
The Rio Grande is one of the principal rivers in the southwest United States and northern Mexico. The Rio Grande begins in south-central Colorado in the United States and flows to the Gulf of Mexico. After passing through the length of New Mexico along the way, it forms part of the Mexico–United States border. According to the International Boundary and Water Commission, its total length was 1,896 miles (3,051 km) in the late 1980s, though course shifts occasionally result in length changes. Depending on how it is measured, the Rio Grande is either the fourth- or fifth-longest river system in North America.

The Continental Divide of the Americas is the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas. The Continental Divide extends from the Bering Strait to the Strait of Magellan, and separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from those river systems that drain into the Atlantic Ocean and, along the northernmost reaches of the Divide, those river systems that drain into the Arctic Ocean.

Delicias is a city in the Mexican state of Chihuahua and serves as the seat of the municipality of the same name. It is located southeast of the state capital, Chihuahua. Delicias was declared an official municipality of the state of Chihuahua on January 7, 1935. Delicias is a small industrial city and a major agricultural center located in the Conchos River Valley. As of 2015, the city of Delicias had a population of 148,045 inhabitants, while the metropolitan area had a population of 223,993 inhabitants. It was founded on 30 April 1933, making it one of Mexico's youngest cities. The municipality of Delicias is one of the smallest in the state in terms of size area.
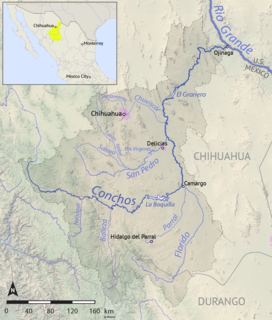
The Río Conchos is a large river in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. It joins the Río Bravo del Norte at the town of Ojinaga, Chihuahua.

The Bolsón de Mapimí is an endorheic or internal drainage basin in which no rivers or streams drain to the sea but rather toward the center of the basin often terminating in swamps and ephemeral lakes. It is located in the center-north of the Mexican Plateau. The Basin is shared by the states of Durango, Coahuila, Chihuahua, and Zacatecas. It takes its name from Mapimí, a town in Durango.
The Guzmán Basin is an endorheic basin of northern Mexico and the southwestern United States. It occupies the northwestern portion of Chihuahua in Mexico, and extends into southwestern New Mexico in the United States.

The Mimbres is a 91-mile-long (146 km) river in southwestern New Mexico. It forms from snow pack and runoff on the south-western slopes of the Black Range at 33°06′58″N107°51′04″W in Grant County. It flows southward into a small endorheic basin east of Deming, New Mexico in Luna County. The uplands watershed are administered by the US Forest Service, while the land in the Mimbres Valley is mostly privately owned. The upper reaches of the river are perennial. The river flows south from the Black Range and the surface flow of the river dissipates in the desert north of Deming, but the river bed and storm drainage continue eastward, any permanent flow remaining underground. The Mimbres River Basin has an area of about 13,000 km² (5,140 mi²) and extends slightly into northern Chihuahua.
The Rio Bavispe or Bavispe River is a river in Mexico which flows briefly north then mainly south by southwest until it joins with the Aros River to become the Yaqui River, eventually joining the Gulf of California.

The Soto La Marina River or Soto la Marina is a river of northeastern Mexico.
The San Pedro River (Chihuahua) is a river of Mexico. It is a tributary of the Rio Conchos, which in turn flows into the Rio Grande.
The Sacramento River is a short river in Mexico, the main tributary of the Chuvíscar River, which runs entirely through the state of Chihuahua
The Río Verde (Chihuahua) is a river of Mexico.

The Patagonia Mountains are a 15-mile-long (24 km) mountain range within the Coronado National Forest, and in Santa Cruz County, Arizona.

The Animas Valley is a lengthy and narrow, north-south 85-mi (137 km) long, valley located in western Hidalgo County, New Mexico in the Bootheel Region; the extreme south of the valley lies in Sonora-Chihuahua, in the extreme northwest of the Chihuahuan Desert, the large desert region of the north-central Mexican Plateau and the Rio Grande valley and river system.
Agriculture in the Southwest United States is very important economically in that region.

El Pandeño hotspring, officially known as "San José de Pandos", is home to the endemic Julimes pupfish considered to be one of the freshwater teleosts that lives at the highest temperatures. This spring is about 700 m2 (7,500 sq ft) in size and located in the Rio Conchos Basin, Chihuahua, Mexico. It is among several springs impacted by increasing pumping that depletes the local groundwater supply. The spring and its aquatic wildlife are under the custody of local NGO Amigos del Pandeño, A.C.

A triple divide or triple watershed is a point on the Earth's surface where three drainage basins meet. A triple divide results from the intersection of two drainage divides. Triple divides range from prominent mountain peaks to minor side peaks, down to simple slope changes on a ridge which are otherwise unremarkable. The elevation of a triple divide can be thousands of meters to barely above sea level. Triple divides are a common hydrographic feature of any terrain that has rivers, streams and/or lakes.
The Chinipas is a large river of Mexico. The Chinipas arises deep in the Sierra Madre Occidental in the state of Chihuahua, and then flows through long rugged canyon systems into the state of Sinaloa until it finally joins the main trunk of the Fuerte River in the western foothills of the Sierra Madre Occidental. The Fuerte River then flows westward over the western coastal plain of Sonora to the Pacific Ocean, emerging very near the port of Topolobampo.












