
Flat Earth is an archaic and scientifically disproven conception of the Earth's shape as a plane or disk. Many ancient cultures subscribed to a flat-Earth cosmography. The model has undergone a recent resurgence as a conspiracy theory.
The history of science covers the development of science from ancient times to the present. It encompasses all three major branches of science: natural, social, and formal.

Johannes Kepler was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws of planetary motion, and his books Astronomia nova, Harmonice Mundi, and Epitome Astronomiae Copernicanae, influencing among others Isaac Newton, providing one of the foundations for his theory of universal gravitation. The variety and impact of his work made Kepler one of the founders and fathers of modern astronomy, the scientific method, natural and modern science.
The noosphere is a philosophical concept developed and popularized by the biogeochemist Vladimir Vernadsky, and philosopher and Jesuit priest Pierre Teilhard de Chardin. Vernadsky defined the noosphere as the new state of the biosphere and described as the planetary "sphere of reason". The noosphere represents the highest stage of biospheric development, that of humankind's rational activities.

The Scientific Revolution was a series of events that marked the emergence of modern science during the early modern period, when developments in mathematics, physics, astronomy, biology and chemistry transformed the views of society about nature. The Scientific Revolution took place in Europe in the second half of the Renaissance period, with the 1543 Nicolaus Copernicus publication De revolutionibus orbium coelestium often cited as its beginning.

An astrolabe is an astronomical instrument dating to ancient times. It serves as a star chart and physical model of visible heavenly bodies. Its various functions also make it an elaborate inclinometer and an analog calculation device capable of working out several kinds of problems in astronomy. In its simplest form it is a metal disc with a pattern of wires, cutouts, and perforations that allows a user to calculate astronomical positions precisely. Historically used by astronomers, it is able to measure the altitude above the horizon of a celestial body, day or night; it can be used to identify stars or planets, to determine local latitude given local time, to survey, or to triangulate. It was used in classical antiquity, the Islamic Golden Age, the European Middle Ages and the Age of Discovery for all these purposes.

Spherical Earth or Earth's curvature refers to the approximation of the figure of the Earth as a sphere. The earliest documented mention of the concept dates from around the 5th century BC, when it appears in the writings of Greek philosophers. In the 3rd century BC, Hellenistic astronomy established the roughly spherical shape of Earth as a physical fact and calculated the Earth's circumference. This knowledge was gradually adopted throughout the Old World during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. A practical demonstration of Earth's sphericity was achieved by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano's circumnavigation (1519–1522).

The history of geodesy (/dʒiːˈɒdɪsi/) began during antiquity and ultimately blossomed during the Age of Enlightenment.
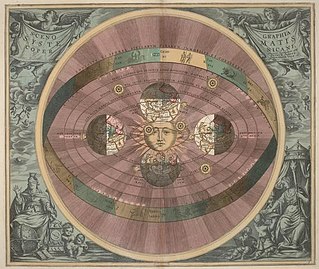
Heliocentrism is a superseded astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at the center. The notion that the Earth revolves around the Sun had been proposed as early as the third century BC by Aristarchus of Samos, who had been influenced by a concept presented by Philolaus of Croton. In the 5th century BC the Greek Philosophers Philolaus and Hicetas had the thought on different occasions that the Earth was spherical and revolving around a "mystical" central fire, and that this fire regulated the universe. In medieval Europe, however, Aristarchus' heliocentrism attracted little attention—possibly because of the loss of scientific works of the Hellenistic period.
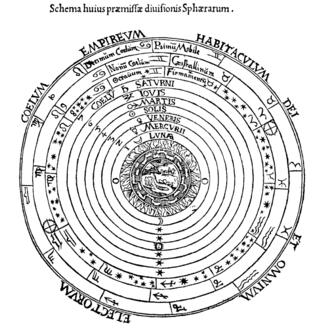
The celestial spheres, or celestial orbs, were the fundamental entities of the cosmological models developed by Plato, Eudoxus, Aristotle, Ptolemy, Copernicus, and others. In these celestial models, the apparent motions of the fixed stars and planets are accounted for by treating them as embedded in rotating spheres made of an aetherial, transparent fifth element (quintessence), like gems set in orbs. Since it was believed that the fixed stars did not change their positions relative to one another, it was argued that they must be on the surface of a single starry sphere.

