Related Research Articles

In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck.

The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the wrist, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger. It runs parallel to the radius, the other long bone in the forearm. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore, the radius is considered to be the larger of the two.

In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.

The tibia, also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates ; it connects the knee with the ankle. The tibia is found on the medial side of the leg next to the fibula and closer to the median plane. The tibia is connected to the fibula by the interosseous membrane of leg, forming a type of fibrous joint called a syndesmosis with very little movement. The tibia is named for the flute tibia. It is the second largest bone in the human body, after the femur. The leg bones are the strongest long bones as they support the rest of the body.

The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as mice, cats, birds and dogs, but not in whales, or most reptiles.

The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint.

The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side : the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal. The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. A bovine hind leg has two metatarsals.

In anatomy, the axis or epistropheus is the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine, immediately inferior to the atlas, upon which the head rests.

The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.
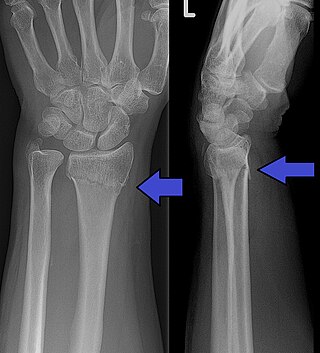
A Colles' fracture is a type of fracture of the distal forearm in which the broken end of the radius is bent backwards. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, deformity, and bruising. Complications may include damage to the median nerve.

A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The ulna bone may also be broken.

A Smith's fracture, is a fracture of the distal radius.

The talus, talus bone, astragalus, or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.

The condyloid process or condylar process is the process on the human and other mammalian species' mandibles that ends in a condyle, the mandibular condyle. It is thicker than the coronoid process of the mandible and consists of two portions: the condyle and the constricted portion which supports it, the neck.
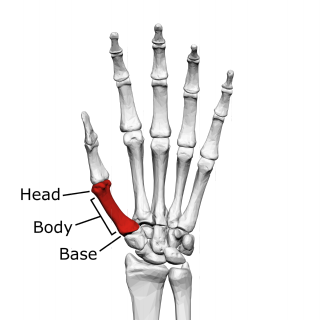
The first metacarpal bone or the metacarpal bone of the thumb is the first bone proximal to the thumb. It is connected to the trapezium of the carpus at the first carpometacarpal joint and to the proximal thumb phalanx at the first metacarpophalangeal joint.

A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.

A calcaneal fracture is a break of the calcaneus. Symptoms may include pain, bruising, trouble walking, and deformity of the heel. It may be associated with breaks of the hip or back.

A Barton's fracture is a type of wrist injury where there is a broken bone associated with a dislocated bone in the wrist, typically occurring after falling on top of a bent wrist. It is an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint.
Lidström classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Lidström classification system there are six types of fractures. The classification system is based on fracture line, direction and degree of displacement, extent of articular involvement and involvement of the distal radioulnar joint, and was first published in 1959.
Nissen-Lie classification is a system of categorizing Colles' fractures. In the Nissen-Lie classification system there are seven types of fractures. The classification system was first published in 1939.