La Paz, officially known as Nuestra Señora de La Paz, also named Chuqi Yapu (Chuquiago) in Aymara, is the seat of government and the de facto national capital of the Plurinational State of Bolivia. With an estimated 789,541 residents as of 2015, La Paz is the third-most populous city in Bolivia.

Sucre is the constitutional capital of Bolivia, the capital of the Chuquisaca Department and the 6th most populated city in Bolivia. Located in the south-central part of the country, Sucre lies at an elevation of 2,810 meters. This relatively high altitude gives the city a cool temperate climate year-round.

Conejos County is one of the 64 counties of the U.S. state of Colorado. As of the 2010 census, the population was 8,256. The county seat is the unincorporated community of Conejos.

Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo, is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. The State is divided into 113 municipalities and its capital city is Morelia. The city was named after José María Morelos, one of the main heroes of the Mexican War of Independence.

La Magdalena Contreras is one of the 16 administrative boroughs of the Federal District of Mexico City. As of the 2010 census, it has a population of 239,086 inhabitants and is the third-least populous of Mexico City's boroughs. It lies at an elevation of 2,365 m (7,759 ft) above sea level. It is named after two historically important communities—La Magdalena Atlitic and Colonia Contreras. The northern end of the borough is urbanized. The rest of Magdalena Contreras, with its mountains and ravines, is designated as a conservation zone. However, urban sprawl has put pressure on these conservation areas. In an effort to preserve the area's forests and natural resources, the borough government has started promoting ecotourism. The largest ecotourism park is Los Dinamos where canyons and ravines are cut by streams and freshwater springs that eventually form the Río Magdalena, Mexico City’s only remaining free-flowing river.

Miacatlán is a city and municipality in the Mexican state of Morelos. It stands at 18°45′N99°21′W.

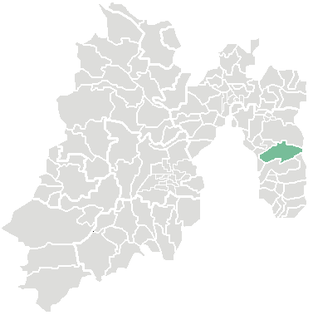
Tenancingo de Degollado is a large municipality, and also the name of a town and the municipal seat of the municipality, in the State of Mexico, Mexico. Both are commonly known as Tenancingo. The municipality is located in the south of the state, in the Tenancingo Valley, just outside the Toluca Valley. Tenancingo de Degollado is often confused with Tenancingo, Tlaxcala, which is a town in a different state.

Uruapan is the second largest city in the Mexican state of Michoacán. It is located at the western edge of the Purépecha highlands, just to the east of the Tierra Caliente Region. Since the colonial period, it has been an important city economically due its location. The city was conquered by the Spanish in 1522, when the last Purépecha ruler fled the Pátzcuaro area to here. The modern city was laid out in 1534 by Friar Juan de San Miguel. It played an important role in the War of Independence, and was the capital of Michoacán during the French Intervention. Today it is the center of Mexico’s avocado growing region, with most of the crop distributed from here nationally and internationally.

Santiago Tianguistenco, often just simply called Tianguistenco, is a city and municipality located in Mexico State about thirty km south of the state capital of Toluca. It is located in the southwest part of the Valley of Toluca at the edge of the Ajusco mountain range that separates it from Mexico City. The name Tianguistenco (Tyanguistengko) is from Nahuatl and means “at the edge of the tianguis,” which is a traditional Aztec market. The section of the city where the industrial park is still bears this name. Historically, the area was known as having one of the richest and best-stocked markets in the Toluca Valley. Today, it is still home to a large permanent municipal market as well as a weekly tianguis that covers much of the historic center.

Franz Tamayo is a province in the Bolivian department of La Paz. It lies in the western part of the nation, and includes the Ulla Ulla National Reserve - which today is part of the Apolobamba Integrated Management Natural Area - in the high Andean plain on the western border with Peru. Its capital is Apolo.
Villa Donato Guerra is the municipal seat of the municipality called Donato Guerra in the State of Mexico, Mexico. The area is also known as Malacatepec and La Asunción Malacatepec. (Villa) Donato Guerra is located in the western part of the State of Mexico. In the region that is identified with Valle de Bravo. The town was named in 1880 in honor of Donato Guerra, a distinguished soldier of the War of La Reforma. It is located around 77 kilometers from Toluca which is the capital of the state, on Federal Highway number 35 Mexico City - Zitácuaro.
Temascaltepec is a city and seat of the municipality of Temascaltepec located in south of the State of Mexico in Mexico. It is 66 km (41 mi) southeast of Toluca and 140 km (87 mi), from Mexico City. Temascaltepec comes from the Náhuatl "temazcalli," which means "steam bath," and "tepetl," which means "hill." The Matlatzincas named the area "Cocalostoc," which means 'cave of crows'.

