
The standard circulating coinage of the United Kingdom, British Crown Dependencies and British Overseas Territories is denominated in pennies and pounds sterling, and ranges in value from one penny sterling to two pounds. Since decimalisation, on 15 February 1971, the pound has been divided into 100 (new) pence. Before decimalisation, twelve pence made a shilling, and twenty shillings made a pound.

The shilling is a historical coin, and the name of a unit of modern currencies formerly used in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, other British Commonwealth countries and Ireland, where they were generally equivalent to 12 pence or one-twentieth of a pound before being phased out during the 20th century.

The History of the English penny from 1485 to 1603 covers the period of the Tudor dynasty.

The double florin, or four-shilling piece, was a British coin produced by the Royal Mint between 1887 and 1890. One of the shortest-lived of all British coin denominations, it was struck in only four years. Its obverse, designed by Joseph Boehm and engraved by Leonard Charles Wyon, depicts Queen Victoria, whilst the reverse, featuring national symbols of the United Kingdom, was designed by Wyon based on the coinage of Charles II.

The guinea was a coin, minted in Great Britain between 1663 and 1814, that contained approximately one-quarter of an ounce of gold. The name came from the Guinea region in West Africa, from where much of the gold used to make the coins was sourced. It was the first English machine-struck gold coin, originally representing a value of 20 shillings in sterling specie, equal to one pound, but rises in the price of gold relative to silver caused the value of the guinea to increase, at times to as high as thirty shillings. From 1717 to 1816, its value was officially fixed at twenty-one shillings.

The half guinea gold coin of the Kingdom of England and later of Great Britain was first produced in 1669, some years after the Guinea entered circulation. It was officially eliminated in the Great Recoinage of 1816, although, like the guinea, it was used in quoting prices until decimalisation.

The British crown was a denomination of sterling coinage worth 1/4 of one pound, or 5 shillings, or 60 (old) pence. The crown was first issued during the reign of Edward VI, as part of the coinage of the Kingdom of England.

The half sovereign is a British gold coin with a nominal value of half of one pound sterling. It is half the weight of its counterpart 'full' sovereign coin.
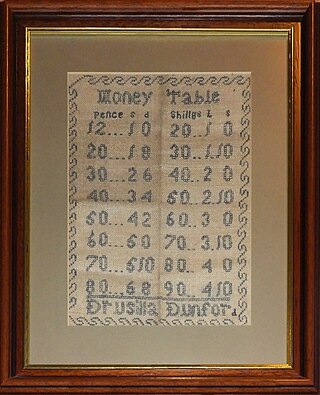
£sd is the popular name for the pre-decimal currencies once common throughout Europe, especially in the British Isles and hence in several countries of the British Empire and subsequently the Commonwealth. The abbreviation originates from the Latin currency denominations librae, solidi, and denarii. In the United Kingdom, these were referred to as pounds, shillings, and pence.
George Edward Kruger Gray was an English artist, best remembered for his designs of coinage and stained glass windows.

The British sixpence piece, sometimes known as a tanner or sixpenny bit, was a denomination of sterling coinage worth 1⁄40 of one pound or half of one shilling. It was first minted in 1551, during the reign of Edward VI, and circulated until 1980. The coin was made from silver from its introduction in 1551 until 1947, and thereafter in cupronickel.

The pound was the currency of New Zealand from 1840 until 1967, when it was replaced by the New Zealand dollar. Like the pound sterling, it was subdivided into 20 shillings each of 12 pence.

The pound was the official currency of Jamaica between 1840 and 1969. It circulated as a mixture of sterling coinage and locally issued coins and banknotes and was always equal to the pound sterling. The Jamaican pound was also used in the Cayman and Turks and Caicos Islands.
The coins of the Rhodesian pound were part of the currency of Southern Rhodesia, which changed its name to Rhodesia, following the break-up of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, when the Rhodesian pound replaced the Rhodesia and Nyasaland pound, which had replaced the Southern Rhodesian pound.

Gun money was an issue of coins made by the forces of James II during the Williamite War in Ireland between 1689 and 1691. They were minted in base metal, and were designed to be redeemed for silver coins following a victory by James II and consequently bore the date in months to allow a gradual replacement. As James lost the war, that replacement never took place, although the coins were allowed to circulate at much reduced values before the copper coinage was resumed. They were mostly withdrawn from circulation in the early 18th century.

The Australian Shilling, informally called a "bob", was a type of silver coinage issued by the Commonwealth of Australia, that circulated prior to the decimalisation of Australian coinage. The Australian shilling was derived from the British pre-decimal sterling pound system and was first issued following the passing of the Australian Coinage Act 1909, which established Australia's first formal currency system. The shilling was issued as part of Australia's silver coinage, which included the two-shilling (florin), the sixpence and the threepence. The shilling was minted from 1910 until 1963. During this period there was one significant modification to the design of the Australian shilling, the change in its reverse design, which occurred in 1938 when the design was altered from the Australian Coat of Arms (1910-1936) to the visage of a Merino ram’s head (1938-1963).

The Australian sixpence circulated from 1910 up until the decimalisation of Australian Currency in 1966. The coins were initially minted in England; however, Australia began to mint their own from the year of 1916 at branches of the Royal Mint in Sydney and Melbourne. The coins which made up Australia's pre-decimal currency were identical to British currency in the characteristics of weight and size. The Coinage Act of 1909–1947, authorised the issue of Australian coins in the select denominations, including the sixpence. By 1916 all silver denominations, including the sixpence, could be minted at the Royal Mint branch in Melbourne. Unique Australian currency was created with decimalisation in 1966.
A Crown of the Rose is an extremely rare gold coin of the Kingdom of England introduced in 1526 during the reign of Henry VIII, in an attempt to compete with the French écu au soleil. The coin was not a success and just a few months later it was replaced by the Crown of the Double-Rose.
The English shilling was a silver coin of the Kingdom of England, when first introduced known as the testoon. A shilling was worth twelve pence, and there were 20 shillings to the pound sterling. The English shilling was introduced in the 16th century and remained in circulation until it became the British shilling as the result of the Union of England and Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707.

Jubilee coinage or Jubilee head coinage are British coins with an obverse featuring a depiction of Queen Victoria by Joseph Edgar Boehm. The design was placed on the silver and gold circulating coinage beginning in 1887, and on the Maundy coinage beginning in 1888. The depiction of Victoria wearing a crown that was seen as too small was widely mocked, and was replaced in 1893. The series saw the entire issuance of the double florin (1887–1890) and, in 1888, the last issue for circulation of the groat, or fourpence piece, although it was intended for use in British Guiana. No bronze coins were struck with the Jubilee design.

















