This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

Alfred the Great was King of Wessex from 871 to c. 886 and King of the Anglo-Saxons from c. 886 to 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf of Wessex. His father died when he was young and three of Alfred's brothers reigned in turn. Alfred took the throne after the death of his brother Æthelred and spent several years dealing with Viking invasions. He won a decisive victory in the Battle of Edington in 878 and made an agreement with the Vikings, creating what was known as Danelaw in the North of England. Alfred also oversaw the conversion of Viking leader Guthrum. He successfully defended his kingdom against the Viking attempt at conquest, and he became the dominant ruler in England. He was also the first King of the West Saxons to style himself King of the Anglo-Saxons. Details of his life are described in a work by 9th-century Welsh scholar and bishop Asser.
Anglo-Saxon may refer to:
Ælle is recorded in early sources as the first king of the South Saxons, reigning in what is now called Sussex, England, from 477 to perhaps as late as 514.

Wessex was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from 519 until England was unified by Æthelstan in the early 10th century.

The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited Great Britain from the 5th century, and the direct ancestors of the majority of the modern British people. They comprise people from Germanic tribes who migrated to the island from continental Europe, their descendants, and indigenous British groups who adopted many aspects of Anglo-Saxon culture and language; the cultural foundations laid by the Anglo-Saxons are the foundation of the modern English legal system and of many aspects of English society; the modern English language owes over half its words – including the most common words of everyday speech – to the language of the Anglo-Saxons. Historically, the Anglo-Saxon period denotes the period in Britain between about 450 and 1066, after their initial settlement and up until the Norman conquest.
The early Anglo-Saxon period includes the creation of an English nation, with many of the aspects that survive today, including regional government of shires and hundreds. During this period, Christianity was established and there was a flowering of literature and language. Charters and law were also established. The term Anglo-Saxon is popularly used for the language that was spoken and written by the Anglo-Saxons in England and eastern Scotland between at least the mid-5th century and the mid-12th century. In scholarly use, it is more commonly called Old English.
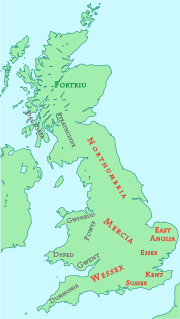
The Kingdom of the South Saxons, today referred to as the Kingdom of Sussex, was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. On the south coast of the island of Great Britain, it was originally a sixth century Saxon colony and later an independent kingdom. The South Saxons were ruled by the kings of Sussex until the country was annexed by Wessex, probably in 827, in the aftermath of the Battle of Ellandun.

The Battle of Stamford Bridge took place at the village of Stamford Bridge, East Riding of Yorkshire, in England on 25 September 1066, between an English army under King Harold Godwinson and an invading Norwegian force led by King Harald Hardrada and the English king's brother Tostig Godwinson. After a bloody battle, both Hardrada and Tostig along with most of the Norwegians were killed. Although Harold Godwinson repelled the Norwegian invaders, his army was defeated by the Normans at Hastings less than three weeks later. The battle has traditionally been presented as symbolising the end of the Viking Age, although major Scandinavian campaigns in Britain and Ireland occurred in the following decades, such as those of King Sweyn Estrithson of Denmark in 1069–1070 and King Magnus Barefoot of Norway in 1098 and 1102–1103.

Anglo-Saxon England was early medieval England, existing from the 5th to the 11th centuries from the end of Roman Britain until the Norman conquest in 1066. It consisted of various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms until 927 when it was united as the Kingdom of England by King Æthelstan. It became part of the short-lived North Sea Empire of Cnut the Great, a personal union between England, Denmark and Norway in the 11th century.
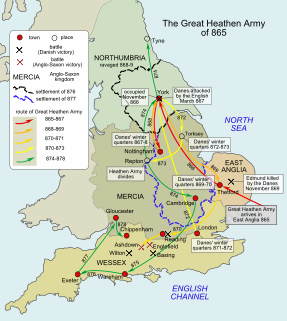
The Great Danish Army, known by the Anglo-Saxons as the Great Heathen Army, was a coalition of Norse warriors, originating in Denmark but also from Norway and Sweden, who came together under a unified command to invade the four Anglo-Saxon kingdoms that constituted England in AD 865.

The Kingdom of the East Angles, today known as the Kingdom of East Anglia, was a small independent kingdom of the Angles comprising what are now the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk and perhaps the eastern part of the Fens. The kingdom formed in the 6th century in the wake of the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. It was ruled by the Wuffingas in the 7th and 8th centuries, but fell to Mercia in 794, and was conquered by the Danes in 869, forming part of the Danelaw. It was conquered by Edward the Elder and incorporated into the Kingdom of England in 918.
*Sowilō or *sæwelō is the reconstructed Proto-Germanic language name of the s-rune, meaning "sun". The name is attested for the same rune in all three Rune Poems. It appears as Old Norse sól, Old English sigel, and Gothic sugil.
The Battle of Mercredesburne was one of three battles fought as part of the conquest of what became the Kingdom of Sussex in southern England. The battles were fought between the Saxon leader Ælle's army and the local Britons.
The archaeology of Anglo-Saxon England
A bed burial is a type of burial in which the deceased person is buried in the ground, lying upon a bed. It is a burial custom that is particularly associated with high status women during the early Anglo-Saxon period, although excavated examples of bed burials are comparatively rare.

The SS Cevic was a steam ship built by Harland and Wolff for the White Star Line for service initially in the North Atlantic. Later she was transferred to the Australia run. On the outbreak of the First World War she was sold to the Admiralty and converted to a dummy capital ship. Later she was transferred to the Royal Fleet Auxiliary. After the war she was sold to the Anglo-Saxon Petroleum Company.

The SS Georgic was a steam ship built by Harland and Wolff for the White Star Line to replace the SS Naronic which was lost at sea. Georgic was a cargo ship designed principally to carry livestock, at the time of entering service in 1895 she was the largest cargo ship in the world with a deadweight tonnage of 12,000 tons.









