| Look up satanist or Satanist in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
A Satanist is an adherent of Satanism.
Contents
Satanist may also refer to:
| Look up satanist or Satanist in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
A Satanist is an adherent of Satanism.
Satanist may also refer to:
| Search for "satanist" on Wikipedia. |
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Satanist. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Page most commonly refers to:

Satanism is a group of ideological and philosophical beliefs based on Satan. Contemporary religious practice of Satanism began with the founding of the Church of Satan in 1966, although a few historical precedents exist. Prior to the public practice, Satanism existed primarily as an accusation by various Christian groups toward perceived ideological opponents, rather than a self-identity. Satanism, and the concept of Satan, has also been used by artists and entertainers for symbolic expression.
A girl is a young female human.

A Black Mass is a ceremony typically celebrated by various satanic groups. It has existed for centuries in different forms and is directly based on a Catholic Mass.

The Satanic Bible is a collection of essays, observations, and rituals published by Anton LaVey in 1969. It is the central religious text of LaVeyan Satanism, and is considered the foundation of its philosophy and dogma. It has been described as the most important document to influence contemporary Satanism. Though The Satanic Bible is not considered to be sacred scripture in the way that the Christian Bible is to Christianity, LaVeyan Satanists regard it as an authoritative text as it is a contemporary text that has attained for them scriptural status. It extols the virtues of exploring one's own nature and instincts. Believers have been described as "atheistic Satanists" because they believe that God is not an external entity, but rather something that each person creates as a projection of their own personality—a benevolent and stabilizing force in their life. There have been thirty printings of The Satanic Bible, selling over a million copies.

Dennis Yeats Wheatley was an English writer whose prolific output of thrillers and occult novels made him one of the world's best-selling authors from the 1930s through the 1960s. His Gregory Sallust series was one of the main inspirations for Ian Fleming's James Bond stories.
Amen is a declaration of affirmation found in the Hebrew Bible and New Testament.
Satan is an embodiment of antagonism, often synonymous with the Devil.
A revolver is a type of firearm.
A predator is an animal that kills other animals to eat.
Dark side, Dark Side, or Darkside may refer to:
A grotto is a natural or artificial cave.
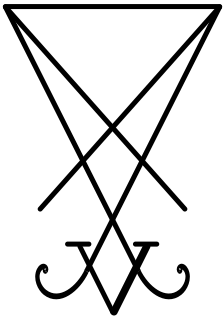
Theistic Satanism or spiritual Satanism is an umbrella term for religious beliefs that consider Satan to be an objectively existing deity, supernatural being, or force which is worthy of worship and supplication, whom individuals may contact, convene with and even praise, rather than just an archetype, a metaphor, a symbol, or an idea as in LaVeyan Satanism. The individuals and organizations which uphold this belief system and/or identify as theistic Satanists are most often very small, loosely affiliated, or independent groups and cabals, which have largely self-marginalized. Another characteristic of theistic Satanism is the use of ceremonial magic.
Satanism is a belief or social phenomenon that features the veneration or admiration of Satan or a similar figure.
Satanic may refer to:
A gentleman is a man of good quality.

The Devil Rides Out, known as The Devil's Bride in the United States, is a 1968 British horror film, based on the 1934 novel of the same name by Dennis Wheatley. It was written by Richard Matheson and directed by Terence Fisher. The film stars Christopher Lee, Charles Gray, Niké Arrighi and Leon Greene.
A midnight sun occurs when the sun is visible at midnight, local time.
Satanic verses may refer to:
Master of War, Warmasters, or variation, may refer to: