Saami or SAAMI may refer to:
- Sámi people, the indigenous people of Norway, Sweden, the Kola Peninsula and Finland
- Sámi languages, languages spoken by the Sámi
- Sporting Arms and Ammunition Manufacturers' Institute
Saami or SAAMI may refer to:

The Sámi are the traditionally Sámi-speaking peoples inhabiting the region of Sápmi, which today encompasses large northern parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and of the Kola Peninsula in Russia. The region of Sápmi was formerly known as Lapland, and the Sámi have historically been known in English as Lapps or Laplanders, but these terms are regarded as offensive by the Sámi, who prefer the area's name in their own languages, e.g. Northern Sámi Sápmi. Their traditional languages are the Sámi languages, which are classified as a branch of the Uralic language family.

Sápmi is the cultural region traditionally inhabited by the Sámi people. Sápmi is in Northern Europe and includes the northern parts of Fennoscandia, also known as the "Cap of the North".

Southern or South Sámi is the southwesternmost of the Sámi languages, and is spoken in Norway and Sweden. It is an endangered language; the strongholds of this language are the municipalities of Snåsa, Røyrvik, Røros and Hattfjelldal in Norway. Of the approximately 2000 Southern Sami, only about 500 still speak fluent Southern Sami. This language belongs to the Saamic group within the Uralic language family.

Kildin Sámi is a Sámi language spoken on the Kola Peninsula of northwestern Russia that today is and historically was inhabited by this group.

Traditional Sámi spiritual practices and beliefs are based on a type of animism, polytheism, and what anthropologists may consider shamanism. The religious traditions can vary considerably from region to region within Sápmi.

The Sámi people are a Native people of northern Europe inhabiting Sápmi, which today encompasses northern parts of Sweden, Norway, Finland, and the Kola Peninsula of Russia. The traditional Sámi lifestyle, dominated by hunting, fishing and trading, was preserved until the Late Middle Ages, when the modern structures of the Nordic countries were established.

Ter Sámi is the easternmost of the Sámi languages. It was traditionally spoken in the northeastern part of the Kola Peninsula, but now it is an extinct language; in 2004, only ten speakers were left. By 2010, the number of speakers had decreased to two. In 2020, they were presumed dead or uncontactable. Other estimates counted about 30 Ter Sámi speakers in Murmansk oblast, as well as in St. Petersburg, in 2007. The mean age of the youngest Ter Sámi speakers at that time was 50.

Ume Sámi is a Sámi language spoken in Sweden and formerly in Norway. It is a moribund language with an estimated 100 speakers. It was spoken mainly along the Ume River in the south of present-day Arjeplog, in Sorsele and in Arvidsjaur.

Pite Sámi or Arjeplog Sámi is a Sámi language traditionally spoken in Sweden and used to be spoken in Norway. It is a critically endangered language that has only about 25–50 native speakers left and is now only spoken on the Swedish side of the border along the Pite River in the north of Arjeplog and Arvidsjaur and in the mountainous areas of the Arjeplog municipality.

Skolt Sámi is a Uralic, Sámi language that is spoken by the Skolts, with approximately 300 speakers in Finland, mainly in Sevettijärvi and approximately 20–30 speakers of the Njuõʹttjäuʹrr (Notozero) dialect in an area surrounding Lake Lovozero in Russia. In Norway, there are fewer than 15 that can speak Skolt Sámi ; furthermore, the language is largely spoken in the Neiden area. It is written using a modified Roman orthography which was made official in 1973.
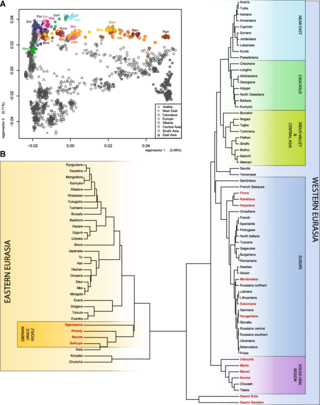
Genetic studies on Sami is the genetic research that have been carried out on the Sami people. The Sami languages belong to the Uralic languages family of Eurasia.

The Saami Council is a voluntary, non-governmental organization of the Sámi people made up of nine Sámi member organizations from Finland, Norway, Russia, and Sweden. Since the founding of the Nordic Saami Council in 1956, among the first indigenous peoples' organizations, the Saami Council has actively dealt with Sámi public policy tasks. In 1992, when Russian Sámi groups joined the council, "Nordic" was removed from the council's name. The secretary was previously sited in both Helsinki and Utsjoki, Finland, but is now in Kárášjohka, Norway. The Saami Council is funded by a range of grants, and its engagements are based on decisions, statements, declarations, and political programs from the Saami Conference held every four years.

Sámi languages, in English also rendered as Sami and Saami, are a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Sámi people in Northern Europe. There are, depending on the nature and terms of division, ten or more Sami languages. Several spellings have been used for the Sámi languages, including Sámi, Sami, Saami, Saame, Sámic, Samic and Saamic, as well as the exonyms Lappish and Lappic. The last two, along with the term Lapp, are now often considered pejorative.
Sámi politics refers to politics that concern the Sámi ethnic group in Norway, Sweden, Finland and Russia. In a more narrow sense, it has come to indicate the government of Sámi affairs by Sámi political institutions. This article deals with Sámi political structures, with an emphasis on the contemporary institutions.
Leif Rantala was a Finnish-Swedish linguist, and a specialist of Sami languages, cultures of history, especially of the Kola Peninsula.

Gollegiella is a pan-Nordic Sámi language award founded in 2004 by the ministers for Sámi affairs and the presidents of the Sámi Parliaments in Norway, Sweden, and Finland with the aim of promoting, developing and preserving the Sámi languages. The biennial award comes with a monetary prize that is currently 15,000 euros.
Sara Wesslin is a Skolt Saami journalist and news anchor from Finland and a strong advocate of the Skolt Sami language, her grandmother Olga's mother tongue. She took on the Finnish Ministry of Education and Culture to secure funding from Finland for the Nordic Resource Centre for the Sami languages.

Paleo-Laplandic is a hypothetical group of extinct but related languages spoken in Sápmi. The speakers of Paleo-Laplandic languages switched to Sámi languages, and the languages became extinct around 500 CE. A considerable amount of words in Sámi languages originate from Paleo-Laplandic; more than 1,000 loanwords from Paleo-Laplandic likely exist. Many toponyms in Sápmi originate from Paleo-Laplandic. Because Sámi language etymologies for reindeers have preserved a large number of words from Paleo-Laplandic, this suggests that Paleo-Laplandic groups influenced Sámi culture.
The Saami Council Literature Prize is a literary prize for Saami literature first awarded by the Saami Council in 1994. At first, the prize was awarded annually, although starting in 2003, it has been awarded roughly once every two years with authors of children's and young adult literature being honored every other time.