The Russian Orthodox Church is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Christian church.
Russian Orthodox Church may also refer to the following buildings:

The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, Greek Orthodox Church, or officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptised members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via local synods. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the head of the Catholic Church. Nevertheless, the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognised by them as primus inter pares, a title formerly given to the patriarch of Rome. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played a prominent role in the history and culture of Western Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern and Southeastern Europe.
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, is a communion composed of up to seventeen separate autocephalous (self-governing) hierarchical churches that profess Eastern Orthodoxy and recognise each other as canonical (regular) Eastern Orthodox Christian churches.

The Russian Orthodox Church, alternatively legally known as the Moscow Patriarchate, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Christian church. It has 194 dioceses inside Russia. The primate of the ROC is the Patriarch of Moscow and all Rus'.
Caucasian may refer to:

Old Believers or Old Ritualists are Eastern Orthodox Christians who maintain the liturgical and ritual practices of the Russian Orthodox Church as they were before the reforms of Patriarch Nikon of Moscow between 1652 and 1666. Resisting the accommodation of Russian piety to the contemporary forms of Greek Orthodox worship, these Christians were anathematized, together with their ritual, in a Synod of 1666–67, producing a division in Eastern Europe between the Old Believers and those who followed the state church in its condemnation of the Old Rite. Russian speakers refer to the schism itself as raskol (раскол), etymologically indicating a "cleaving-apart".

The history of Christianity in Ukraine dates back to the earliest centuries of the history of Christianity, to the Apostolic Age, with mission trips along the Black Sea and a legend of Andrew the Apostle even ascending the hills of Kyiv. The first Christian community on territory of modern Ukraine is documented as early as the 9th century with the establishment of the Metropolitanate of Gothia, which was centered in the Crimean peninsula. However, on territory of the Old Rus in Kyiv, Christianity became the dominant religion since its official acceptance in 989 by Vladimir the Great, who brought it from Byzantine Crimea and installed it as the state religion of medieval Kyivan Rus (Ruthenia), with the metropolitan see in Kyiv.

The Russian Orthodox Church Outside of Russia, also called Russian Orthodox Church Outside Russia or ROCOR, or Russian Orthodox Church Abroad (ROCA), is a semi-autonomous part of the Russian Orthodox Church. Currently, the position of First-Hierarch of the ROCOR is occupied by Metropolitan Nicholas (Olhovsky).
Ukrainian Orthodox Church may refer to:

The Ukrainian Orthodox Church (UOC), commonly referred to by the exonym Ukrainian Orthodox Church of the Moscow Patriarchate (UOC-MP), is an Eastern Orthodox church in Ukraine.

Russian Orthodox bell ringing has a history starting from the baptism of Rus in 988 and plays an important role in the traditions of the Russian Orthodox Church.
Muscovy or Moscovia is an alternative name for the Principality of Moscow (1263–1547) and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721).

Kirill or Cyril is a Russian Orthodox bishop. He became Patriarch of Moscow and all Rus' and Primate of the Russian Orthodox Church on 1 February 2009.
Church of the Resurrection or Holy Resurrection Church may refer to:
Cathedral of the Dormition of the Theotokos or Cathedral of the Dormition of the Mother of God may refer to:
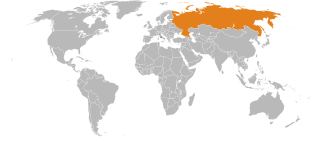
Holy See–Russia relations are the bilateral relations between the Holy See and Russia. The Holy See has an Apostolic Nunciature in Moscow. Russia has a permanent representative to the Holy See based in Rome.
Memory eternal is an exclamation, an encomium like the polychronion, used at the end of a Byzantine Rite funeral or memorial service, as followed by the Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic Churches. It is the liturgical counterpart to the Western Rite prayer "Eternal Rest."
Russian True Orthodox Church may refer to:
The term Diocese of Western Europe or Eparchy of Western Europe may refer to:
Assyrian Church may refer to:

In 1996 a schism between Moscow and Constantinople occurred; this schism began on 23 February 1996, when the Russian Orthodox Church severed full communion with the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, and ended on 16 May 1996 when the Russian Orthodox Church and the Ecumenical Patriarchate reached an agreement.