Scarlet fever is a relatively common disease.
Scarlet Fever may also refer to:
Scarlet fever is a relatively common disease.
Scarlet Fever may also refer to:
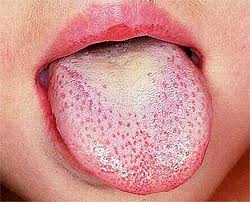
Scarlet fever, also known as scarlatina, is an infectious disease caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, a Group A streptococcus (GAS). The infection is a type of Group A streptococcal infection. It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The face is flushed and the rash is red and blanching. It typically feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy. The rash occurs as a result of capillary damage by exotoxins produced by S.pyogenes. On darker-pigmented skin the rash may be hard to discern.

Streptococcal pharyngitis, also known as streptococcal sore throat, is pharyngitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, a gram-positive, group A streptococcus. Common symptoms include fever, sore throat, red tonsils, and enlarged lymph nodes in the front of the neck. A headache and nausea or vomiting may also occur. Some develop a sandpaper-like rash which is known as scarlet fever. Symptoms typically begin one to three days after exposure and last seven to ten days.

Roseola, also known as sixth disease, is an infectious disease caused by certain types of human herpes viruses. Most infections occur before the age of three. Symptoms vary from absent to the classic presentation of a fever of rapid onset followed by a rash. The fever generally lasts for three to five days, while the rash is generally pink and lasts for less than three days. Complications may include febrile seizures, with serious complications being rare.

A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.

An antitoxin is an antibody with the ability to neutralize a specific toxin. Antitoxins are produced by certain animals, plants, and bacteria in response to toxin exposure. Although they are most effective in neutralizing toxins, they can also kill bacteria and other microorganisms. Antitoxins are made within organisms, and can be injected into other organisms, including humans, to treat an infectious disease. This procedure involves injecting an animal with a safe amount of a particular toxin. The animal's body then makes the antitoxin needed to neutralize the toxin. Later, blood is withdrawn from the animal. When the antitoxin is obtained from the blood, it is purified and injected into a human or other animal, inducing temporary passive immunity. To prevent serum sickness, it is often best to use an antitoxin obtained from the same species.

A petechia is a small red or purple spot that can appear on the skin, conjunctiva, retina, and mucous membranes which is caused by haemorrhage of capillaries. The word is derived from Italian petecchia, 'freckle,' of obscure origin. It refers to one of the three descriptive types of hematoma differentiated by size, the other two being ecchymosis and purpura. The term is always used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant.

The Scarlet Spider is an alias used by several fictional characters appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics, most notably Ben Reilly and Kaine Parker, both of whom are genetic replicates of the superhero Spider-Man.
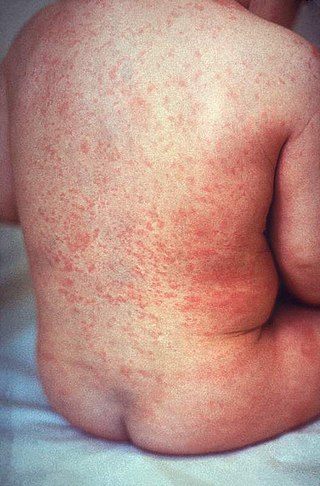
An exanthem is a widespread rash occurring on the outside of the body and usually occurring in children. An exanthem can be caused by toxins, drugs, or microorganisms, or can result from autoimmune disease.
Scarlet may refer to:
John McCormick may refer to:
DramaFever was a video streaming website owned by Warner Bros. that offered on-demand streaming video of documentaries, movies, and TV shows with subtitles. DramaFever's content offering was both ad-supported for regular users and available in high definition for premium subscribers.
T12 may refer to:
Scarlet fever serum was used beginning in November 1900 after its development in the Sero-Therapeutic Laboratory of Rudolph Hospital in Vienna, Austria. The serum was taken from the blood of horses. Infected children were injected in their abdominal skin by Dr. Paul Moser. Mortality rates from scarlet fever declined significantly following the use of the blood serum.

Scarlet Fever is an all-female backing band that toured with Cee Lo Green during 2010 and 2011. Originally formed for promotional tour events, the popularity of the "Fuck You" single and The Lady Killer album led to multiple television appearances reaching an audience of millions in Europe and North America. With Green, they performed full length concerts and as an opening act for other major performers.
Far East scarlet-like fever is an infectious disease caused by the gram negative bacillus Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. In Japan it is called Izumi fever.

Marianne Crawford Stanley is an American basketball coach. She previously served as the head coach of the Washington Mystics and Indiana Fever of the Women's National Basketball Association (WNBA).

Diseases and epidemics of the 19th century included long-standing epidemic threats such as smallpox, typhus, yellow fever, and scarlet fever. In addition, cholera emerged as an epidemic threat and spread worldwide in six pandemics in the nineteenth century.
The 2017 Pro12 Grand Final was the final match of the 2016–17 Pro12 season. The 2016–17 season was the third with Guinness as the title sponsor and the eighth ever League Grand Final. The final was played at the Aviva Stadium in Dublin. The game was contested by Scarlets and Munster with Scarlets winning 46-22.

Scarlet Envy, is the stage name of Jacob James Grady, an American drag queen, reality television personality, singer, and performer who is best known for competing on the eleventh season of RuPaul's Drag Race, the sixth season of its spin-off, RuPaul's Drag Race All Stars, and the upcoming second series of RuPaul's Drag Race: UK vs. the World.

A fever hospital or isolation hospital is a hospital for infectious diseases such as Scarlet fever, Tuberculosis, Lassa fever and Smallpox. Their purpose is to treat affected people while isolating them from the general population. Early examples included the Liverpool Fever Hospital (1801) and the London Fever Hospital (1802). Other examples occurred elsewhere in the British Isles and India.