
Nonograms, also known as Picross or Griddlers, are picture logic puzzles in which cells in a grid must be colored or left blank according to numbers at the side of the grid to reveal a hidden picture. In this puzzle type, the numbers are a form of discrete tomography that measures how many unbroken lines of filled-in squares there are in any given row or column. For example, a clue of "4 8 3" would mean there are sets of four, eight, and three filled squares, in that order, with at least one blank square between successive groups.

Kakuro or Kakkuro is a kind of logic puzzle that is often referred to as a mathematical transliteration of the crossword. Kakuro puzzles are regular features in many math-and-logic puzzle publications across the world. In 1966, Canadian Jacob E. Funk, an employee of Dell Magazines, came up with the original English name Cross Sums and other names such as Cross Addition have also been used, but the Japanese name Kakuro, abbreviation of Japanese kasan kurosu, seems to have gained general acceptance and the puzzles appear to be titled this way now in most publications. The popularity of Kakuro in Japan is immense, second only to Sudoku among Nikoli's famed logic-puzzle offerings.

Sudoku is a logic-based, combinatorial number-placement puzzle. The objective is to fill a 9×9 grid with digits so that each column, each row, and each of the nine 3×3 subgrids that compose the grid contain all of the digits from 1 to 9. The puzzle setter provides a partially completed grid, which for a well-posed puzzle has a single solution.

Nurikabe is a binary determination puzzle named for Nurikabe, an invisible wall in Japanese folklore that blocks roads and delays foot travel. Nurikabe was apparently invented and named by Nikoli; other names for the puzzle include Cell Structure and Islands in the Stream.

Yajilin (ヤジリン) is a type of logic puzzle published by Nikoli. It has been published in English under the name Arrow Ring, such as in the 2005 U.S. qualifier for the World Puzzle Championship.

Hitori is a type of logic puzzle published by Nikoli.

Hashiwokakero is a type of logic puzzle published by Nikoli. It has also been published in English under the name Bridges or Chopsticks. It has also appeared in The Times under the name Hashi. In France, Denmark, the Netherlands, and Belgium it is published under the name Ai-Ki-Ai.
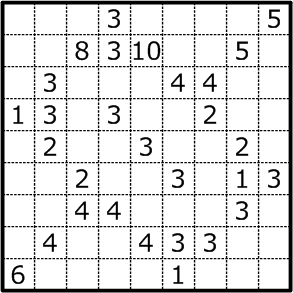
Fillomino (フィルオミノ) is a type of logic puzzle published by many publishers. Other published titles for the puzzle include Allied Occupation.
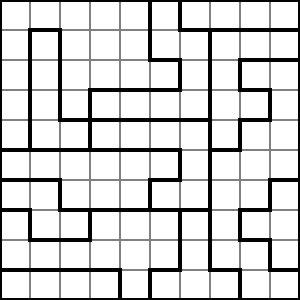
LITS, formerly known as Nuruomino (ヌルオミノ), is a binary determination puzzle published by Nikoli.

Masyu ) is a type of logic puzzle designed and published by Nikoli. The purpose of its creation was to present a puzzle that uses no numbers or letters and yet retains depth and aesthetics.

Heyawake is a binary-determination logic puzzle published by Nikoli. As of 2013, five books consisting entirely of Heyawake puzzles have been published by Nikoli. It first appeared in Puzzle Communication Nikoli #39.

Kuromasu is a binary-determination logic puzzle published by Nikoli. As of 2005, one book consisting entirely of Kuromasu puzzles has been published by Nikoli.
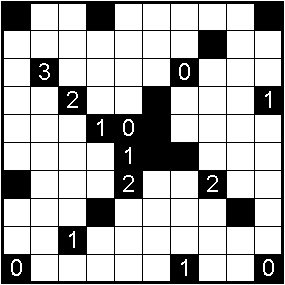
Light Up, also called Akari, is a binary-determination logic puzzle published by Nikoli. As of 2011, three books consisting entirely of Light Up puzzles have been published by Nikoli.

This is a glossary of Sudoku terms and jargon. It is organized thematically, with links to references and example usage provided as ([1]). Sudoku with a 9×9 grid is assumed, unless otherwise noted.

Inshi no heya is a type of logic puzzle published by Nikoli.

Gokigen Naname is a binary-determination logic puzzle published by Nikoli.
Yajisan-Kazusan is a binary determination logic puzzle published by Nikoli.
KenKen and KenDoku are trademarked names for a style of arithmetic and logic puzzle invented in 2004 by Japanese math teacher Tetsuya Miyamoto, who intended the puzzles to be an instruction-free method of training the brain. The name derives from the Japanese word for cleverness . The names Calcudoku and Mathdoku are sometimes used by those who do not have the rights to use the KenKen or KenDoku trademarks.
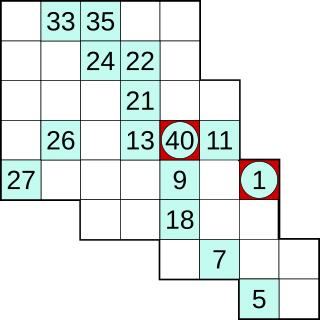
Hidato, also known as "Hidoku", is a logic puzzle game invented by Dr. Gyora M. Benedek, an Israeli mathematician. The goal of Hidato is to fill the grid with consecutive numbers that connect horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. The name Hidato is a registered trademark of Doo-Bee Toys and Games LTD, a company co-founded by Benebek himself. Some publishers use different names for this puzzle such as Number Snake, Snakepit, Jadium or Numbrix.
Takuzu, also known as Binairo, is a logic puzzle involving placement of two symbols, often 1s and 0s, on a rectangular grid. The objective is to fill the grid with 1s and 0s, where there is an equal number of 1s and 0s in each row and column and no more than two of either number adjacent to each other. Additionally, there can be no identical rows or columns. Similar to Sudoku, each puzzle begins with several squares in the grid already filled.

















