Related Research Articles

The United States Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) is a Cabinet department in the executive branch of the United States federal government. Although its beginnings were in the House and Home Financing Agency, it was founded as a Cabinet department in 1965, as part of the "Great Society" program of President Lyndon Johnson, to develop and execute policies on housing and metropolises.
The Low-Income Housing Tax Credit is a dollar-for-dollar tax credit in the United States for affordable housing investments. It was created under the Tax Reform Act of 1986 (TRA86) and gives incentives for the utilization of private equity in the development of affordable housing aimed at low-income Americans. LIHTC accounts for the majority of all affordable rental housing created in the United States today. As the maximum rent that can be charged is based upon the Area Median Income ("AMI"), LIHTC housing remains unaffordable to many low-income renters. The credits are also commonly called Section 42 credits in reference to the applicable section of the Internal Revenue Code. The tax credits are more attractive than tax deductions as the credits provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in a taxpayer's federal income tax, whereas a tax deduction only provides a reduction in taxable income. The "passive loss rules" and similar tax changes made by TRA86 greatly reduced the value of tax credits and deductions to individual taxpayers. Less than 10% of current credit expenditures are claimed by individual investors.
Section 8 of the Housing Act of 1937, often called Section 8, as repeatedly amended, authorizes the payment of rental housing assistance to private landlords on behalf of low-income households in the United States. Fort Lauderdale, Florida Housing Authority Director, William H. Lindsey, upon the advice of Housing Authority attorney, J.Richard Smith, initially developed 11(b) financing in the early 1970's to accommodate a local savings and loan interested in assisting with urban renewal projects Mr. Lindsey eventually brought to fruition. This was the initial impetus for the subsequent development of the now well known Section 8 Program. Of the 5.2 million American Households that received rental assistance in 2018, approximately 1.2 million of those households received a Section 8 based voucher. 68% of total rental assistance in the United States goes to seniors, children, and those with disabilities. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development manages Section 8 programs.

An FHA insured loan is a US Federal Housing Administration mortgage insurance backed mortgage loan which is provided by an FHA-approved lender. FHA insured loans are a type of federal assistance and have historically allowed lower income Americans to borrow money for the purchase of a home that they would not otherwise be able to afford. Because this type of loan is more geared towards new house owners rather than real-estate investors, FHA loans are different from conventional loan in the sense that the house must be owner occupant for at least a year. Since loans with lower down-payments usually involve more risk to the lender, the home-buyer must pay a two-part mortgage insurance which involves a one-time bulk payment in addition to a monthly payment to compensate for the increased risk.

The Community Reinvestment Act is a United States federal law designed to encourage commercial banks and savings associations to help meet the needs of borrowers in all segments of their communities, including low- and moderate-income neighborhoods. Congress passed the Act in 1977 to reduce discriminatory credit practices against low-income neighborhoods, a practice known as redlining.
The Federal Home Loan Banks are 11 U.S. government-sponsored banks that provide reliable liquidity to member financial institutions to support housing finance and community investment. With their members, the FHLBanks represents the largest collective source of home mortgage and community credit in the United States.

Real estate economics is the application of economic techniques to real estate markets. It tries to describe, explain, and predict patterns of prices, supply, and demand. The closely related field of housing economics is narrower in scope, concentrating on residential real estate markets, while the research on real estate trends focuses on the business and structural changes affecting the industry. Both draw on partial equilibrium analysis, urban economics, spatial economics, basic and extensive research, surveys, and finance.
The Rural Housing Service (RHS) is an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Located within the Department's Rural Development mission area. RHS operates a broad range of programs to provide moderate- low- and very-low-income Americans in rural communities with:
A VA loan is a mortgage loan in the United States guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). The program is for American veterans, military members currently serving in the U.S. military, reservists and select surviving spouses and can be used to purchase single-family homes, condominiums, multi-unit properties, manufactured homes and new construction. The VA does not originate loans, but sets the rules for who may qualify, issues minimum guidelines and requirements under which mortgages may be offered and financially guarantees loans that qualify under the program.

