
Poitiers is a city on the River Clain in west-central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and the historical centre of Poitou. In 2017 it had a population of 88,291. Its agglomeration has 130,853 inhabitants in 2016 and is the center of an urban area of 261,795 inhabitants. It is a city of art and history, still known as "Ville aux cent clochers".

Poitou was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.

The geography of France consists of a terrain that is mostly flat plains or gently rolling hills in the north and west and mountainous in the south and the east. Metropolitan France has a total size of 551,695 km2 (213,011 sq mi). It is the third largest country in Europe by area and the largest in Western Europe.

Charente is a department in the administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine, south western France. It is named after the river Charente, the most important and longest river in the department, and also the river beside which the department's two largest towns, Angoulême and Cognac, are sited. In 2019, it had a population of 352,015.

Haute-Loire is a landlocked department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of south-central France. Named after the Loire River, it is surrounded by the departments of Loire, Ardèche, Lozère, Cantal and Puy-de-Dôme. In 2019, it had a population of 227,570; its inhabitants are called Altiligériens in French.

Poitou-Charentes was an administrative region on the southwest coast of France. It is part of the new region Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It comprised four departments: Charente, Charente-Maritime, Deux-Sèvres and Vienne. It included the historical provinces of Angoumois, Aunis, Saintonge and Poitou.

The Vosges are a range of medium mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single geomorphological unit and low mountain range of around 8,000 km2 (3,100 sq mi) in area. It runs in a north-northeast direction from the Burgundian Gate to the Börrstadt Basin, and forms the western boundary of the Upper Rhine Plain.

Limousin is a former administrative region of southwest-central France. On 1 January 2016, it became part of the new administrative region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It comprised three departments: Corrèze, Creuse, and Haute-Vienne.
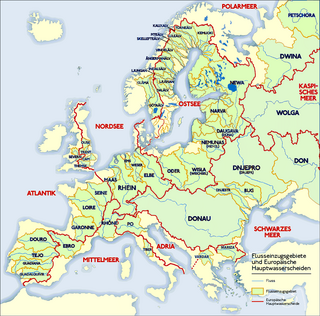
The main European watershed is the drainage divide ("watershed") which separates the basins of the rivers that empty into the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea and the Baltic Sea from those that feed the Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea and the Black Sea. It stretches from the tip of the Iberian Peninsula at Gibraltar in the southwest to the endorheic basin of the Caspian Sea in Russia in the northeast.

The Alps form a large mountain range dominating Central Europe, including parts of Italy, France, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Austria, Slovenia, Germany and Hungary.
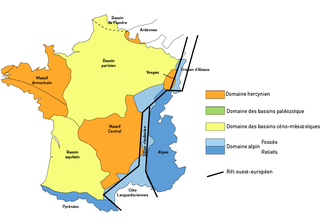
The Paris Basin is one of the major geological regions of France. It developed since the Triassic over remnant uplands of the Variscan orogeny. The sedimentary basin, no longer a single drainage basin, is a large sag in the craton, bordered by the Armorican Massif to the west, the Ardennes-Brabant axis to the north, the Massif des Vosges to the east, and the Massif Central to the south.

Chabichou is a traditional semi-soft, unpasteurized, natural-rind French goat cheese with a firm and creamy texture. Chabichou is formed in a cylindrical shape which is called a "bonde", per the shape of the bunghole of a wine barrel. and is aged for 10 to 20 days. It is the only goat cheese that is soft ripened allowed by Protected Designation of Origin regulations to be produced using pasteurized milk. Chabichou is very white and smooth, and flexible to the palate, with a fine caprine odor.

Les Adjots is a commune in the Charente department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region of southwestern France.
Asnières-sur-Blour is a commune in the Vienne department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region in western France. The commune has 180 inhabitants (2019).
The Aquitaine Basin is the second largest Mesozoic and Cenozoic sedimentary basin in France after the Paris Basin, occupying a large part of the country's southwestern quadrant. Its surface area covers 66,000 km2 onshore. It formed on Variscan basement which was peneplained during the Permian and then started subsiding in the early Triassic. The basement is covered in the Parentis Basin and in the Subpyrenean Basin—both sub-basins of the main Aquitaine Basin—by 11,000 m of sediment.
The Massif Central is one of the two large basement massifs in France, the other being the Armorican Massif. The Massif Central's geological evolution started in the late Neoproterozoic and continues to this day. It has been shaped mainly by the Caledonian orogeny and the Variscan orogeny. The Alpine orogeny has also left its imprints, probably causing the important Cenozoic volcanism. The Massif Central has a very long geological history, underlined by zircon ages dating back into the Archaean 3 billion years ago. Structurally it consists mainly of stacked metamorphic basement nappes.
Mount Gurage or Zebidar terraria is a mountain located in central Ethiopia. It is the highest point in both the Gurage Zone and the entire Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region. The mountain has a latitude and longitude of 8°17′N38°23′E and an elevation of 3900 meters above sea level.or 12,300 square feet To the north is the village of Anige, while to the east is Bu'i.

The Gier is a French river that flows in a northeast direction through the Loire and Rhône departments. It is a tributary of the Rhône, which it enters from the right bank. The Gier valley was formerly heavily industrialized with coal and iron mines and factories.

Nouvelle-Aquitaine is the largest administrative region in France by area, spanning the west and southwest of Metropolitan France. The region was created in 2014 by the merging of Aquitaine, Limousin, and Poitou-Charentes in a territorial reform. Nouvelle-Aquitaine has an area of 84,035.7 km2 (32,446.4 sq mi) – more than 1⁄7 of Metropolitan France – and has a population of 6,033,952 as of 2020. The new region was established on 1 January 2016, following the regional elections in December 2015.

The French Great South-West is a geographical, sociological, economic and cultural entity bringing together the administrative regions of Nouvelle-Aquitaine and Occitanie, resulting from the merger on January 1, 2016, of five previous regions; in these two regions combined, it covers 156,000 km2, or 29% of the territory of metropolitan France. It is a grouping devoid of its own political or administrative structures, set up, with the objective of an interregional reflection on spatial planning at the level of new European issues, at the initiative of the Interministerial Delegation at territory planning and regional attractiveness.















