Related Research Articles
Cardiothoracic surgery is the field of medicine involved in surgical treatment of organs inside the thoracic cavity — generally treatment of conditions of the heart, lungs, and other pleural or mediastinal structures.

A Pancoast tumor is a tumor of the apex of the lung. It is a type of lung cancer defined primarily by its location situated at the top end of either the right or left lung. It typically spreads to nearby tissues such as the ribs and vertebrae. Most Pancoast tumors are non-small-cell lung cancers.

Lymphadenectomy, or lymph node dissection, is the surgical removal of one or more groups of lymph nodes. It is almost always performed as part of the surgical management of cancer. In a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed; in a radical lymph node dissection, most or all of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed.
Colectomy is bowel resection of the large bowel (colon). It consists of the surgical removal of any extent of the colon, usually segmental resection. In extreme cases where the entire large intestine is removed, it is called total colectomy, and proctocolectomy denotes that the rectum is included.
Transurethral needle ablation is a technique that uses low energy radio frequency delivered through two needles to ablate excess prostate tissue. A cystoscope/catheter deploys the needles toward the obstructing prostate tissue and is inserted into the urethra directly through the penis under local anesthetic before the procedure begins. The energy from the probe heats the abnormal prostate tissue without damaging the urethra. The resulting scar tissue later atrophies, reducing the size of the prostate which in turn reduces the constriction of the urethra. It can be done with a local anesthetic on an outpatient basis. It takes about an hour to perform the procedure. It takes about 30 days for the ablated prostate tissue to resorb.
Hepatectomy is the surgical resection of the liver. While the term is often employed for the removal of the liver from a liver transplant donor, this article will focus on partial resections of hepatic tissue and hepatoportoenterostomy.

A bowel resection or enterectomy is a surgical procedure in which a part of an intestine (bowel) is removed, from either the small intestine or large intestine. Often the word enterectomy is reserved for the sense of small bowel resection, in distinction from colectomy, which covers the sense of large bowel resection. Bowel resection may be performed to treat gastrointestinal cancer, bowel ischemia, necrosis, or obstruction due to scar tissue, volvulus, and hernias. Some patients require ileostomy or colostomy after this procedure as alternative means of excretion. Complications of the procedure may include anastomotic leak or dehiscence, hernias, or adhesions causing partial or complete bowel obstruction. Depending on which part and how much of the intestines are removed, there may be digestive and metabolic challenges afterward, such as short bowel syndrome.
Wedge resection of the lung is a surgical operation where a part of a lung is removed. It is done to remove a localized portion of diseased lung, such as early stage lung cancer.
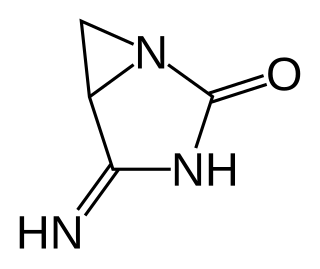
Imexon is a substance that is being studied in the treatment of some types of cancer, including pancreatic, lung, breast, prostate, melanoma, and multiple myeloma. It is a cyanoaziridine derivative.
Stereotactic radiation therapy (SRT), also called stereotactic external-beam radiation therapy and stereotaxic radiation therapy, is a type of external radiation therapy that uses special equipment to position the patient and precisely deliver radiation to a tumor. The total dose of radiation is divided into several smaller doses given over several days. Stereotactic radiation therapy is used to treat brain tumors and other brain disorders. It is also being studied in the treatment of other types of cancer, such as lung cancer. What differentiates Stereotactic from conventional radiotherapy is the precision with which it is delivered. There are multiple systems available, some of which use specially designed frames which physically attach to the patient's skull while newer more advanced techniques use thermoplastic masks and highly accurate imaging systems to locate the patient. The end result is the delivery of high doses of radiation with sub-millimetre accuracy.
A mediastinoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument used to examine the tissues and lymph nodes in the area between the lungs (mediastinum) in a procedure known as mediastinoscopy. These tissues include the heart and its large blood vessels, trachea, esophagus, and bronchi. The mediastinoscope has a light and a lens for viewing and may also have a tool to remove tissue. It is inserted into the chest through a cut above the breastbone.
Transsphenoidal surgery is a type of surgery in which an endoscope or surgical instruments are inserted into part of the brain by going through the nose and the sphenoid bone into the sphenoidal sinus cavity. Transsphenoidal surgery is used to remove tumors of the pituitary gland..
Wedge resection is a surgical procedure to remove a triangle-shaped slice of tissue. It may be used to remove a tumor or some other type of tissue that requires removal and typically includes a small amount of normal tissue around it. It is easy to repair, does not greatly distort the shape of the underlying organ and leaves just a single stitch line as a residual.

Hemihypertrophy, now more commonly referred to as hemihyperplasia in the medical literature, is a condition in which one side of the body or a part of one side of the body is larger than the other to an extent considered greater than the normal variation. As establishing a set of clinical criteria for diagnosis of hemihyperplasia is difficult, the dictum is often used that the clinician should be able to see the asymmetry "from the end of the bed".
Isolated lung perfusion is a surgical procedure during which the circulation of blood to the lungs is separated from the circulation of blood through the rest of the body, and a drug is delivered directly into the lung circulation. This allows a higher concentration of chemotherapy to reach tumors in the lungs.
Embryoma is a mass of rapidly growing cells believed to originate in embryonic (fetal) tissue. Embryonal tumors may be benign or malignant, and include neuroblastomas and Wilms tumors. Also called embryoma. Embryomas have been defined as: "Adult neoplasms expressing one or more embryo-exclusive genes."
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) lobectomy is an approach to lung cancer surgery.
Nivolumab, sold under the brand name Opdivo, is a medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes melanoma, lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma, renal cell carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, head and neck cancer, urothelial carcinoma, colon cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, liver cancer, gastric cancer, and esophageal or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer. It is used by slow injection into a vein.

Pembrolizumab, sold under the brand name Keytruda, is a humanized antibody used in cancer immunotherapy that treats melanoma, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, stomach cancer, cervical cancer, and certain types of breast cancer. It is given by slow injection into a vein.

Lung surgery is a type of thoracic surgery involving the repair or removal of lung tissue, and can be used to treat a variety of conditions ranging from lung cancer to pulmonary hypertension. Common operations include anatomic and nonanatomic resections, pleurodesis and lung transplants. Though records of lung surgery date back to the Classical Age, new techniques such as VATS continue to be developed.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from Dictionary of Cancer Terms. U.S. National Cancer Institute.
This article incorporates public domain material from Dictionary of Cancer Terms. U.S. National Cancer Institute.