A mortgage loan or simply mortgage is used either by purchasers of real property to raise funds to buy real estate, or alternatively by existing property owners to raise funds for any purpose while putting a lien on the property being mortgaged. The loan is "secured" on the borrower's property through a process known as mortgage origination. This means that a legal mechanism is put into place which allows the lender to take possession and sell the secured property to pay off the loan in the event the borrower defaults on the loan or otherwise fails to abide by its terms. The word mortgage is derived from a Law French term used in Britain in the Middle Ages meaning "death pledge" and refers to the pledge ending (dying) when either the obligation is fulfilled or the property is taken through foreclosure. A mortgage can also be described as "a borrower giving consideration in the form of a collateral for a benefit (loan)".
The Housing and Economic Recovery Act of 2008 was designed primarily to address the subprime mortgage crisis. It authorized the Federal Housing Administration to guarantee up to $300 billion in new 30-year fixed rate mortgages for subprime borrowers if lenders wrote down principal loan balances to 90 percent of current appraisal value. It was intended to restore confidence in Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac by strengthening regulations and injecting capital into the two large U.S. suppliers of mortgage funding. States are authorized to refinance subprime loans using mortgage revenue bonds. Enactment of the Act led to the government conservatorship of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
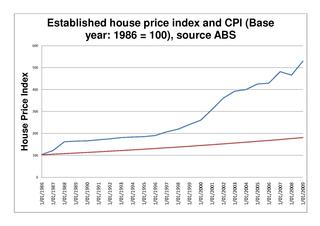
The Australian property bubble is the subject of the Australian property market becoming significantly overpriced and due for a significant downturn. Some commentators, including one Treasury official, claim the Australian property market is in a significant bubble.
Section 523 loans are a mutual self-help rural housing program in the United States authorized under Section 523 of the Housing Act of 1949 and administered by the Rural Housing Service (RHS). Nonprofit organizations may obtain 2-year loans to purchase and develop land that is to be subdivided into building sites for housing. The interest rate is 3% for these loans. Applicants must demonstrate a need for the proposed building sites in the locality. Sponsors also may obtain technical assistance (TA) grants to pay for all or part of the cost of developing, administering, and coordinating programs of technical and supervisory assistance to the families who are building their own homes. Each family is expected to contribute at least 700 hours of labor in building homes for each other. Applicants must demonstrate that:
Section 502 loans are a rural housing loan program, administered by the Rural Housing Service (RHS), authorized under Section 502 of the Housing Act of 1949. Borrowers may obtain loans for purchasing or repairing new or existing single-family housing. Loans are made directly by RHS or by private lenders with a USDA guarantee. Borrowers with income of 80% or less of the area median may be eligible for 33- year direct loans and may receive interest credit to bring the interest rate to as low as 1%. In a given fiscal year, at least 40% of the units financed under this section must be made available only to very low-income families or individuals with terms up to 38 years. Borrowers must have the means to repay the loans, but be unable to secure reasonable credit terms elsewhere. Borrowers with income of up to 115% of the area median may be eligible for 30-year guaranteed loans from private lenders. Priority is given to first-time home buyers, and the RHS may require that borrowers complete a home ownership counseling program.
Priority Sector Lending is an important role given by the (RBI) to the banks for providing a specified portion of the bank lending to few specific sectors like agriculture and allied activities, micro and small enterprises, poor people for housing, students for education and other low income groups and weaker sections.. This is essentially meant for an all round development of the economy as opposed to focusing only on the financial sector.
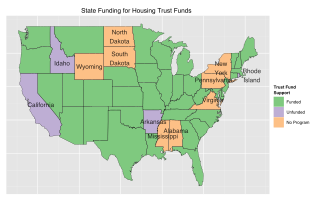
Housing trust funds are established sources of funding for affordable housing construction and other related purposes created by governments in the United States (U.S.). Housing Trust Funds (HTF) began as a way of funding affordable housing in the late 1970s. Since then, elected government officials from all levels of government in the U.S. have established housing trust funds to support the construction, acquisition, and preservation of affordable housing and related services to meet the housing needs of low-income households. Ideally, HTFs are funded through dedicated revenues like real estate transfer taxes or document recording fees to ensure a steady stream of funding rather than being dependent on regular budget processes. As of 2016, 400 state, local and county trust funds existed across the U.S.
Non-profit housing developers build affordable housing for individuals under-served by the private market. The non-profit housing sector is composed of community development corporations (CDC) and national and regional non-profit housing organizations whose mission is to provide for the needy, the elderly, working households, and others that the private housing market does not adequately serve. Of the total 4.6 million units in the social housing sector, non-profit developers have produced approximately 1.547 million units, or roughly one-third of the total stock. Since non-profit developers seldom have the financial resources or access to capital that for-profit entities do, they often use multiple layers of financing, usually from a variety of sources for both development and operation of these affordable housing units.

A USDA Home Loan from the USDA loan program, also known as the USDA Rural Development Guaranteed Housing Loan Program, is a mortgage loan offered to rural property owners by the United States Department of Agriculture.

Howard County Housing is the umbrella organization for the Howard County Department of Housing and Community Development and the Howard County Housing Commission. The Department is Howard County Government’s housing agency and the Commission is a public housing authority and non-profit. Both have boards that meet monthly.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) is an initiative by Government of India in which affordable housing will be provided to the urban poor with a target of building 20 million affordable houses by 31 March 2022. It has two components: Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana(Urban) (PMAY-U) for the urban poor and Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana (Gramin) for the rural poor. This scheme is converged with other schemes to ensure houses have a toilet, Saubhagya Yojana electricity connection, Ujjwala Yojana LPG gas connection, access to drinking water and Jan Dhan banking facilities, etc. Total 1 cr homes are approved against total demand of 1.12Cr as of 28 December 2019.
References
