Rotarit (or Rotharit) (died Turin, 702) was a Lombard duke, the last Duke of Bergamo.

Turin is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Turin and of the Piedmont region, and was the first capital city of Italy from 1861 to 1865. The city is located mainly on the western bank of the Po River, in front of Susa Valley, and is surrounded by the western Alpine arch and Superga Hill. The population of the city proper is 878,074 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat to be 1.7 million inhabitants. The Turin metropolitan area is estimated by the OECD to have a population of 2.2 million.
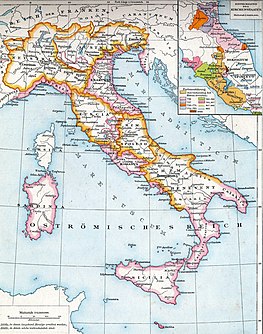
The Lombards or Longobards were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
Among the Lombards, the duke or dux was the man who acted as political and military commander of a set of "military families", irrespective of any territorial appropriation.
In 700, fighting broke out over the succession of the just disappeared king, Cunipert (to which was faithful), Rotarit stood in favor of his son, Liutpert, who was still underage, and his tutor Ansprand. Opposing him was the Duke of Turin Raginpert, the son of Godepert and therefore an exponent of the ruling Bavarian dynasty. The fighting ended with a battle fought at Novara in early 701, during which Rotarit and his ally Ansprand succumbed. Raginpert, supported by the Lombards of Neustria (the Northwest region of the kingdom) ascended to the throne and immediately associated his son, the future Aripert II.

Cunincpert was king of the Lombards from 688 to 700. He succeeded his father Perctarit, though he was associated with the throne from 680.
Liutpert was the Lombard king of Italy from 700 and to 702, with interruption. Upon succeeding his father, King Cunincpert, at a young age, he ruled together with his tutor, Ansprand, the duke of Asti. After eight months, he was deposed by Raginpert, the duke of Turin and son of Godepert, Liutpert's great-uncle, but succeeded in returning to the throne several months later upon Raginpert's death, only to be deposed again, taken captive from Pavia, and drowned by Aripert II, Raginpert's son.
Ansprand was king of the Lombards briefly in 712. Before that he was the duke of Asti and regent during the minority of Liutpert (700–701). He was defeated at Novara by Raginpert and exiled during the subsequent war over the succession, fleeing to the court of Theudebert, duke of Bavaria, in 702.
With the death of Raginpert, which occurred a few months after the battle of Novara, Rotarit and Ansprand imprisoned Aripert II and restored Liutpert to the throne. Aripert II, however, managed to escape and the following year (702) defeated the protectors of Liutpert at Pavia, deposed and imprisoned the young king, and crowned himself in his place. Rotarit, back in Bergamo, proclaimed himself king but was defeated after a bloody siege by Aripert. After forcing Rotarit to shave his beard and his head as a sign of great dishonor, Aripert moved him to Turin where he killed him in 702.

Bergamo is a city in the alpine Lombardy region of northern Italy, approximately 40 km (25 mi) northeast of Milan, and about 30 km (19 mi) from Switzerland, the alpine lakes Como and Iseo and 70 km (43 mi) from Garda and Maggiore. The Bergamo Alps begin immediately north of the city.
The 700s decade ran from January 1, 700, to December 31, 709.

Year 711 (DCCXI) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 711 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 712 (DCCXII) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 712 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

700 (DCC)
was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 700th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 700th year of the 1st millennium, the 100th and last year of the 7th century, and the 1st year of the 700s decade. As of the start of 700, the Gregorian calendar was
3 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which was the dominant calendar of the time. The denomination 700 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

King of Italy was the title given to the ruler of the Kingdom of Italy after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The first to take the title was Odoacer, a "barbarian" military leader, in the late 5th century, followed by the Ostrogothic kings up to the mid-6th century. With the Frankish conquest of Italy in the 8th century, the Carolingians assumed the title, which was maintained by subsequent Holy Roman Emperors throughout the Middle Ages. The last Emperor to claim the title was Charles V in the 16th century. During this period, the holders of the title were crowned with the Iron Crown of Lombardy.

