
The Free Trade Area of the Americas was a proposed agreement to eliminate or reduce the trade barriers among all countries in the Americas, excluding Cuba. Negotiations to establish the FTAA ended in failure, however, with all parties unable to reach an agreement by the 2005 deadline they had set for themselves.
The World Summit on Sustainable Development 2002, took place in South Africa, from 26 August to 4 September 2002. It was convened to discuss sustainable development organizations, 10 years after the first Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro.

The Association of Southeast Asian Nations, commonly abbreviated as ASEAN, is a political and economic union of 10 states in Southeast Asia. Together, its member states represent a population of more than 600 million people and land area of over 4.5 million km2 (1.7 million sq mi). The bloc generated a purchasing power parity (PPP) gross domestic product (GDP) of around US$10.2 trillion in 2022, constituting approximately 6.5% of global GDP (PPP). ASEAN member states include some of the fastest growing economies in the world, and the institution plays an integral role in East Asian regionalism.

Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. Following the success of ASEAN's series of post-ministerial conferences launched in the mid-1980s, APEC started in 1989, in response to the growing interdependence of Asia-Pacific economies and the advent of regional trade blocs in other parts of the world; it aimed to establish new markets for agricultural products and raw materials beyond Europe. Headquartered in Singapore, APEC is recognized as one of the highest-level multilateral blocs and oldest forums in the Asia-Pacific region, and exerts significant global influence.
Carlo Giuliani was an Italian anti-globalization protester who was shot dead while attacking a Carabinieri van with a fire extinguisher, by an officer who was inside the van, during the anti-globalization riots outside the July 2001 G8 summit in Genoa, Italy, making his the first death during an anti-globalization demonstration since the movement's rise from the 1999 Seattle WTO protests.
The Summit of the Americas (SOA) are institutionalized gatherings of heads of state and government of the member states of the Western Hemisphere where leaders discuss common policy issues, affirm shared values and commit to concerted actions at the national and regional level to address continuing and new challenges faced by countries in the Americas.

The Summit League, or The Summit, is an NCAA Division I intercollegiate athletic conference with its membership mostly located in the Midwestern United States, from Minnesota in the east, to the Dakotas, Nebraska and Colorado to the West, and Missouri and Oklahoma to the South. Founded as the Association of Mid-Continent Universities in 1982, it rebranded as the Mid-Continent Conference in 1989, then again as the Summit League on June 1, 2007. The league headquarters are in Sioux Falls, South Dakota.

Wilton Daniel Gregory is an American Catholic prelate who served as Archbishop of Washington from 2019 to 2025. Pope Francis made him a cardinal in 2020, the first of African-American descent.

The G20 or Group of 20 is an intergovernmental forum comprising 19 sovereign countries, the European Union (EU), and the African Union (AU). It works to address major issues related to the global economy, such as international financial stability, climate change mitigation and sustainable development, through annual meetings of Heads of State and Heads of Government.

The ASEAN Summit is a biannual meeting held by the members of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) in relation to economic, political, security, and socio-cultural development of Southeast Asian countries. In addition, it serves as a prominent regional (Asia) and international (worldwide) conference, with world leaders attending its related summits and meetings to discuss various problems and global issues, strengthening co-operation, and making decisions. The summit has been praised by world leaders for its success and ability to produce results on a global level.
In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, a number of countries have passed laws aimed at reducing discrimination against people with disabilities. These laws have begun to appear as the notion of civil rights has become more influential globally, and follow other forms of anti-discrimination and equal opportunity legislation aimed at preventing racial discrimination and sexism which began to emerge in the second half of the 20th century. Many of these Acts aim to reduce barriers for persons with disabilities in the areas of customer service, employment, built environment, transportation, and information and communications.
Washington Summit Publishers (WSP) is a white nationalist publisher based in Augusta, Georgia, which produces and sells books on race and intelligence and related topics. The company is run by white supremacist Richard B. Spencer, who also ran the defunct white supremacist National Policy Institute.
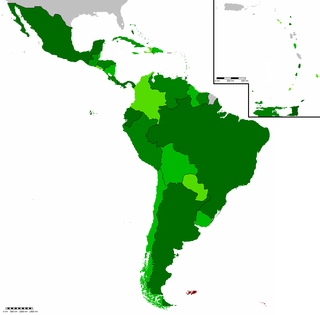
The Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC) is a bloc of Latin American and Caribbean states, consisting of 33 countries, and has five official working languages. It is seen as an alternative to the Organization of American States (OAS), and includes all OAS member states plus includes the nation of Cuba. Initially proposed on February 23, 2010, at the Rio Group–Caribbean Community Unity Summit, CELAC is seen as the successor of the Rio Group and the Latin American and Caribbean Summit on Integration and Development (CALC). CELAC was created to deepen Latin American integration and to reduce hegemony within the politics and economics of the region. The date of creation was on December 3, 2011, in Caracas, Venezuela, with the signing of the Declaration of Caracas.
Durban III is an informal name for a high-level United Nations General Assembly meeting marking the 10th anniversary of the adoption of The Durban Declaration and Programme of Action that was held in New York City on 22 September 2011. It was mandated by United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) resolution 64/148 of 18 December 2009 to commemorate the World Conference against Racism 2001, and given additional form and visibility by a UNGA Third Committee draft resolution adopted on 24 November 2010. It followed the Durban Review Conference, the official name of the 2009 United Nations World Conference Against Racism (WCAR), also known as Durban II.

BRICS is an intergovernmental organization consisting of ten countries—Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Egypt, Ethiopia, Indonesia, Iran and the United Arab Emirates. It is considered to be a counterpart and alternative to the G7 bloc of the world's largest economies and combined represent nearly half of the world's population.

Greenlandic independence is a political ambition of some political parties, advocacy groups, and individuals of Greenland, an autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, to become an independent sovereign state.

The United Nations Climate Change Conferences are yearly conferences held in the framework of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). They serve as the formal meeting of the UNFCCC parties – the Conference of the Parties (COP) – to assess progress in dealing with climate change, and beginning in the mid-1990s, to negotiate the Kyoto Protocol to establish legally binding obligations for developed countries to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. Starting in 2005 the conferences have also served as the "Conference of the Parties Serving as the Meeting of Parties to the Kyoto Protocol" (CMP); also parties to the convention that are not parties to the protocol can participate in protocol-related meetings as observers. From 2011 to 2015, the meetings were used to negotiate the Paris Agreement as part of the Durban platform, which created a general path towards climate action. Any final text of a COP must be agreed by consensus.
Intersex Trust of Aotearoa New Zealand is a nonprofit organization based in New Zealand that serves as the national advocacy and peer support organization for intersex people. Operating under the name Intersex Aotearoa, and previously known as Intersex Awareness New Zealand, it is recognized as the peak body representing intersex persons, those with variations of sex characteristics, or Ira Tangata. The organization was founded in 1996 by Mani Mitchell, a prominent intersex activist and advocate.

The 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP 21 or CMP 11 was held in Paris, France, from 30 November to 12 December 2015. It was the 21st yearly session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the 11th session of the Meeting of the Parties (CMP) to the 1997 Kyoto Protocol.
Mary Kathryn Nagle is a playwright and an attorney specializing in tribal sovereignty of Native nations and peoples. She was born in Oklahoma City, OK, and is an enrolled citizen of the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma. She previously served as the executive director of the Yale Indigenous Performing Arts Program (YIPAP) from 2015 to 2019.