Biogeochemistry is the scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natural environment. In particular, biogeochemistry is the study of biogeochemical cycles, the cycles of chemical elements such as carbon and nitrogen, and their interactions with and incorporation into living things transported through earth scale biological systems in space and time. The field focuses on chemical cycles which are either driven by or influence biological activity. Particular emphasis is placed on the study of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, iron, and phosphorus cycles. Biogeochemistry is a systems science closely related to systems ecology.

De sphaera mundi is a medieval introduction to the basic elements of astronomy written by Johannes de Sacrobosco c. 1230. Based heavily on Ptolemy's Almagest, and drawing additional ideas from Islamic astronomy, it was one of the most influential works of pre-Copernican astronomy in Europe.

Ancient Greek astronomy is the astronomy written in the Greek language during classical antiquity. Greek astronomy is understood to include the Ancient Greek, Hellenistic, Greco-Roman, and late antique eras. It is not limited geographically to Greece or to ethnic Greeks, as the Greek language had become the language of scholarship throughout the Hellenistic world following the conquests of Alexander. This phase of Greek astronomy is also known as Hellenistic astronomy, while the pre-Hellenistic phase is known as Classical Greek astronomy. During the Hellenistic and Roman periods, many of the Greek and non-Greek astronomers working in the Greek tradition studied at the Museum and the Library of Alexandria in Ptolemaic Egypt.
The three brothers Abū Jaʿfar, Muḥammad ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir ; Abū al‐Qāsim, Aḥmad ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir and Al-Ḥasan ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir, were Persian scholars who lived and worked in Baghdad. They are collectively known as the Banū Mūsā.

The Discoverers is a non-fiction historical work by Daniel Boorstin, published in 1983, and is the first in the Knowledge Trilogy, which also includes The Creators and The Seekers. The book, subtitled A History of Man's Search to Know His World and Himself, is a history of human discovery. Discovery in many forms is described: exploration, science, medicine, mathematics, and more-theoretical ones, such as time, evolution, plate tectonics, and relativity. Boorstin praises the inventive, human mind and its eternal quest to discover the universe and humanity's place in it.

A History of the Life and Voyages of Christopher Columbus is a fictional biographical account of Christopher Columbus written by Washington Irving in 1828. It was published in four volumes in Britain and in three volumes in the United States. The work was the most popular treatment of Columbus in the English-speaking world until the publication of Samuel Eliot Morison's biography Admiral of the Ocean Sea in 1942. It is one of the first examples of American historical fiction and one of several attempts at nationalistic myth-making undertaken by American writers and poets of the 19th century. It also helped to perpetuate the myth of the flat Earth.

The myth of the flat Earth, or the flat-Earth error, is a modern historical misconception that European scholars and educated people during the Middle Ages believed the Earth to be flat.

Most scientific and technical innovations prior to the scientific revolution were achieved by societies organized by religious traditions. Ancient Christian scholars pioneered individual elements of the scientific method. Historically, Christianity has been and still is a patron of sciences. It has been prolific in the foundation of schools, universities and hospitals, and many Christian clergy have been active in the sciences and have made significant contributions to the development of science.
Stephen George Brush is a scholar in the field of history of science whose career spanned the late twentieth and early twenty-first century. His research resulted in hundreds of journal articles and over a dozen books.

Historical models of the Solar System began during prehistoric periods and are updated to this day. The models of the Solar System throughout history were first represented in the early form of cave markings and drawings, calendars and astronomical symbols. Then books and written records became the main source of information that expressed the way the people of the time thought of the Solar System.















