A sarcoma is a cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal origin. Thus, malignant tumors made of cancellous bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues are, by definition, considered sarcomas. This is in contrast to a malignant tumor originating from epithelial cells, which are termed carcinoma. Human sarcomas are quite rare. Common malignancies, such as breast, colon, and lung cancer, are almost always carcinoma. The term is from the Greek σάρξ sarx meaning "flesh".

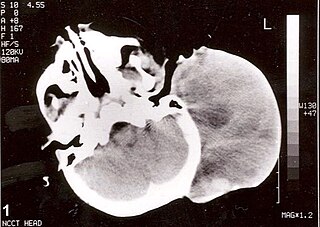
Osteosclerosis is a disorder that is characterized by abnormal hardening of bone and an elevation in bone density. It may predominantly affect the medullary portion and/or cortex of bone. Plain radiographs are a valuable tool for detecting and classifying osteosclerotic disorders. It can manifest in localized or generalized osteosclerosis. Localized osteosclerosis can be caused by Legg–Calvé–Perthes disease, sickle-cell disease and osteoarthritis among others. Osteosclerosis can be classified in accordance with the causative factor into acquired and hereditary.
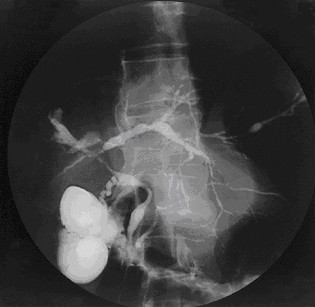
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may have no symptoms or may experience signs and symptoms of liver disease such as yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes, itching, and abdominal pain.
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) is a rare form of chronic progressive brain inflammation caused by measles virus. The condition primarily affects children and young adults. It has been estimated that about 1 in 10,000 people who get measles will eventually develop SSPE. However, a 2016 study estimated that the rate for babies who contracted measles was as high as 1 in 609. No cure for SSPE exists and the condition is often fatal. However, SSPE may be manageable by medication if treatment is started at an early stage. SSPE should not be confused with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis which has a similar cause but very different timing and course.

The PAX3 gene encodes a member of the paired box or PAX family of transcription factors. The PAX family consists of nine human (PAX1-PAX9) and nine mouse (Pax1-Pax9) members arranged into four subfamilies. Human PAX3 and mouse Pax3 are present in a subfamily along with the highly homologous human PAX7 and mouse Pax7 genes. The human PAX3 gene is located in the 2q36.1 chromosomal region, and contains 10 exons within a 100 kb region.
Sarcoma botryoides or botryoid sarcoma or botryoid rhabdomyosarcoma is a subtype of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, that can be observed in the walls of hollow, mucosa lined structures such as the nasopharynx, common bile duct, urinary bladder of infants and young children or the vagina in females, typically younger than age 8. The name comes from the gross appearance of "grape bunches".
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS) is a sub-type of the rhabdomyosarcoma soft tissue cancer family whose lineage is from mesenchymal cells and are related to skeletal muscle cells. ARMS tumors resemble the alveoli tissue that can be found in the lungs. Tumor location varies from patient to patient, but is commonly found in the head and neck region, male and female urogenital tracts, the torso, and extremities. Two fusion proteins can be associated with ARMS, but are not necessary, PAX3-FKHR. and PAX7-FKHR. In children and adolescents ARMS accounts for about 1 percent of all malignancies, has an incidence rate of 1 per million, and most cases occur sporadically with no genetic predisposition. PAX3-FOXO1 is now known to drive cancer-promoting gene expression programs through creation of distant genetic elements called super enhancers.
Mandibuloacral dysplasia is a rare autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by mandibular hypoplasia, delayed cranial suture closure, dysplastic clavicles, abbreviated and club-shaped terminal phalanges, acroosteolysis, atrophy of the skin of the hands and feet, and typical facial changes.
Secondary sclerosing cholangitis (SSC) is a chronic cholestatic liver disease. It is an aggressive and rare disease with complex and multiple causes. It is characterized by inflammation, fibrosis, destruction of the biliary tree and biliary cirrhosis. It can be treated with minor interventions, antibiotics, and monitoring, or with more serious cases, surgery, endoscopic intervention, and liver transplantation.
Sclerosing lymphangitis is a skin condition characterized by a cordlike structure encircling the coronal sulcus of the penis, or running the length of the shaft, that has been attributed to trauma during vigorous sexual play.
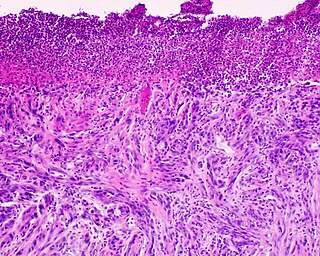
Desmoplastic melanoma is a rare cutaneous condition characterized by a deeply infiltrating type of melanoma with an abundance of fibrous matrix. It usually occurs in the head and neck region of older people with sun-damaged skin. Diagnosis can be difficult as it has a similar appearance to sclerosing melanocytic nevi as well as some nonmelanocytic skin lesions such as scars, fibromas, or cysts.
Poikiloderma is a skin condition that consists of areas of hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, telangiectasias and atrophy. Poikiloderma is most frequently seen on the chest or the neck, characterized by red colored pigment on the skin that is commonly associated with sun damage.
Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenita and sclerosing keratoderma syndrome is a rare cutaneous condition characterized by ichthyosis and keratoderma.
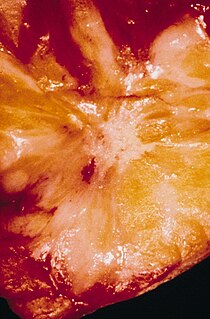
A radial scar of the breast, formally radial scar of the breast, is a benign breast lesion that can radiologically mimic malignancy, i.e. cancer.
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) is a rare histological form of cancer of connective tissue wherein the mesenchymally-derived malignant cells resemble the primitive developing skeletal muscle of the embryo. It is the most common soft tissue sarcoma occurring in children. ERMS is also known as Fusion-Negative rhabdomyosarcoma (FN-RMS), as tumors of this subtype are unified by their lack of a PAX3-FOXO1 fusion oncogene.

Idiopathic sclerosing mesenteritis (ISM) or mesenteric panniculitus is a rare disease of the small intestine, characterized by chronic inflammation and eventual fibrosis of the mesentery. It has also been called mesenteric lipodystrophy, or retractile mesenteritis.
Hypotrichosis–acro-osteolysis–onychogryphosis–palmoplantar keratoderma–periodontitis syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by a prominent palmoplantar keratoderma.
Childhood rhabdomyosarcoma is a cancer that develops out of the cells that form skeletal muscles. These cells are called rhabdomyoblasts.
Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis is a chronic (long-lasting) inflammatory condition affecting the salivary gland. Relatively rare in occurrence, this condition is benign, but presents as hard, indurated and enlarged masses that are clinically indistinguishable from salivary gland neoplasms or tumors. It is now regarded as a manifestation of IgG4-related disease.