Liutprand was the King of the Lombards from 712 to 744 and is chiefly remembered for his Donation of Sutri, in 728, and his long reign, which brought him into a series of conflicts, mostly successful, with most of Italy. He is often regarded as the most successful Lombard monarch, notable for the Donation of Sutri, which was the first accolade of sovereign territory to the Papacy.

The Agilolfings were a noble family that ruled the Duchy of Bavaria on behalf of their Merovingian suzerains from about 550 until 788. A cadet branch of the Agilolfings also ruled the Kingdom of the Lombards intermittently from 616 to 712.
They are mentioned as the leading dynasty in the Lex Baiuvariorum. Their Bavarian residence was at Regensburg.

Aripert II was the king of the Lombards from 701 to 712. Duke of Turin and son of King Raginpert, and thus a scion of the Bavarian Dynasty, he was associated with the throne as early as 700. He was removed by Liutpert, who reigned from 700 to 702, with the exception of the year 701, when Raginpert seized the throne. After his father's death, he tried to take the throne, too. He defeated Liutpert and the regent Ansprand's men at Pavia and captured the king, whom he later had strangled in his bath. He seized the capital and forced Ansprand over the Alps. He was firmly in power by 703.
Godepert was king of the Lombards, eldest son and successor of Aripert I. He was an Arian who governed from the ancient capital, Pavia, while his brother, Perctarit, a Roman Catholic, governed from Milan. In a war with his brother - begun with the year - he beckoned Duke Grimoald I of Benevento, who assassinated him in his Pavian palace, the Reggia. His son Raginpert managed to escape and would later rule. But first, Grimoald seized the throne.
Raginpert was the Duke of Turin and then King of the Lombards briefly in 701. He was the son of Godepert and grandson of Aripert I. He usurped the throne in 701 and removed Liutpert, his grandnephew, putting his son Aripert in line for the succession. He and his Neustrians went out to meet the regent, Ansprand, in battle and defeated him at Novara, but died shortly after. His son Aripert did not succeed in taking the throne right away.
Grimoald I was duke of Benevento (647–662) and king of the Lombards (662–671).
The Bavarian dynasty was those kings of the Lombards who were descended from Garibald I, the Agilolfing duke of Bavaria. They came to rule the Lombards through Garibald's daughter Theodelinda, who married the Lombard king Authari in 588. The Bavarians were really a branch of the Agilolfings, and were themselves two branches: the branch descended in the female line through Garibald's eldest child and daughter, Theodelinda, and the branch descended from Garibald's eldest son Gundoald. Of the first branch, only Adaloald, Theodelinda's son by her second husband, whom she had chosen to be king, Agilulf, reigned, though her son-in-law Arioald also ruled. Through Gundoald, six kings reigned in succession, broken only by the usurper Grimuald, who married Gundoald's granddaughter:
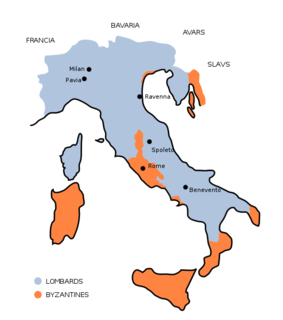
The Kingdom of the Lombards also known as the Lombard Kingdom; later the Kingdom of (all) Italy, was an early medieval state established by the Lombards, a Germanic people, on the Italian Peninsula in the latter part of the 6th century. The king was traditionally elected by the highest-ranking aristocrats, the dukes, as several attempts to establish a hereditary dynasty failed. The kingdom was subdivided into a varying number of duchies, ruled by semi-autonomous dukes, which were in turn subdivided into gastaldates at the municipal level. The capital of the kingdom and the center of its political life was Pavia in the modern northern Italian region of Lombardy.
Ado was the Duke of Friuli after the usurper Ausfrid was defeated at Verona in 694. According to Paul the Deacon, he was a brother of the former duke Rodoald and ruled for a year and seven months. The actual length of his reign is disputed, as is the year of its occurrence. He appears with the title loci servator (caretaker) and may have only held the duchy as regent on behalf of the king.
Austria was, according to the early medieval geographical classification, the eastern portion of Langobardia Major, the north-central part of the Lombard Kingdom, extended from the Adda to Friuli and opposite to Neustria. The partition had not only been territorial, but also implied significant cultural and political differences.
Duke of Turin was the title of a line of dukes mong the Lombards when they ruled Italy in the Early Middle Ages.










