
A scuba set is any breathing apparatus that is carried entirely by an underwater diver and provides the diver with breathing gas at the ambient pressure. Scuba is an anacronym for self-contained underwater breathing apparatus. Although strictly speaking the scuba set is only the diving equipment which is required for providing breathing gas to the diver, general usage includes the harness by which it is carried, and those accessories which are integral parts of the harness and breathing apparatus assembly, such as a jacket or wing style buoyancy compensator and instruments mounted in a combined housing with the pressure gauge, and in the looser sense it has been used to refer to any diving equipment used by the scuba diver, though this would more commonly and accurately be termed scuba equipment or scuba gear. Scuba is overwhelmingly the most common underwater breathing system used by recreational divers and is also used in professional diving when it provides advantages, usually of mobility and range, over surface supplied diving systems, and is allowed by the relevant code of practice.

A self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA), sometimes referred to as a compressed air breathing apparatus (CABA) or simply breathing apparatus (BA), is a device worn to provide breathable air in an atmosphere that is immediately dangerous to life or health. They are typically used in firefighting and industry. The term self-contained means that the SCBA is not dependent on a remote supply of breathing gas. If designed for use under water, it is also known as a Scuba set. When not used underwater, they are sometimes called industrial breathing sets. Unofficial names include air pack, air tank, oxygen cylinder or simply pack, which are mostly used in firefighting.

A rebreather is a breathing apparatus that absorbs the carbon dioxide of a user's exhaled breath to permit the rebreathing (recycling) of the substantially unused oxygen content, and unused inert content when present, of each breath. Oxygen is added to replenish the amount metabolised by the user. This differs from open-circuit breathing apparatus, where the exhaled gas is discharged directly into the environment. The purpose is to extend the breathing endurance of a limited gas supply, and, for covert military use by frogmen or observation of underwater life, eliminating the bubbles produced by an open circuit system. A rebreather is generally understood to be a portable unit carried by the user. The same technology on a vehicle or non-mobile installation is more likely to be referred to as a life-support system.
SCR, or scr, may refer to:

The Clearance Divers Breathing Apparatus (CDBA) is a type of rebreather made by Siebe Gorman in England.
A breathing set or breathing apparatus is equipment which allows a person to breathe in a hostile environment where breathing would otherwise be impossible or hazardous, and may refer to:
A breathing mask is a mask that covers the mouth, and usually other parts of the face or head, designed to direct the wearer's breath to and/or from a particular apparatus. It may mean, or be part of, one of these:

Siebe Gorman & Company Ltd was a British company that developed diving equipment and breathing equipment and worked on commercial diving and marine salvage projects. The company advertised itself as 'Submarine Engineers'. It was founded by Augustus Siebe, a German-born British engineer chiefly known for his contributions to diving equipment.
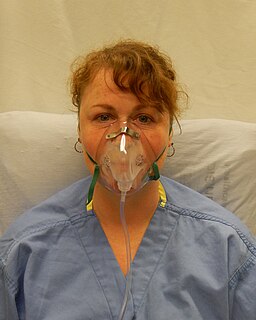
An oxygen mask provides a method to transfer breathing oxygen gas from a storage tank to the lungs. Oxygen masks may cover only the nose and mouth or the entire face. They may be made of plastic, silicone, or rubber. In certain circumstances, oxygen may be delivered via a nasal cannula instead of a mask.

A hazmat suit is a piece of personal protective equipment that consists of an impermeable whole-body garment worn as protection against hazardous materials. Such suits are often combined with self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) to ensure a supply of breathable air. Hazmat suits are used by firefighters, emergency medical technicians, paramedics, researchers, personnel responding to toxic spills, specialists cleaning up contaminated facilities, and workers in toxic environments.
A firefighter assist and search team (FAST), also known as a rapid intervention team/rapid intervention crew/rapid intervention dispatch (RIT/RIC/RID), is a team of two or more firefighters dedicated solely to the search and rescue of other firefighters in distress. Firefighter Assist and Search Team personnel shall have no other operational assignment during any incident. Multiple alarm fires may require multiple FAST/RIC teams.

Porpoise is a tradename for scuba developed by Ted Eldred in Australia and made there from the late 1940s onwards. The first Porpoise was a closed circuit oxygen rebreather, and the following models were all single hose open circuit regulators.

Mine rescue or mines rescue is the specialised job of rescuing miners and others who have become trapped or injured in underground mines because of mining accidents, roof falls or floods and disasters such as explosions.

The Davis Submerged Escape Apparatus, was an early type of oxygen rebreather invented in 1910 by Sir Robert Davis, head of Siebe Gorman and Co. Ltd., inspired by the earlier Fleuss system, and adopted by the Royal Navy after further development by Davis in 1927. While intended primarily as an emergency escape apparatus for submarine crews, it was soon also used for diving, being a handy shallow water diving apparatus with a thirty-minute endurance, and as an industrial breathing set.

An escape set is a breathing set that allows its wearer to survive for a time in an environment without (sufficiently) breathable air.

Henry Albert Fleuss was a pioneering diving engineer, and Master Diver for Siebe, Gorman & Co. of London.

An oxygen breathing apparatus (OBA) is a rebreather. It is used primarily in firefighting. Its oxygen is generated by chemicals contained in the green canister, which is inserted at the base of the breathing device. The canister uses potassium superoxide as both a CO2 scrubber and an O2 generator. A sodium chlorate candle in the base generates additional oxygen when first beginning use as the canister has to achieve a high internal temperature before it will start generating oxygen on its own. It is the circulation of exhaled air through the canister that starts the chemical process, usually taking less than five minutes, the normal burn time of the "candle" and the mask will initially fill with a light, harmless smoke. The extreme heat of the chemical reaction requires the use of thick leather gloves for handling spent canisters. The bags along either side of the chest unit cool the air mixture before inhalation and is a surprisingly effective system, with the air being quite cool when entering the face mask. There is a 60-minute timer at the top of the chest unit which, during the fighting of a casualty, is set for only 45 minutes. This would give the user a 15-minute window to evacuate to a safe atmosphere. Though it looks bulky and unwieldy it is a light and comfortable device to wear and does not much interfere with the user's freedom of movement.
The Lambertsen Amphibious Respiratory Unit (LARU) is an early model of closed circuit oxygen rebreather used by military frogmen. Christian J. Lambertsen designed a series of them in the US in 1940 and in 1944.
A breathing tube is a device or tool that can serve as a conduit for breathing. Various types of breathing tubes are available for different specific applications.

A Diving rebreather is an underwater breathing apparatus that absorbs the carbon dioxide of a diver's exhaled breath to permit the rebreathing (recycling) of the substantially unused oxygen content, and unused inert content when present, of each breath. Oxygen is added to replenish the amount metabolised by the diver. This differs from open-circuit breathing apparatus, where the exhaled gas is discharged directly into the environment. The purpose is to extend the breathing endurance of a limited gas supply, and, for covert military use by frogmen or observation of underwater life, to eliminate the bubbles produced by an open circuit system. A diving rebreather is generally understood to be a portable unit carried by the user, and is therefore a type of self-contained underwater breathing apparatus (scuba). A semi-closed rebreather carried by the diver may also be known as a gas extender. The same technology on a submersible or surface installation is more likely to be referred to as a life-support system.












