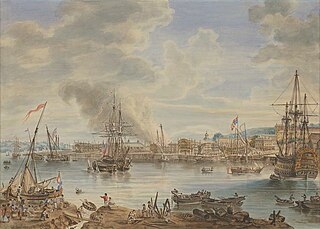Medway is a conurbation and unitary authority in Kent in the region of South East England. It had a population in 2014 of 274,015. The unitary authority was formed in 1998 when the City of Rochester-upon-Medway amalgamated with Gillingham Borough Council and part of Kent County Council to form Medway Council, a unitary authority independent of Kent County Council.

The Isle of Sheppey is an island off the northern coast of Kent, England, neighbouring the Thames Estuary, centred 42 miles (68 km) from central London. It has an area of 36 square miles (93 km2). The island forms part of the local government district of Swale. Sheppey is derived from Old English Sceapig, meaning "Sheep Island".

Woolwich Dockyard was an English naval dockyard along the river Thames at Woolwich in north-west Kent, where a large number of ships were built from the early 16th century until the late 19th century. William Camden called it 'the Mother Dock of all England'. By virtue of the size and quantity of vessels built there, Woolwich Dockyard is described as having been 'among the most important shipyards of seventeenth-century Europe'. During the Age of Sail, the yard continued to be used for shipbuilding and repair work more or less consistently; in the 1830s a specialist factory within the dockyard oversaw the introduction of steam power for ships of the Royal Navy. At its largest extent it filled a 56-acre site north of Woolwich Church Street, between Warspite Road and New Ferry Approach; 19th-century naval vessels were fast outgrowing the yard, however, and it eventually closed in 1869. The former dockyard area is now partly residential, partly industrial, with remnants of its historic past having been restored.

Gillingham is a town in the county of Kent in South East England. For local government purposes it is also in the unitary authority of Medway. The town includes the settlements of Brompton, Hempstead, Wigmore, Parkwood, Rainham which has its own significant retail and leisure hub, Rainham Mark and Twydall.
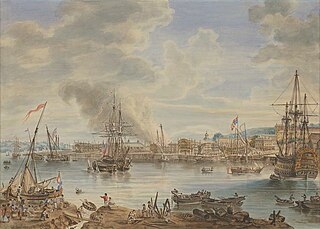
Chatham Dockyard was a Royal Navy Dockyard located on the River Medway in Kent. Established in Chatham in the mid-16th century, the dockyard subsequently expanded into neighbouring Gillingham.

Royal Navy Dockyards were harbour facilities where commissioned ships were either built or based, or where ships were overhauled and refitted. Historically, the Royal Navy maintained a string of dockyards around the world; these publicly owned establishments were officially designated Royal Dockyards or HM Dockyards until the late 1960s. Today, the few shipbuilding/maintenance yards that remain operational have been privatized ; and Babcock International, which in 2011 acquired freehold ownership of the working North Yard at Devonport from the MOD, has reverted to calling it Devonport Royal Dockyard.

The North Kent Line is a railway which runs from a junction of Britain's South East Main Line, east of St Johns railway station, Greater London to a point south-west of Strood station by the River Medway in Medway where it links to the Chatham Main Line. The London terminus is Charing Cross station.

Her Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy. Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is located on the eastern shore of Portsmouth Harbour, north of the Solent and the Isle of Wight. Until the early 1970s, it was officially known as Portsmouth Royal Dockyard ; the shipbuilding, repair and maintenance element of the base was privatized in the late-1990s/early-2000s. Around the year 2000, the designation HMS Nelson was extended to cover the entire base.

The Sheerness line is located in Kent, England, and connects Sheerness-on-Sea on the Isle of Sheppey with Sittingbourne on the mainland, and with the Chatham Main Line for trains towards London, Ramsgate or Dover Priory. It opened on 19 July 1860.

Chatham railway station is on the Chatham Main Line in England, serving the town of Chatham, Kent. It is 34 miles 25 chains (55.2 km) down the line from London Victoria and is situated between Rochester and Gillingham.

Kemsley railway station is on the Sheerness Line in north Kent, England, and serves the village of Kemsley. It is 45 miles 20 chains (72.8 km) down the line from London Victoria. Train services are provided by Southeastern.

Queenborough railway station is on the Sheerness Line, on the Isle of Sheppey in North Kent, and serves the town of Queenborough. It is 49 miles 22 chains (79.3 km) down the line from London Victoria.

Dockyard railway station is a Great Western Railway suburban station on the Cornish Main Line in Devonport, Plymouth, England. As the name implies, it serves Devonport Dockyard. It is 247 miles 47 chains (398.5 km) from London Paddington via Bristol Temple Meads.

Keyham railway station is a suburban station in the city of Plymouth, Devon, England. It is 248 miles 12 chains (399.4 km) from London Paddington via Bristol Temple Meads.
The Eastleigh–Fareham line is the railway line from Eastleigh to Fareham in the United Kingdom. At Eastleigh, trains join the South Western Main Line for onward travel to Basingstoke, Reading or to London Waterloo. At Fareham trains join the West Coastway Line for onward travel to Portsmouth or Brighton.

The Commander-in-Chief, The Nore was an operational commander of the Royal Navy. His subordinate units, establishments, and staff were sometimes informally known as the Nore Station or Nore Command.
Rushbrooke is a populated area on the western side of Cobh on Great Island in Cork Harbour, Ireland. It is in the townland of Ringacoltig.