
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz, broadly construed. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz, or between 1 and 3000 GHz . The prefix micro- in microwave is not meant to suggest a wavelength in the micrometer range; rather, it indicates that microwaves are small, compared to the radio waves used in prior radio technology.

A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carrier frequency. It was invented by French radio engineer and radio manufacturer Lucien Lévy. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle.

A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve, or tube is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.

In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency (IF) is a frequency to which a carrier wave is shifted as an intermediate step in transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called heterodyning, resulting in a signal at the difference or beat frequency. Intermediate frequencies are used in superheterodyne radio receivers, in which an incoming signal is shifted to an IF for amplification before final detection is done.

A regenerative circuit is an amplifier circuit that employs positive feedback. Some of the output of the amplifying device is applied back to its input to add to the input signal, increasing the amplification. One example is the Schmitt trigger, but the most common use of the term is in RF amplifiers, and especially regenerative receivers, to greatly increase the gain of a single amplifier stage.

In radio communications, a radio receiver, also known as a receiver, a wireless, or simply a radio, is an electronic device that receives radio waves and converts the information carried by them to a usable form. It is used with an antenna. The antenna intercepts radio waves and converts them to tiny alternating currents which are applied to the receiver, and the receiver extracts the desired information. The receiver uses electronic filters to separate the desired radio frequency signal from all the other signals picked up by the antenna, an electronic amplifier to increase the power of the signal for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through demodulation.

The term All American Five is a colloquial name for mass-produced, superheterodyne radio receivers that used five vacuum tubes in their design. These radio sets were designed to receive amplitude modulation (AM) broadcasts in the medium wave band, and were manufactured in the United States from the mid-1930s until the early 1960s. By eliminating a power transformer, cost of the units was kept low; the same principle was later applied to television receivers. Variations in the design for lower cost, shortwave bands, better performance or special power supplies existed, although many sets used an identical set of vacuum tubes.

Grimeton Radio Station in southern Sweden, close to Varberg in Halland, is an early longwave transatlantic wireless telegraphy station built in 1922–1924, that has been preserved as a historical site. From the 1920s through the 1940s it was used to transmit telegram traffic by Morse code to North America and other countries, and during World War II was Sweden's only telecommunication link with the rest of the world. It is the only remaining example of an early pre-electronic radio transmitter technology called an Alexanderson alternator. It was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2004, with the statement: "Grimeton Radio Station, Varberg is an exceptionally well preserved example of a type of telecommunication centre, representing the technological achievements by the early 1920s, as well as documenting the further development over some three decades." The radio station is also an anchor site for the European Route of Industrial Heritage. The transmitter is still in operational condition, and each year on a day called Alexanderson Day is started up and transmits brief Morse code test transmissions, which can be received all over Europe.
Radio receiver design includes the electronic design of different components of a radio receiver which processes the radio frequency signal from an antenna in order to produce usable information such as audio. The complexity of a modern receiver and the possible range of circuitry and methods employed are more generally covered in electronics and communications engineering. The term radio receiver is understood in this article to mean any device which is intended to receive a radio signal in order to generate useful information from the signal, most notably a recreation of the so-called baseband signal which modulated the radio signal at the time of transmission in a communications or broadcast system.

The Soviet A-7 VHF radio transceiver was developed during World War II and used for communication in rifle brigades and regiments. The complete station was designed to be transported by an individual soldier.

The autodyne circuit was an improvement to radio signal amplification using the De Forest Audion vacuum tube amplifier. By allowing the tube to oscillate at a frequency slightly different from the desired signal, the sensitivity over other receivers was greatly improved. The autodyne circuit was invented by Edwin Howard Armstrong of Columbia University, New York, NY. He inserted a tuned circuit in the output circuit of the Audion vacuum tube amplifier. By adjusting the tuning of this tuned circuit, Armstrong was able to dramatically increase the gain of the Audion amplifier. Further increase in tuning resulted in the Audion amplifier reaching self-oscillation.

Survival radios are carried by pilots and search and rescue teams to facilitate rescue in an emergency. They are generally designed to transmit on international distress frequencies. Maritime systems have been standardized under the Global Maritime Distress Safety System. Civil and military organisation's utilized different frequencies to communicate and no infringement on either sector would take place. For emergencies involving civilian aircraft, the radio frequency used is VHF 121.5 MHz and for military aircraft incidents, the frequency used is UHF 243 MHz.

The SCR-300 was a portable radio transceiver used by US Signal Corps in World War II. This backpack-mounted unit was the first radio to be nicknamed a "walkie talkie".

The BC-342 was a World War II U.S. Army Signal Corps high frequency radio receiver. It was used primarily as part of field installations such as the SCR-188A, but could be used with mobile sets such as the 2 1/2 ton mounted SCR-399. First designed at Fort Monmouth, New Jersey by the U.S. Army Signal Corps, it was built by various manufacturers including RCA. Many of the later units that are encountered today were manufactured by the Farnsworth Television and Radio Corporation of Fort Wayne, Indiana. Variants include the low frequency coverage BC-344 receiver, and the battery or dynamotor powered BC-312 receiver.
The SCR-68 was a military radiotelephone used by the US Army Signal Corps as an aircraft radio in the waning months of World War I. Due to its many problems, primarily its inability to communicate with other radios, like its ground component the SCR-67 or the larger truck mounted SCR-108, over large distances, the SCR-68 quickly became obsolete. Nonetheless, the SCR-68 was one of the first steps towards developing more effective messaging between pilots and commanders, even beyond military usage.

The Radio tractor was a mobile Signal Corps Radio used by the U.S. Army for ground communications before and during World War I. Prior to World War I, trucks were referred to as "tractors", and there were also telegraph tractors, and telephone tractors.

The SCR-508 radio was a mobile Signal Corps Radio used by the U.S. Army during World War II, for short range ground communications. The SCR-508 series radio represented the Army's commitment to both FM and crystal tuning, and was used extensively by armor and mechanized units. The turret bustle of late series light and medium tanks was designed around this radio.
A magnetoquasistatic field is a class of electromagnetic field in which a slowly oscillating magnetic field is dominant. A magnetoquasistatic field is typically generated by low-frequency induction from a magnetic dipole or a current loop. The magnetic near-field of such an emitter behaves differently from the more commonly used far-field electromagnetic radiation. At low frequencies the rate of change of the instantaneous field strength with each cycle is relatively slow, giving rise to the name "magneto-quasistatic". The near field or quasistatic region typically extends no more than a wavelength from the antenna, and within this region the electric and magnetic fields are approximately decoupled.
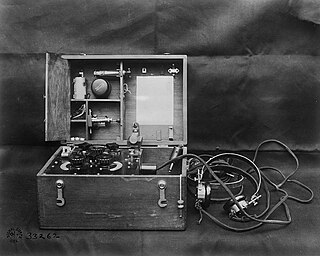
The SCR-54 was a tunable, portable crystal radio receiver used by the U. S. Army during World War I for fire control in conjunction with airplanes.



















