Related Research Articles

An assault is the act of inflicting physical harm or unwanted physical contact upon a person or, in some specific legal definitions, a threat or attempt to commit such an action. It is both a crime and a tort and, therefore, may result in criminal prosecution, civil liability, or both. Generally, the common law definition is the same in criminal and tort law.
Negligence is a failure to exercise appropriate and/or ethical ruled care expected to be exercised amongst specified circumstances. The area of tort law known as negligence involves harm caused by failing to act as a form of carelessness possibly with extenuating circumstances. The core concept of negligence is that people should exercise reasonable care in their actions, by taking account of the potential harm that they might foreseeably cause to other people or property.
In law and insurance, a proximate cause is an event sufficiently related to an injury that the courts deem the event to be the cause of that injury. There are two types of causation in the law: cause-in-fact, and proximate cause. Cause-in-fact is determined by the "but for" test: But for the action, the result would not have happened. The action is a necessary condition, but may not be a sufficient condition, for the resulting injury. A few circumstances exist where the but for test is ineffective. Since but-for causation is very easy to show, a second test is used to determine if an action is close enough to a harm in a "chain of events" to be legally valid. This test is called proximate cause. Proximate cause is a key principle of Insurance and is concerned with how the loss or damage actually occurred. There are several competing theories of proximate cause. For an act to be deemed to cause a harm, both tests must be met; proximate cause is a legal limitation on cause-in-fact.
Delict is a term in civil law jurisdictions for a civil wrong consisting of an intentional or negligent breach of duty of care that inflicts loss or harm and which triggers legal liability for the wrongdoer; however, its meaning varies from one jurisdiction to another. Other civil wrongs include breach of contract and breach of trust. Liability is imposed on the basis of moral responsibility, i.e. a duty of care or to act, and fault (culpa) is the main element of liability. The term is used in mixed legal systems such as Scotland, South Africa, Louisiana and the Philippines, but tort is the equivalent legal term used in common law jurisdictions.
The concept of justifiable homicide in criminal law is a defense to culpable homicide. Generally, there is a burden of production of exculpatory evidence in the legal defense of justification. In most countries, a homicide is justified when there is sufficient evidence to disprove the alleged criminal act or wrongdoing. The key to this legal defense is that it was reasonable for the subject to believe that there was an imminent and otherwise unavoidable danger of death or grave bodily harm to the innocent by the deceased when they committed the homicide. A homicide in this instance is blameless. Although it does not constitute homicide, charges and claims of assaults, batteries, and other similar criminal charges and claims of wrongdoing are similarly defensible under the legal defense of self defense.
Causation is the "causal relationship between the defendant's conduct and end result". In other words, causation provides a means of connecting conduct with a resulting effect, typically an injury. In criminal law, it is defined as the actus reus from which the specific injury or other effect arose and is combined with mens rea to comprise the elements of guilt. Causation only applies where a result has been achieved and therefore is immaterial with regard to inchoate offenses.
Murder is an offence under the common law of England and Wales. It is considered the most serious form of homicide, in which one person kills another with the intention to cause either death or serious injury unlawfully. The element of intentionality was originally termed malice aforethought, although it required neither malice nor premeditation. Baker, chapter 14 states that many killings done with a high degree of subjective recklessness were treated as murder from the 12th century right through until the 1974 decision in DPP v Hyam.
Causation in English law concerns the legal tests of remoteness, causation and foreseeability in the tort of negligence. It is also relevant for English criminal law and English contract law.

Edwin CameronSCOB is a retired judge who served as a Justice of the Constitutional Court of South Africa. He is well known for his HIV/AIDS and gay-rights activism and was hailed by Nelson Mandela as "one of South Africa's new heroes". President Ramaphosa appointed him as Inspecting Judge of Correctional Services from 1 January 2020 and in October 2019 he was elected Chancellor of Stellenbosch University.
Legal malpractice is the term for negligence, breach of fiduciary duty, or breach of contract by a lawyer during the provision of legal services that causes harm to a client.
Manslaughter is a common law legal term for homicide considered by law as less culpable than murder. The distinction between murder and manslaughter is sometimes said to have first been made by the ancient Athenian lawmaker Draco in the 7th century BC.
R v Blaue (1975) 61 Cr App R 271 is an English criminal law appeal in which the Court of Appeal decided, being a court of binding precedent thus established, that the refusal of a Jehovah's Witness to accept a blood transfusion after being stabbed did not constitute an intervening act for the purposes of legal causation. This upheld the decision of Mocatta J. in the court below.
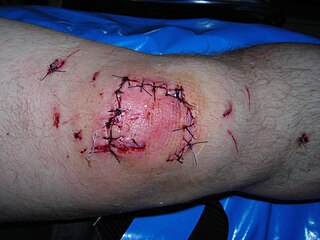
R v Dear [1996] is an English criminal law case, dealing with homicide and causation. The court ruled, slightly extending R v Holland, that even if a victim aggravates his wounds sufficiently to cause otherwise avoidable death, the chain of causation is not broken.
R. v. Smith [1959] 2 QB 35, [1959] A.C. is an English criminal law case, dealing with causation and homicide. The court ruled that negligence of medical staff, nor being dropped on the way from a stretcher twice, does not break the chain of causation in murder cases.
Fault, as a legal term, refers to legal blameworthiness and responsibility in each area of law. It refers to both the actus reus and the mental state of the defendant. The basic principle is that a defendant should be able to contemplate the harm that his actions may cause, and therefore should aim to avoid such actions. Different forms of liability employ different notions of fault, in some there is no need to prove fault, but the absence of it.

R v Jordan (1956) 40 Cr App R 152 was an English criminal law case that has been distinguished by two later key cases of equal precedent rank for its ruling that some situations of medical negligence following a wounding are those of breaking the chain of causation, capable of absolving a person who has inflicted bodily harm of guilt for an offence of the severity resulting from a consequent decline in bodily condition, in particular, homicide. The facts were ones whereby a wound was should to be almost certain, with no treatment, to heal itself. The medical attempt to facilitate recovery from the wound resulted in a non-prosecutable death as it was shown to have been negligent and principally an antibiotic error though far from unknown and well-intentioned. The appropriate charge(s) would be ones relating to wounding or disorder of the defendant, rather than homicide which could not have been said to have been caused by the defendant in any meaningful way.
South African criminal law is the body of national law relating to crime in South Africa. In the definition of Van der Walt et al., a crime is "conduct which common or statute law prohibits and expressly or impliedly subjects to punishment remissible by the state alone and which the offender cannot avoid by his own act once he has been convicted." Crime involves the infliction of harm against society. The function or object of criminal law is to provide a social mechanism with which to coerce members of society to abstain from conduct that is harmful to the interests of society.
S v Tembani may refer to either of two important cases in South African criminal law:
In S v Tembani, an important case in South African criminal law, the Supreme Court of Appeal held that the deliberate infliction of an intrinsically dangerous wound, from which the victim was likely to die without medical intervention, must generally lead to liability for an ensuing death, whether or not the wound was readily treatable, and even if the medical treatment given later was substandard or negligent—unless the victim had so recovered that at the time of the negligent treatment the original injury no longer posed a danger to his life.
R v Mubila is an important case in South African and Zimbabwean criminal law, heard on August 17, 1955, in which the accused was charged with murder. DP McCormac appeared for the Crown, and John Morris for the accused.
References
- S v Tembani 1999 (1) SACR 192 (W).