the first third of the 20th century. There are, however, a number of notable differences between the Zeppelin NT and original Zeppelins as well as between the Zeppelin NT and usual non-rigid airships known as blimps. The Zeppelin NT is classified as a semi-rigid airship.

An aerostat is a lighter-than-air aircraft that gains its lift through the use of a buoyant gas. Aerostats include unpowered balloons and powered airships. A balloon may be free-flying or tethered. The average density of the craft is lower than the density of atmospheric air, because its main component is one or more gasbags, a lightweight skin containing a lifting gas to provide buoyancy, to which other components such as a gondola containing equipment or people are attached. Especially with airships, the gasbags are often protected by an outer envelope.
Luftschiffbau Zeppelin GmbH is a German aircraft manufacturing company. It is perhaps best known for its leading role in the design and manufacture of rigid airships, commonly referred to as Zeppelins due to the company's prominence. The name 'Luftschiffbau' is a German word meaning building of airships.
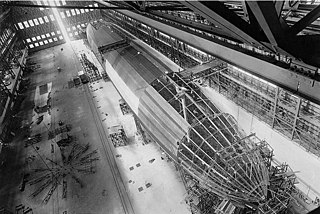
A rigid airship is a type of airship in which the envelope is supported by an internal framework rather than by being kept in shape by the pressure of the lifting gas within the envelope, as in blimps and semi-rigid airships. Rigid airships are often commonly called Zeppelins, though this technically refers only to airships built by the Luftschiffbau Zeppelin company.
Vickers Limited was a British engineering conglomerate. The business began in Sheffield in 1828 as a steel foundry and became known for its church bells, going on to make shafts and propellers for ships, armour plate and then artillery. Entire large ships, cars, tanks and torpedoes followed. Airships and aircraft were added, and Vickers jet airliners were to remain in production until 1965.

Utrecht Centraal, officially Station Utrecht Centraal, is the transit hub that integrates three bicycle parkings, two bus stations, two tram stops and the central railway station for the city of Utrecht in the province of Utrecht, Netherlands. It is the biggest train station in The Netherlands.

A semi-rigid airship is an airship which has a stiff keel or truss supporting the main envelope along its length. The keel may be partially flexible or articulated and may be located inside or outside the main envelope. The outer shape of the airship is maintained by gas pressure, as with the non-rigid "blimp". Semi-rigid dirigibles were built in significant quantity from the late 19th century but in the late 1930s they fell out of favour along with rigid airships. No more were constructed until the semi-rigid design was revived by the Zeppelin NT in 1997.

Eneco, the trading name of Eneco Groep N.V., is a producer and supplier of natural gas, electricity and heat in the Netherlands, serving more than 2 million business and residential customers. Eneco headquarters are located in Rotterdam. It also carries out energy trading and is involved in sustainable energy projects. Eneco is the largest power company in South Holland.

HNLMS Rotterdam is the lead ship in the Rotterdam-class landing platform dock of the Royal Netherlands Navy. The ship is named after the Dutch city of Rotterdam.
The Netherlands' mainstream video games market, not taking into consideration the serious and casual games, is the sixth largest in Europe. In 2008, the Dutch market took up 3.95% of the entire European market in total sales and 4.19% in software sales.

's-Hertogenbosch is a railway station located in 's-Hertogenbosch in North Brabant, Netherlands. The station and all services operating from it are run by Nederlandse Spoorwegen, the national Dutch train operating company.
A mooring mast, or mooring tower, is a structure designed to allow for the docking of an airship outside of an airship hangar or similar structure. More specifically, a mooring mast is a mast or tower that contains a fitting on its top that allows for the bow of the airship to attach its mooring line to the structure. When it is not necessary or convenient to put an airship into its hangar between flights, airships can be moored on the surface of land or water, in the air to one or more wires, or to a mooring mast. After their development mooring masts became the standard approach to mooring airships as considerable manhandling was avoided.

Airship Industries was a British manufacturers of modern non-rigid airships (blimps) active under that name from 1980 to 1990 and controlled for part of that time by Alan Bond. The first company, Aerospace Developments, was founded in 1970, and a successor, Hybrid Air Vehicles, remains active as of 2022. Airship Industries itself was active between 1980 and 1990.

Antoni Scholtens Folkers is a Dutch architect, urbanist and researcher. Folkers studied at the Faculty of Architecture and Urban Planning at Delft University of Technology where he also received his Ph.D. in 2011. His doctoral dissertation was later published as the book Modern Architecture in Africa. Folkers is one of the founding partners of the research and educational platforms ArchiAfrika and African Architecture Matters.















