
Algae is an informal term for a large, diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms that are not necessarily closely related, and is thus polyphyletic. Including organisms ranging from unicellular microalgae genera, such as Chlorella and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to 50 m in length. Most are aquatic and autotrophic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem, and phloem, which are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a division of green algae which includes, for example, Spirogyra and the stoneworts.

Seagrasses are flowering plants (angiosperms) which grow in marine environments. There are 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families, all in the order Alismatales. Seagrasses evolved from terrestrial plants which migrated back into the ocean about 75-100 million years ago.

Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae, typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist individually, or in chains or groups. Depending on the species, their sizes can range from a few micrometers (µm) to a few hundred micrometers. Unlike higher plants, microalgae do not have roots, stems, or leaves. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces. Microalgae, capable of performing photosynthesis, are important for life on earth; they produce approximately half of the atmospheric oxygen and use simultaneously the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide to grow photoautotrophically. Microalgae, together with bacteria, form the base of the food web and provide energy for all the trophic levels above them. Microalgae biomass is often measured with chlorophyll a concentrations and can provide a useful index of potential production. The standing stock of microphytes is closely related to that of its predators. Without grazing pressures the standing stock of microphytes dramatically decreases.
Algal nutrient solutions are made up of a mixture of chemical salts and water. Sometimes referred to as "Growth Media", nutrient solutions, provide the materials needed for algae to grow. Nutrient solutions, as opposed to fertilizers, are designed specifically for use in aquatic environments and their composition is much more precise.

Botryococcus braunii is a green, pyramid-shaped planktonic microalga that is of potentially great importance in the field of biotechnology. Colonies held together by a lipid biofilm matrix can be found in temperate or tropical oligotrophic lakes and estuaries, and will bloom when in the presence of elevated levels of dissolved inorganic phosphorus. The species is notable for its ability to produce high amounts of hydrocarbons, especially oils in the form of Triterpenes, that are typically around 30–40% of their dry weight. Compared to other green alge species it has a relatively thick cell wall that is accumulated from previous cellular divisions; making extraction of cytoplasmic components rather difficult. Much of the useful hydrocarbon oil is outside of the cell.

Algae fuel, algal biofuel, or algal oil is an alternative to liquid fossil fuels that uses algae as its source of energy-rich oils. Also, algae fuels are an alternative to commonly known biofuel sources, such as corn and sugarcane. Several companies and government agencies are funding efforts to reduce capital and operating costs and make algae fuel production commercially viable. Like fossil fuel, algae fuel releases CO2 when burnt, but unlike fossil fuel, algae fuel and other biofuels only release CO2 recently removed from the atmosphere via photosynthesis as the algae or plant grew. The energy crisis and the world food crisis have ignited interest in algaculture (farming algae) for making biodiesel and other biofuels using land unsuitable for agriculture. Among algal fuels' attractive characteristics are that they can be grown with minimal impact on fresh water resources, can be produced using saline and wastewater, have a high flash point, and are biodegradable and relatively harmless to the environment if spilled. Algae cost more per unit mass than other second-generation biofuel crops due to high capital and operating costs, but are claimed to yield between 10 and 100 times more fuel per unit area. The United States Department of Energy estimates that if algae fuel replaced all the petroleum fuel in the United States, it would require 15,000 square miles (39,000 km2), which is only 0.42% of the U.S. map, or about half of the land area of Maine. This is less than 1⁄7 the area of corn harvested in the United States in 2000.

Trophic State Index (TSI) is a classification system designed to rate bodies of water based on the amount of biological activity they sustain. Although the term "trophic index" is commonly applied to lakes, any surface body of water may be indexed.

