Robin A. Finlayson was appointed to the Provincial Court of Manitoba on February 1, 2006.
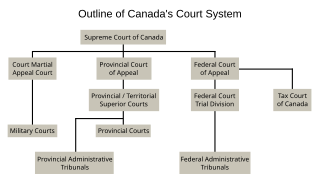
The Provincial Court of Manitoba hears cases relating to criminal law and family law and other statutes.
Judge Finlayson graduated from the University of Manitoba Law School in 1975. He articled with Manitoba Justice and practiced law as a Crown attorney from 1976 until his appointment to the bench. He held the positions of senior Crown attorney and Director of Prosecutions before being appointed Assistant Deputy Attorney General in 1998.
The University of Manitoba is a public research university in Manitoba, Canada. Its main campus is located in the Fort Garry neighbourhood of southern Winnipeg with other campuses throughout the city. Founded in 1877, it is Western Canada's first university. The university maintains a reputation as a top research-intensive post-secondary educational institution and conducts more research annually than any other university in the region.
Judge Finlayson has served on a number of federal and provincial committees, including the Uniform Law Conference of Canada and the federal, provincial and territorial Heads of Prosecutions Committee. He was appointed by the Attorney General to co-chair the Child Online Protection Committee to establish Cybertip.ca. It is now Canada’s national tip line for reporting online child pornography and internet luring incidents to police and it provides related information to the public.

Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres, making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Canada's southern border with the United States is the world's longest bi-national land border. Its capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. As a whole, Canada is sparsely populated, the majority of its land area being dominated by forest and tundra. Consequently, its population is highly urbanized, with over 80 percent of its inhabitants concentrated in large and medium-sized cities, many near the southern border. Canada's climate varies widely across its vast area, ranging from arctic weather in the north, to hot summers in the southern regions, with four distinct seasons.
Child pornography is pornography that exploits children for sexual stimulation. It may be produced with the direct involvement or sexual assault of a child or it may be simulated child pornography. Abuse of the child occurs during the sexual acts or lascivious exhibitions of genitals or pubic areas which are recorded in the production of child pornography. Child pornography may use a variety of media, including writings, magazines, photos, sculpture, drawing, cartoon, painting, animation, sound recording, film, video, and video games.

A police service is a constituted body of persons empowered by a state to enforce the law, to protect people and property, and to prevent crime and civil disorder. Their powers include the power of arrest and the legitimized use of force. The term is most commonly associated with police services of a sovereign state that are authorized to exercise the police power of that state within a defined legal or territorial area of responsibility. Police forces are often defined as being separate from military or other organizations involved in the defense of the state against foreign aggressors; however, gendarmerie are military units charged with civil policing. The police force is usually a public sector service, funded through taxes.
Judge Finlayson also chaired a working group of Crown attorneys and chiefs of police that produced a report in January 2005 exploring possibilities for the prevention of miscarriages of justice.