
Narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) is a personality disorder characterized by a life-long pattern of exaggerated feelings of self-importance, an excessive need for admiration, and a diminished ability to empathize with other people's feelings. Narcissistic personality disorder is one of the sub-types of the broader category known as personality disorders. It is often comorbid with other mental disorders and associated with significant functional impairment and psychosocial disability.

Schizoid personality disorder is a personality disorder characterized by a lack of interest in social relationships, a tendency toward a solitary or sheltered lifestyle, secretiveness, emotional coldness, detachment, and apathy. Affected individuals may be unable to form intimate attachments to others and simultaneously possess a rich and elaborate but exclusively internal fantasy world. Other associated features include stilted speech, a lack of deriving enjoyment from most activities, feeling as though one is an "observer" rather than a participant in life, an inability to tolerate emotional expectations of others, apparent indifference when praised or criticized, all forms of asexuality, and idiosyncratic moral or political beliefs.

Dependent personality disorder (DPD) is a personality disorder characterized by a pervasive psychological dependence on other people. This personality disorder is a long-term condition in which people depend on others to meet their emotional and physical needs. Dependent personality disorder is a cluster C personality disorder, which is characterized by excessive fear and anxiety. It begins prior to early adulthood, and it is present in a variety of contexts and is associated with inadequate functioning. Symptoms can include anything from extreme passivity, devastation or helplessness when relationships end, avoidance of responsibilities, and severe submission.
Drew Westen is a professor in the Departments of Psychology and Psychiatry at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia; the founder of Westen Strategies, LLC, a strategic messaging consulting firm that serves nonprofits and political organizations. Additionally, Westen is a writer. He is also the co-founder, alongside Joel Weinberger, of Implicit Strategies, a market research firm that measures consumers' unconscious responses to advertising and brands.
The Beck Depression Inventory, created by Aaron T. Beck, is a 21-question multiple-choice self-report inventory, one of the most widely used psychometric tests for measuring the severity of depression. Its development marked a shift among mental health professionals, who had until then, viewed depression from a psychodynamic perspective, instead of it being rooted in the patient's own thoughts.
The Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale (LSAS) is a short questionnaire developed in 1987 by Michael Liebowitz, a psychiatrist and researcher at Columbia University and the New York State Psychiatric Institute. Its purpose is to assess the range of social interaction and performance situations feared by a patient in order to assist in the diagnosis of social anxiety disorder. It is commonly used to study outcomes in clinical trials and, more recently, to evaluate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral treatments. The scale features 24 items, which are divided into two subscales. 13 questions relate to performance anxiety and 11 concern social situations. The LSAS was originally conceptualized as a clinician-administered rating scale, but has since been validated as a self-report scale.
The Yale–Brown Obsessive–Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS) is a test to rate the severity of obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) symptoms.
A depression rating scale is a psychometric instrument (tool), usually a questionnaire whose wording has been validated with experimental evidence, having descriptive words and phrases that indicate the severity of depression for a time period. When used, an observer may make judgements and rate a person at a specified scale level with respect to identified characteristics. Rather than being used to diagnose depression, a depression rating scale may be used to assign a score to a person's behaviour where that score may be used to determine whether that person should be evaluated more thoroughly for a depressive disorder diagnosis. Several rating scales are used for this purpose.
The Health Dynamics Inventory (HDI) is a 50 item self-report questionnaire developed to evaluate mental health functioning and change over time and treatment. The HDI was written to evaluate the three aspects of mental disorders as described in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM): "clinically significant behavioral or psychological syndrome or pattern...associated with present distress...or disability". This also corresponds to the phase model described by Howard and colleagues Accordingly, the HDI assesses (1) the experience of emotional or behavioral symptoms that define mental illness, such as dysphoria, worry, angry outbursts, low self-esteem, or excessive drinking, (2) the level of emotional distress related to these symptoms, and (3) the impairment or problems fulfilling the major roles of one's life.
The Bipolar Spectrum Diagnostic Scale (BSDS) is a psychiatric self-rating scale created by Ronald Pies in screening for bipolar disorder (BD). Its initial version consists of a descriptive narrative aimed to capture the nuances and milder variants of BD. Upon revision by Nassir Ghaemi and colleagues, the scale was developed into two sections for a total of 20 questions. The BSDS is widely accepted as an important measure of bipolar disorder alongside other diagnostic tools such as the Mood Disorder Questionnaire and the Bipolar Depression Rating Scale.
In personality pathology, dimensional models of personality disorders conceptualize personality disorders as qualitatively rather than quantitatively different from normal personality. They consist of extreme, maladaptive levels of certain personality characteristics. Within the context of personality psychology, a "dimension" refers to a continuum on which an individual can have various levels of a characteristic, in contrast to the dichotomous categorical approach in which an individual does or does not possess a characteristic. According to dimensional models personality disorders are classified according to which characteristics are expressed at which levels. This stands in contrast to the traditional categorical models of classification, which are based on the boolean presence or absence of symptoms and do not take into account levels of expression of a characteristic or the presence of any underlying dimension.
The Child Mania Rating Scales (CMRS) is a 21-item diagnostic screening measure designed to identify symptoms of mania in children and adolescents aged 9–17 using diagnostic criteria from the DSM-IV, developed by Pavuluri and colleagues. There is also a 10-item short form. The measure assesses the child's mood and behavior symptoms, asking parents or teachers to rate how often the symptoms have caused a problem for the youth in the past month. Clinical studies have found the CMRS to be reliable and valid when completed by parents in the assessment of children's bipolar symptoms. The CMRS also can differentiate cases of pediatric bipolar disorder from those with ADHD or no disorder, as well as delineating bipolar subtypes. A meta-analysis comparing the different rating scales available found that the CMRS was one of the best performing scales in terms of telling cases with bipolar disorder apart from other clinical diagnoses. The CMRS has also been found to provide a reliable and valid assessment of symptoms longitudinally over the course of treatment. The combination of showing good reliability and validity across multiple samples and clinical settings, along with being free and brief to score, make the CMRS a promising tool, especially since most other checklists available for youths do not assess manic symptoms.
The Dimensional Obsessive-Compulsive Scale (DOCS) is a 20-item self-report instrument that assesses the severity of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) symptoms along four empirically supported theme-based dimensions: (a) contamination, (b) responsibility for harm and mistakes, (c) incompleteness/symmetry, and (d) unacceptable (taboo) thoughts. The scale was developed in 2010 by a team of experts on OCD led by Jonathan Abramowitz, PhD to improve upon existing OCD measures and advance the assessment and understanding of OCD. The DOCS contains four subscales that have been shown to have good reliability, validity, diagnostic sensitivity, and sensitivity to treatment effects in a variety of settings cross-culturally and in different languages. As such, the DOCS meets the needs of clinicians and researchers who wish to measure current OCD symptoms or assess changes in symptoms over time.
The Clinically Administered PTSD Scale (CAPS) is an in-person clinical assessment for measuring posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The CAPS includes 30 items administered by a trained clinician to assess PTSD symptoms, including their frequency and severity. The CAPS distinguishes itself from other PTSD assessments in that it can also assess for current or past diagnoses of PTSD.

