Saraswati , or Sarasvati, is a Hindu goddess.
Contents
Saraswati or Sarasvati may also refer to:
Saraswati , or Sarasvati, is a Hindu goddess.
Saraswati or Sarasvati may also refer to:
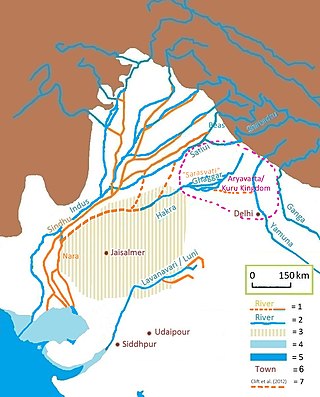
The Sarasvati River is a deified mythological river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Vedic religion, appearing in all but the fourth book of the Rigveda.

Saraswati, also spelled as Sarasvati, is the Hindu goddess of knowledge, music, flowing water, abundance and wealth, art, speech, wisdom, and learning. She is one of the Tridevi, along with the goddesses Lakshmi and Parvati. She is a pan-Indian deity, also revered in Jainism and Buddhism.
Bhat is a surname in the Indian subcontinent. Bhat and Bhatt are shortened renditions of Brahmbhatt or Bhatta.
Saraswat Brahmins are Hindu Brahmins, who are spread over widely separated regions spanning from Kashmir and Punjab in North India to Konkan in West India to Kanara and Kerala in South India. The word Saraswat is derived from the Rigvedic Sarasvati River.
Kamat or Kamath is a surname from Goa, Maharashtra and coastal Karnataka in India. It is found among Hindus of the Goud Saraswat Brahmin, Saraswat and Rajapur Saraswat Brahmin communities following Madhva Sampradaya of either Gokarna Matha or Kashi Matha.
Chitrapur Saraswats are a small Konkani-speaking community of Hindu Brahmins in India. They are traditionally found along the Kanara coast and call themselves Bhanaps in the Konkani language.
Mukherjee, also Mukerjee, Mookerjee, Mukerji, Mukherji, Mukhujje or Mookherjee, is a Bengali Hindu Kulin Brahmin surname originating from the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent. The traditional Bengali version is Mukhopaddhae, which is sometimes written Mukhopadhyay.
Saraswata Kingdom was an ancient kingdom, territory or region that was situated on the banks of the river Sarasvati River during the pre-historic ages. This region is mentioned in detail in as many as 20 chapters in the Mahabharata from (9:35) to (9:54). Balarama traced the Saraswati river through its partially dried up course from the ocean near Prabhasa to its origin in the Himalayas.
Gaud Saraswat Brahmins (GSB) are a Hindu Brahmin community, who are part of the larger Saraswat Brahmin community that migrated to Konkan from Gaud, as per the Skanda Purana in ancient India. They belong to the Pancha Gauda Brahmins group. They primarily speak Konkani and its various dialects as their mother tongue.
Ojha is a Brahmin surname. The term Ojha' or Oza is a Hindu Brahmin caste that has settled in north and central India and are found in the states of Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh and some parts of Bihar and Madhya Pradesh. Ojha is a surname for Hindu Sikhwal Brahmins, Shrimali Brahmins, Atri Gotra Brahmin, Saraswat Brahmin, Bhumihar Brahmins, Kanya Kubj Brahmin, Saryuparin Brahmin, Maithil Brahmin of Nepal, Nepali, Nagar Brahmin, and Bengali Brahmin of India and Nepal. Ojhas are considered to be worshipers of Durga, Saraswati, Hanuman, Mahalakshmi and Shiva. The surname is used amongst speakers of Nepali, Bhojpuri, Rajasthani, Gujarati, Hindi, Oriya, Maithili, Kumaoni and Bengali as well as the Santhals.
Prabhu means master or prince in Sanskrit and many of the Indian languages; it is a name sometimes applied to God. The term is also used by devotees of the Hindu God Lord Krishna/Vishnu as a title and form of address. It is also appended after a devotee's name, for example "Madhava Prabhu". In Indonesia, especially in Balinese, Javanese, and Sundanese culture, the term "Prabhu" is used as a part of royal titles, especially to address Kings such as Prabhu Siliwangi, Prabu Kiansantang, etc.
Konkani cuisine is the cuisine of the Saraswat Brahmins from the Konkan region on the western coast of India. Konkani cuisine differs within the Saraswat Brahmin subsects and within the Konkan-Canara region. Konkani cuisine originally hails from the Konkan region including Uttara Kannada, Udupi district, Dakshina Kannada, Damaon, and Goa, India. Konkani cuisine is popular served in many restaurants throughout the western coast of India, and especially in the cities of Bombay and Bangalore. Each variation has its unique flavour and makes uses of different vegetables and fruits available in the region. Konkani cuisine is usually pesco-vegetarian, except acharyas and purohits who follow a strictly saatvik vegetarian diet. According the Konkani folklore, fish, meats are regarded as sea vegetables. Historically, they have refrained from eating any terrestrial animals in general.
Giri may refer to:
Mangaloreans are a collection of diverse ethnic groups that hail from the historical locales of South Canara (Tulunaad) on the south western coast of Karnataka, India, particularly the residents native to Mangaluru.

