
The American Locomotive Company was an American manufacturer of locomotives, diesel generators, steel, and tanks that operated from 1901 to 1969.

Montreal Locomotive Works (MLW) was a Canadian railway locomotive manufacturer which existed under several names from 1883 to 1985, producing both steam and diesel locomotives. For a number of years it was a subsidiary of the American Locomotive Company. MLW's headquarters and manufacturing facilities were in Montreal, Quebec.

A steam dummy or dummy engine, in the United States and Canada, was a steam locomotive enclosed in a wooden box structure made to resemble a passenger railroad car. Steam dummies had some popularity in the first decades of railroading in the U.S., from the 1830s but passed from favor after the American Civil War.

Lima Locomotive Works was an American firm that manufactured railroad locomotives from the 1870s through the 1950s. The company took the most distinctive part of its name from its main shop's location in Lima, Ohio. The shops were located between the Erie Railroad main line, the Baltimore & Ohio's Cincinnati-Toledo main line and the Nickel Plate Road main line and shops.

The Cooke Locomotive and Machine Works, located in Paterson, New Jersey, manufactured steam railroad locomotives from 1852 until it was merged with seven other manufacturers to form American Locomotive Company (ALCO) in 1901.

4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles, four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.
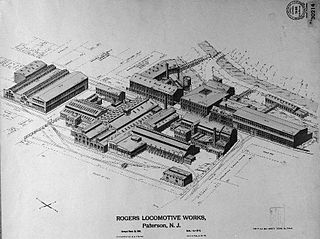
Rogers Locomotive and Machine Works was a manufacturer of railroad steam locomotives based in Paterson, in Passaic County, New Jersey, in the United States. Between its founding in 1832 and its acquisition in 1905, the company built more than 6,000 steam locomotives for railroads around the world. Most 19th-century U.S. railroads owned at least one Rogers-built locomotive. The company's most famous product was a locomotive named The General, built in December 1855, which was one of the principals of the Great Locomotive Chase of the American Civil War.

The Vulcan Foundry Limited was an English locomotive builder sited at Newton-le-Willows, Lancashire.

Hinkley Locomotive Works was a steam locomotive manufacturer based in Boston, Massachusetts in the 19th century.

The Canadian Locomotive Company, commonly referred to as CLC, was a Canadian manufacturer of railway locomotives located in Kingston, Ontario. Its works were located on the south side of Ontario Street between William and Gore streets on Kingston's waterfront.

The North British Locomotive Company was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company, Neilson, Reid and Company and Dübs and Company, creating the largest locomotive manufacturing company in Europe and the British Empire.

Beyer, Peacock and Company was an English railway locomotive manufacturer with a factory in Openshaw, Manchester. Founded by Charles Beyer, Richard Peacock and Henry Robertson, it traded from 1854 until 1966. The company exported locomotives, and machine tools to service them, throughout the world.

The Norris Locomotive Works was a steam locomotive manufacturing company based in Philadelphia, that produced nearly one thousand railroad engines between 1832 and 1866. It was the dominant American locomotive producer during most of that period and the first major exporter of American locomotives, selling its popular 4-2-0 engines to railways in Europe and building the first locomotive used in South America.

Dickson Manufacturing Company was an American manufacturer of boilers, blast furnaces and steam engines used in various industries but most known in railway steam locomotives. The company also designed and constructed steam powered mine cable hoists. It was founded in Scranton, Pennsylvania by Thomas Dickson in 1856. In total, the company produced 1,334 steam locomotives until it was taken over by ALCO in 1901.

Richmond Locomotive Works was a steam locomotive manufacturing firm located in Richmond, Virginia.
Dick, Kerr and Company was a locomotive and tramcar manufacturer based in Kilmarnock, Scotland and Preston, England.

The New Zealand Railways Department, NZR or NZGR and often known as the "Railways", was a government department charged with owning and maintaining New Zealand's railway infrastructure and operating the railway system. The Department was created in 1880 and was corporatised on 1 April 1982 into the New Zealand Railways Corporation. Originally, railway construction and operation took place under the auspices of the former provincial governments and some private railways, before all of the provincial operations came under the central Public Works Department. The role of operating the rail network was subsequently separated from that of the network's construction. From 1895 to 1993 there was a responsible Minister, the Minister of Railways. He was often also the Minister of Public Works.
New York Locomotive Works. Breese Kneeland and Company was a nineteenth century builder of steam locomotive engines located at Jersey City, New Jersey. Initially styled the New York Locomotive Works, the company was active under various ownerships in building steam locomotives from 1853 until 1873. The original proprietors were Charles Kneeland, William Hamilton and S. Breese. Encrease Personette Gould (1822-1876), usually known as E. P. Gould, a well known mechanic and formerly the mechanical superintendent of the Hudson River Railroad was the first shop foreman and designer.
