Vittorio Lingiardi is an Italian psychiatrist and psychoanalyst, Full Professor of Dynamic Psychology and past Director of the Clinical Psychology Specialization Program (2006-2013), Faculty of Medicine and Psychology, Sapienza University of Rome, Italy. He has coordinated with Nancy McWilliams the second edition of the Psychodynamic Diagnostic Manual, the PDM-2.
The Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia (K-SADS) is a semi-structured interview aimed at early diagnosis of affective disorders such as depression, bipolar disorder, and anxiety disorder. There are different versions of the test that have use different versions of diagnostic criteria, cover somewhat different diagnoses and use different rating scales for the items. All versions are structured to include interviews with both the child and the parents or guardians, and all use a combination of screening questions and more comprehensive modules to balance interview length and thoroughness.
The nine-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) is a depressive symptom scale and diagnostic tool introduced in 2001 to screen adult patients in primary care settings. The instrument assesses for the presence and severity of depressive symptoms and a possible depressive disorder. The PHQ-9 is a component of the larger self-administered Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ), but can be used as a stand-alone instrument. The PHQ is part of Pfizer's larger suite of trademarked products, called the Primary Care Evaluation of Mental Disorders (PRIME-MD). The PHQ-9 takes less than three minutes to complete. It is scored by simply adding up the individual items' scores. Each of the nine items reflects a DSM-5 symptom of depression. Primary care providers can use the PHQ-9 to screen for possible depression in patients.
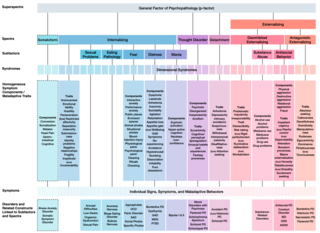
The Hierarchical Taxonomy Of Psychopathology (HiTOP) consortium was formed in 2015 as a grassroots effort to articulate a classification of mental health problems based on recent scientific findings on how the components of mental disorders fit together. The consortium is developing the HiTOP model, a classification system, or taxonomy, of mental disorders, or psychopathology, aiming to prioritize scientific results over convention and clinical opinion. The motives for proposing this classification were to aid clinical practice and mental health research. The consortium was organized by Drs. Roman Kotov, Robert Krueger, and David Watson. At inception it included 40 psychologists and psychiatrists, who had a record of scientific contributions to classification of psychopathology The HiTOP model aims to address limitations of traditional classification systems for mental illness, such as the DSM-5 and ICD-10, by organizing psychopathology according to evidence from research on observable patterns of mental health problems.
The Zanarini Rating Scale for Borderline Personality Disorder (ZAN-BPD) is a standardized, diagnostic rating scale designed to measure the severity and changes in the symptoms of borderline personality disorder (BPD) over time. The assessment was developed by Mary Zanarini and her colleagues at McLean Hospital and released in 2003.