Cellana, Inc. is a Hawaii- and San Diego-based developer of algae-based bioproducts for high-value nutrition, ink, and bioenergy applications, including Omega-3 nutraceutical applications, sustainable ink, aquaculture and animal feeds, human food ingredients, pigments, specialty chemicals, and biofuels. Cellana has received multiple multimillion-dollar grants from the United States Department of Energy and United States Department of Agriculture. In 2018, Cellana and POS Bio-Sciences announced the signing of a letter of intent for the joint development and commercialization of high-value EPA Omega-3 oils from Cellana’s algae biomass. In December 2016, the United States Department of Energy published a funding opportunity announcement in which Cellana's lead commercial algae strains KA32 and CO46, and the biomass yields demonstrated from these strains as part of the DOE-funded Algae Testbed Public-Private Partnership (ATP3), were designated as DOE's "State of Technology" for the photosynthetic algae sector in the United States. In 2017, Cellana and Living Ink Technologies announced the signing of a letter of intent for the joint development and commercialization of inks containing Cellana’s renewable algae biomass. In 2013, Cellana and Neste Oil, the world's largest refiner of renewable diesel, announced the signing of a multi-year, commercial-scale off-take agreement for algae-based biocrude oil.
Algae fuel in the United States, as with other countries, is under study as a source of biofuel.

Scallop aquaculture is the commercial activity of cultivating (farming) scallops until they reach a marketable size and can be sold as a consumer product. Wild juvenile scallops, or spat, were collected for growing in Japan as early as 1934. The first attempts to fully cultivate scallops in farm environments were not recorded until the 1950s and 1960s. Traditionally, fishing for wild scallops has been the preferred practice, since farming can be expensive. However worldwide declines in wild scallop populations have resulted in the growth of aquaculture. Globally the scallop aquaculture industry is now well established, with a reported annual production totalling over 1,200,000 metric tonnes from about 12 species. China and Japan account for about 90% of the reported production.
Nasrin Moazami is an Iranian medical microbiologist and biotechnologist. She received her Ph.D. in 1976, from the Faculty of Medicine at Laval University. Moazami is the pioneer of biotechnology and microalgae-based fuels in Iran.
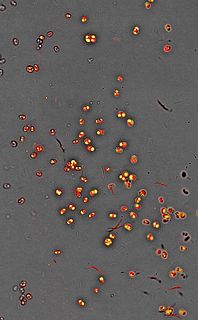
Nannochloropsis is a genus of alga within the heterokont line of eukaryotes, that is being investigated for biofuel production. One marine Nannochloropsis species has been shown to be suitable for algal biofuel production due to its ease of growth and high oil content, mainly unsaturated fatty acids and a significant percentage of palmitic acid. It also contains enough unsaturated fatty acid linolenic acid and polyunsaturated acid for a quality biodiesel.
The Spanish Bank of Algae is a national R&D service attached to the Marine Biotechnology Center of the University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria (ULPGC), which objectives are the isolation, identification, characterization, conservation and provisioning of microalgae and cyanobacteria. It was previously known as the National Bank of Algae (BNA).

Carbon-neutral fuel is energy fuel or energy systems which have no net greenhouse gas emissions or carbon footprint. One class is synthetic fuel produced from renewable, sustainable or nuclear energy used to hydrogenate carbon dioxide directly captured from the air (DAC), recycled from power plant flue exhaust gas or derived from carbonic acid in seawater. Renewable energy sources include wind turbines, solar panels, and hydroelectric power stations. Another type of renewable energy source is biofuel. Such fuels are potentially carbon-neutral because they do not result in a net increase in atmospheric greenhouse gases.
Michael Melkonian is a German botanist and professor of botany at the University of Cologne.
Phycotechnology refers to the technological applications of algae, both micro- and macroalgae. Algae is extremely useful in various fields. An example for natural phycotechnology is the converting of atmospheric nitrogen into bioaccessible nitrogenous compounds by diazotrophic cyanobacteria. Species of cyanobacteria like Nostoc, Arthrospira (Spirulina) and Aphanizomenon are used as food and feed due to their easy digestibility and nutrient content. Species of Dunaliella provide products like glycerol, carotenoids, and proteins. Algal-produced proteins can be biofactories for the production of therapeutic substances. Algae is also being used to assist in the remediation of pollution, to create bio-fuels, and as a bio-insecticide.

Sammy Boussiba is a professor emeritus at the French Associates Institute for Agriculture and Biotechnology of Drylands at the Jacob Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel.






















