In NATO, a STANdardization AGreement (STANAG) defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the alliance. Each NATO state ratifies a STANAG and implements it within their own military. The purpose is to provide common operational and administrative procedures and logistics, so one member nation's military may use the stores and support of another member's military. STANAGs also form the basis for technical interoperability between a wide variety of communication and information systems (CIS) essential for NATO and Allied operations. The Allied Data Publication 34 (ADatP-34) NATO Interoperability Standards and Profiles which is covered by STANAG 5524, maintains a catalogue of relevant information and communication technology standards.

The FAMAS is a bullpup-styled assault rifle designed and manufactured in France by MAS located in Saint-Étienne, which is now a member of the French government-owned Nexter group. It is being replaced as the service rifle of the French military by the HK416F. It is known by French troops as Le Clairon due to its distinctive shape. The FAMAS is recognized for its high rate of fire at 1,100 rounds per minute.

The Negev is a 5.56×45mm NATO light machine gun developed by the Israeli firearm manufacturer, Israel Weapon Industries (IWI).

A magazine is an ammunition storage and feeding device within or attached to a repeating firearm. Magazines can be removable (detachable) or integral (internal/fixed) to the firearm. The magazine functions by moving the cartridges stored within it into a position where they may be loaded into the barrel chamber by the action of the firearm. The detachable magazine is often colloquially referred to as a clip, although this is technically inaccurate.

NATO Joint Military Symbology is the NATO standard for military map marking symbols. Originally published in 1986 as Allied Procedural Publication 6 (APP-6), NATO Military Symbols for Land Based Systems, the standard has evolved over the years and is currently in its fourth version (APP-6C). The symbols are designed to enhance NATO's joint interoperability by providing a standard set of common symbols. APP-6 constituted a single system of joint military symbology for land, air, space and sea-based formations and units, which can be displayed for either automated map display systems or for manual map marking. It covers all of the joint services and can be used by them.

The 105 mm M101A1 howitzer was an artillery piece developed and used by the United States. It was the standard U.S. light field howitzer in World War II and saw action in both the European and Pacific theaters. Entering production in 1941, it quickly gained a reputation for accuracy and a powerful punch. The M101A1 fired 105 mm (4.1 in) high explosive (HE) semi-fixed ammunition and had a range of 12,330 yards (11,270 m), making it suitable for supporting infantry.
The G41 is a German 5.56×45mm NATO assault rifle introduced in 1981 and produced in limited quantities by Heckler & Koch. It was designed to replace the 5.56mm Heckler & Koch HK33 in service providing a more modern weapon compatible with contemporary NATO standards. It is chambered for the 5.56×45mm NATO cartridge and can use both SS109 and M193 ammunition. Assembly of the G41 has been discontinued by Heckler & Koch, however, production rights to the rifle were acquired by the Italian arms manufacturer Luigi Franchi.

The 105 mm Howitzer M3 was a U.S. light howitzer designed for use by airborne troops. The gun utilized the barrel of the 105 mm Howitzer M2, shortened and fitted to a slightly modified split trail carriage of the 75 mm pack howitzer.
The NATO Codification System is a Standardization Agreement approach to identify, classify and number items of supply. This is applicable to items that are repetitively used and stocked. The System has been agreed by all signatories of the NATO and sponsored non-NATO nations for use in identifying equipment and supplies. The result is a unique identification and a data set that can be easily shared and understood by a wide range of users. The data set may be shared in the form of printed catalogs, on line systems, electronic data exchange, etc. Users include logisticians and manufacturers.

A STANAG magazine or NATO magazine is a type of detachable firearm magazine proposed by NATO in October 1980. Shortly after NATO's acceptance of the 5.56×45mm NATO rifle cartridge, Draft Standardization Agreement (STANAG) 4179 was proposed in order to allow NATO members to easily share rifle ammunition and magazines down to the individual soldier level. The U.S. M16 rifle's magazine proportions were proposed for standardization. Many NATO members, but not all, subsequently developed or purchased rifles with the ability to accept this type of magazine. However the standard was never ratified and remains a "Draft STANAG".
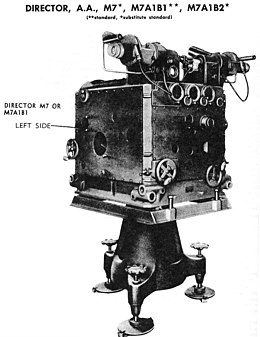
A director, also called an auxiliary predictor, is a mechanical or electronic computer that continuously calculates trigonometric firing solutions for use against a moving target, and transmits targeting data to direct the weapon firing crew.

NATO EPVAT testing is one of the three recognized classes of procedures used in the world to control the safety and quality of firearms ammunition.

The 7.62×51mm NATO is a rimless bottlenecked rifle cartridge developed in the 1950s as a standard for small arms among NATO countries. It should not be confused with the similarly named Russian 7.62×54mmR cartridge, a slightly longer rimmed cartridge.

STANAG 4355 - The Modified Point Mass and Five Degrees of Freedom Trajectory Model is a NATO Standardization Agreement for surface to surface exterior ballistic modelling in support of Artillery, mortar and rocket systems. This model is not as time consuming to solve as the rigid body system, and uses a force system, axial spin and an estimate of the yaw of repose.

STANAG 6022 - Adoption of a Standard Gridded Data Meteorological Message is a NATO Standardization Agreement for gridded meteorological data for operational use in Artillery fire control systems, NBC Automated Warning, Reporting and Prediction Systems, and various computer-based Battlefield Decision Aids (BDAs). The message format is referred to as METGM.

STANAG 4140 - Adoption of a Standard Target Acquisition Meteorological Message (METTA) is a NATO Standardization Agreement to provide meteorological information such as refractive index, temperature, pressure and cloud cover for remotely piloted vehicles, drones, weapon locating radars and sound ranging systems.

STANAG 4082 - Adoption of a Standard Artillery Computer Meteorological Message (METCM) is a NATO Standardization Agreement to provide meteorological information for External ballistics. The information consists of virtual temperature, pressure, and wind speed/direction.
STANAG 4586(NATO Standardization Agreement 4586) is a NATO Standard Interface of the Unmanned Control System (UCS) Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) interoperability. It defines architectures, interfaces, communication protocols, data elements and message formats. It includes data link, command and control, and human/computer interfaces. The current revision is STANAG 4586 Edition No 4 with mission phase enhancements, an updated list of vehicle identifiers etc.

The NATO Standardization Office (NSO) is a NATO agency created in 2001 to handle standardization activities for NATO. The NSA was formed through the merger of the Military Agency for Standardization and the Office for NATO Standardization. The NSA is the executive branch of the NATO Standardization Organization (NSO), which is headed by the Director of the NATO Standardization Agency (DNSA).













