Related Research Articles

Ajaccio is a French commune, prefecture of the department of Corse-du-Sud, and head office of the Collectivité territoriale de Corse. It is also the largest settlement on the island. Ajaccio is located on the west coast of the island of Corsica, 210 nautical miles (390 km) southeast of Marseille.

Corsican is a Romance language consisting of the continuum of the Italo-Dalmatian dialects spoken on the Mediterranean island of Corsica (France) and on the northern end of the island of Sardinia (Italy). Corsican is related to the varieities of Tuscan from the Italian peninsula, and therefore also to the Florentine-based standard Italian.

Gallurese is a Romance dialect of the Italo-Dalmatian family spoken in the region of Gallura, northeastern Sardinia. Gallurese is variously described as a distinct southern dialect of Corsican or transitional language of the dialect continuum between Corsican and Sardinian. "Gallurese International Day" takes place each year in Palau (Sardinia) with the participation of orators from other areas, including Corsica.

Filippo Antonio Pasquale de' Paoli was a Corsican patriot, statesman, and military leader who was at the forefront of resistance movements against the Genoese and later French rule over the island. He became the President of the Executive Council of the General Diet of the People of Corsica and wrote the Constitution of the state.

The Corsican nuthatch is a species of bird in the nuthatch family Sittidae. It is a relatively small nuthatch, measuring about 12 cm (4.7 in) in overall length. The upperparts are bluish gray, the underparts grayish white. The male is distinguished from the female by its entirely black crown. The species is sedentary, territorial and not very shy. It often feeds high in Corsican pines, consuming mainly pine nuts, but also catching some flying insects. The breeding season takes place between April and May; the nest is placed in the trunk of an old pine, and the clutch has five to six eggs. The young fledge 22 to 24 days after hatching.

Corsican immigration to Puerto Rico resulted in the 19th century from widespread economic and political changes in Europe that made life difficult for the peasant and agricultural classes in Corsica and other territories. The Second Industrial Revolution drew more people into urban areas for work, widespread crop failure resulted from long periods of drought, and crop diseases, and political discontent rose. In the early nineteenth century, Spain lost most of its possessions in the so-called "New World" as its colonies won independence. It feared rebellion in its last two Caribbean colonies: Puerto Rico and Cuba. The Spanish Crown had issued the Royal Decree of Graces of 1815 which fostered and encouraged the immigration of European Catholics, even if not of Spanish origin, to its Caribbean colonies.

Asterix in Corsica is the twentieth volume of the Asterix comic book series, by René Goscinny (stories) and Albert Uderzo (artwork). It was originally serialized in Pilote issues 687–708 in 1973. It is the best-selling title in the history of the series, owing to its sales in the French market, but is one of the least-selling titles in the English language.

Patrick Chouchayan, known by his stage name Patrick Fiori, is a French singer of Armenian descent.

Corsica is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the French mainland, west of the Italian Peninsula and immediately north of the Italian island of Sardinia, which is the land mass nearest to it. A single chain of mountains makes up two-thirds of the island. As of January 2023, it had a population of 351,255.

The history of Corsica in the medieval period begins with the collapse of the Western Roman Empire and the invasions of various Germanic peoples in the fifth century AD, and ends with the complete subjection of the island to the authority of the Bank of San Giorgio in 1511.

The Corsican Guard was a military unit of the Papal States composed exclusively of Corsican mercenaries on duty in Rome, having the functions of an urban militia and guard for the Pope.
The Unione Corse is a term designating the Corsican organized crime as a whole during the period 1930s–1970s, in the context of the French Connection, an international heroin trade network operated at that time between Turkey, Southern France, and the United States. A 1972 Time article described the "Unione Corse" as a Corsican-based unified and secretive crime syndicate akin to the American Five Families. The local situation in Southern France during this period was in reality more complex, with a nebula of mainly Corsican and Italian-French clans cooperating or fighting each other according to the circumstances and opportunities. If they constituted a key element of the wider French Connection, flooding the American market with Marseille-produced heroin from the 1950s to early 1970s, those clans remained overshadowed by the much more powerful Italian-American Mafia.

Italian irredentism in Corsica was a cultural and historical movement promoted by Italians and by people from Corsica who identified themselves as part of Italy rather than France, and promoted the Italian annexation of the island.

The Corsican Brothers is a novella by Alexandre Dumas, père, first published in 1844. It is the story of two conjoined brothers who, although separated at birth, can still feel each other's physical distress. It has been adapted many times on the stage and in film.

The Corsican Brothers is a 1941 swashbuckler film starring Douglas Fairbanks Jr. in a dual role as the titular conjoined twins who are separated at birth and raised in entirely different circumstances. Both thirst for revenge against the man who killed their parents, both fall in love with the same woman. The story is very loosely based on the 1844 novella Les frères Corses by French writer Alexandre Dumas, père.

A Prophet is a 2009 French prison crime film directed by Jacques Audiard with a screenplay by Audiard, Thomas Bidegain, Abdel Raouf Dafri and Nicolas Peufaillit, from a story by Dafri. The film stars Tahar Rahim in the title role as an imprisoned petty criminal of Algerian origins who rises in the prison hierarchy, becoming a mob associate and drug trafficker as he is absorbed into the Corsican mafia and then ingratiates himself into the Maghrebi crime syndicate.

The French conquest of Corsica was a successful expedition by French forces of the Kingdom of France under Comte de Vaux, against Corsican forces under Pasquale Paoli of the Corsican Republic. The expedition was launched in May 1768, in the aftermath of the Seven Years' War. A French expeditionary force was landed on the island of Corsica, then ruled by the Corsican Republic. Marching inland to overcome any Corsican opposition, the French force initially suffered an unexpected defeat at the Battle of Borgo. But a new commander, the Comte de Vaux, was appointed to lead the expedition, and decisively defeated the Corsican army at the Battle of Ponte Novu in 1769, effectively bringing an end to Corsican resistance.

The 2015 Corsican protests were a series of marches by several hundred Corsican nationalists that began on 25 December, in Ajaccio, capital of Corsica. During the initial demonstrations, a Muslim prayer hall was burned down and Qur'ans were set alight. Further protests were organised after the initial march despite a government ban on protests until 4 January 2016. The protesters claimed to be acting in revenge for an incident that occurred the day prior when firefighters and police were assaulted in the neighbourhood of Les Jardins de l'Empereur; however, outside observers labeled the ensuing riots as anti-Arab and anti-Muslim. The Corsican nationalist politicians have claimed their view does not legitimise xenophobia, blaming the protest on French nationalism instead. Scholarly opinions on this claim are divided.
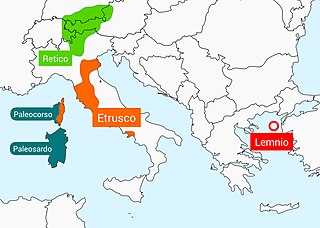
The Paleo-Corsican language is an extinct language spoken in Corsica and presumably in the northeastern part of Sardinia by the ancient Corsi populations during the Bronze and Iron Ages. The scanty evidence of the language, which comes mainly from toponymy, would indicate a type of Pre-Indo-European language or, according to others, Indo-European, with Ligurian and Iberian affinity.