Tlalmanalco is a town and municipality located in the far south-eastern part of the State of Mexico. The name is from the Nahuatl language, meaning “flat area.” The municipality’s seal shows flat land, with a pyramid on it, representing its pre-Hispanic history, surrounded by small mountains, which is how the area was represented in Aztec codices. The municipality is bordered by the municipalities of Chalco, Ixtapaluca, Cocotitlan, Temamatla, Tenango del Aire, Ayapango and Amecameca. It also shares a border with the neighboring state of Puebla. Much of the municipality borders the Iztaccihuatl-Popocatepetl National Park. For this reason, Iztaccihuatl volcano dominates the landscape. The town has been designated as a “Pueblo con Encanto” by the government of the State of Mexico.

Ozumba is a town and municipality located in the southeast portion of the Valley of Mexico, 70 km southeast of Mexico City near the Mexico City-Cuautla highway. The main feature of this area is the Parish of the Immaculate Conception which began as a Franciscan monastery in the 16th century. The entrance to the cloister area contains murals related to the early evangelization efforts of this order. They include scenes such as Hernán Cortés greeting the first Franciscan missionaries in Mexico, the martyrdom of some of the first young converts to Christianity and even a scene where the monks are flogging Cortés. The church itself inside has suffered the theft of a number of its antique pieces. The name Ozumba comes from Nahuatl meaning “over the streams of water”. “de Alzate” was added to the formal name in honor of the scientist José Antonio Alzate y Ramirez Santillana who was born here.

San Andrés Cholula Municipality is a municipality in Puebla in south-eastern Mexico. It forms part of the Metropolitan area of Puebla, and as of 2011, it is the fastest-growing municipality that conforms the Metropolitan Area, partly because the presence of universities and the wealthiest neighborhoods are located on San Andres Cholula. Along with San Pedro Cholula and Santa Isabel Cholula, it conforms the most ancient still inhabited city in the Americas, Cholula de Rivadabia.

San Pedro Cholula is a municipality in the Mexican state of Puebla and one of two municipalities which made up the city of Cholula. The city has been divided into two sections since the pre Hispanic era, when revolting Toltec-Chichimecas pushed the formerly dominant Olmec-Xicallanca to the eastern side of the city in the 13th century. The new lords called themselves Cholutecas and built a new temple to Quetzalcoatl on the San Pedro side, which eventually eclipsed the formerly prominent Great Pyramid of Cholula, now on the San Andrés side. When the Spanish arrived in the 16th century, the city of Cholula was an important religious and economic center, but the center of power was on the San Pedro side, centered on what is now the main city plaza and the San Gabriel monastery. The division of the city persisted and San Pedro remained the more dominant, with Spanish families moving onto that side and the rest of the population quickly becoming mestizo. Today, San Pedro is still more commercial and less residential than neighboring San Andrés with most of its population employed in industry, commerce and services rather than agriculture. Although Cholula's main tourist attraction, the Pyramid, is in San Andrés, San Pedro has more tourism infrastructure such as hotels, restaurants and bars.

Hueypoxtla is the municipality located in Zumpango Region, the northeastern part of the state of Mexico in Mexico. The municipality is located at a northern pass leading out of the Valley of Mexico and Mezquital Valley to—kilometers north of Mexico City and about km northeast of the state capital of Toluca. The name comes from Nahuatl and means "place of great merchants".

Huandacareo is a town and municipality in the north of the Mexican state of Michoacán, on the northwest side of Lake Cuitzeo. It is a small rural community located 48 km north of the state capital of Morelia. The area was part of the Tarascan state during the pre Hispanic period, then came under the control of the Augustinians. It was part of the territory of neighboring Cuitzeo until 1919, when it became an independent municipality. Its economic base from the colonial period to the present has been agriculture, growing corn, other crops, pigs and domestic fowl. There is also some tourism, mostly to the municipality’s two archeological sites and its colonial churches.

The Santa Ana Church, also known as the Parish of Our Lady of the Abandoned, is a Spanish colonial period church located in the district of Santa Ana in Manila, Philippines. The parish was established by the Franciscan missionaries in 1578 under the patronage of Saint Anne. The present stone church was constructed by Father Vicente Inglés, OFM from 1720 to 1725 and was dedicated to its present patron, the Our Lady of the Abandoned. The revered image of its patron was made in Valencia,Spain in 1713 and arrived in the Philippines in 1717.