Shri Gaudapadacharya Math, also known as Kavaḷē maṭha, located in Kavale, Ponda, Goa, is the oldest matha of the Smarthan Saraswat Brahman Samaj. It was founded by Gauḍapāda around 740 AD, whose student was Govinda Bhagavatpada, the guru of Adi Shankara, a highly influential figure in Hinduism. There is also a belief that Gauḍapāda himself established the Shri Gaudapadacharya matha when he lived in Gomantak (Goa). Thus, the matha came to be known as Shri Saunstan Gaudapadacharya matha. Unlike other mathas, Shri Gaudapadacharya matha is not a polemical center established to influence the faith of all Hindus, its jurisdiction is limited to only Dakshinatya Saraswat Brahmins. The Peetadhipathi "head monk" is Śrī Gauḍapadācārya. Smartist Goud Saraswat Brahman Samaj and Rajapur Saraswat Brahmin are its main disciples.
Shri Katyayani Baneshwar Temple ,(Sanskrit:श्री क़ात्यायनी बाणेश्व् र मन्दिर), or the Aversa Hindu Narayani is a Hindu temple in the coastal town of Aversa near Ankola, in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka. It is around 100 km (62 mi) from Goa, India, 500 km (310 mi) from Bangalore and 136 km from Hubli.
Adi Badri, also Sri Sarasvati Udgam Tirath, is a tourist site of archaeological, religious and ecological significance in a forest area in the foothills of the Sivalik Hills in Bhabar area, situated in northern part of Yamunanagar district, of the north Indian state of Haryana. There are remains of many Buddhist stupas and monasteries, which are about 1500–2000 years old, and there is also a group of Hindu temples from the 9th century. Based on the multiple archaeological excavations undertaken here, archaeologists have sent the proposal to Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) to include this site in the list of protected heritage site. Several popular annual festivals are held here, including the five day long National Saraswati Festival in January, Adi Badri Akha Teej Mela in Vaisakh around April–May, week-long Adi Badri-Kapal Mochan Kartik Purnima religious mela around November.

Madhva Brahmins, are Hindu Brahmin communities in India, who follow Sadh Vaishnavism and Dvaita philosophy propounded by Madhvacharya. They are found mostly in the Indian states of Karnataka, Maharashtra, Goa, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
The Indori river, is a rain-fed river originates from Aravalli Range from Sikar district and flows through Alwar district of Rajasthan to Rewari district of Haryana and it is the longest tributary of Sahibi River which stretches to 50 km. In Delhi, it is called the Najafgarh drain or Najafgarh Nallah.