Shipping is the transportation of cargo.
Shipping or Shipped may also refer to:
Enterprise may refer to:
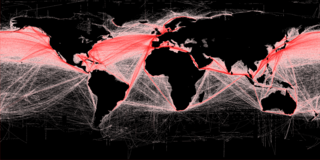
Freight transport, also referred to as freight forwarding, is the physical process of transporting commodities and merchandise goods and cargo. The term shipping originally referred to transport by sea but in American English, it has been extended to refer to transport by land or air as well. "Logistics", a term borrowed from the military environment, is also used in the same sense.
USS Enterprise may refer to the following ships and other vessels:

Containerization is a system of intermodal freight transport using intermodal containers. Containerization, also referred as container stuffing or container loading, is the process of unitization of cargoes in exports. Containerization is the predominant form of unitization of export cargoes today, as opposed to other systems such as the barge system or palletization. The containers have standardized dimensions. They can be loaded and unloaded, stacked, transported efficiently over long distances, and transferred from one mode of transport to another—container ships, rail transport flatcars, and semi-trailer trucks—without being opened. The handling system is mechanized so that all handling is done with cranes and special forklift trucks. All containers are numbered and tracked using computerized systems.
The Incoterms or International Commercial Terms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. Incoterms define the responsibilities of exporters and importers in the arrangement of shipments and the transfer of liability involved at various stages of the transaction. They are widely used in international commercial transactions or procurement processes and their use is encouraged by trade councils, courts and international lawyers. A series of three-letter trade terms related to common contractual sales practices, the Incoterms rules are intended primarily to clearly communicate the tasks, costs, and risks associated with the global or international transportation and delivery of goods. Incoterms inform sales contracts defining respective obligations, costs, and risks involved in the delivery of goods from the seller to the buyer, but they do not themselves conclude a contract, determine the price payable, currency or credit terms, govern contract law or define where title to goods transfers.

Intermodal freight transport involves the transportation of freight in an intermodal container or vehicle, using multiple modes of transportation, without any handling of the freight itself when changing modes. The method reduces cargo handling, and so improves security, reduces damage and loss, and allows freight to be transported faster. Reduced costs over road trucking is the key benefit for inter-continental use. This may be offset by reduced timings for road transport over shorter distances.

In transportation, freight refers to goods conveyed by land, water or air, while cargo refers specifically to freight when conveyed via water or air. In economics, freight refers to goods transported at a freight rate for commercial gain. The term cargo is also used in case of goods in the cold-chain, because the perishable inventory is always in transit towards a final end-use, even when it is held in cold storage or other similar climate-controlled facilities, including warehouses.

FOB is a term in international commercial law specifying at what point respective obligations, costs, and risk involved in the delivery of goods shift from the seller to the buyer under the Incoterms standard published by the International Chamber of Commerce. FOB is only used in non-containerized sea freight or inland waterway transport. As with all Incoterms, FOB does not define the point at which ownership of the goods is transferred.

A reefer ship is a refrigerated cargo ship typically used to transport perishable cargo, which require temperature-controlled handling, such as fruits, meat, vegetables, dairy products, and similar items.

"Mudd's Women" is the sixth episode of the first season of the American science fiction television series Star Trek. Written by Stephen Kandel, based on a story by Gene Roddenberry, and directed by Harvey Hart, it first aired on October 13, 1966.
"Horizon" is the twentieth episode of the second season of the science fiction television series Star Trek: Enterprise, and originally aired on April 16, 2003, on UPN. The episode was written by André Bormanis and directed by James A. Contner. The episode's guest stars included Nicole Forester, who had previously appeared in Star Trek: Deep Space Nine; Joan Pringle; and Corey Mendell Parker.

CMA CGM is a French shipping and logistics company founded in 1978 by Jacques Saadé.
Truckload shipping is freight transport in which a semi-trailer or intermodal container is filled entirely with one type of cargo. It differs from less-than-truckload shipping (LTL) in which freight from multiple customers is combined in one trailer. A truckload carrier is a trucking company that contracts entire trailer-load to a single customer.

A freight rate is a price at which a certain cargo is delivered from one point to another. The price depends on the form of the cargo, the mode of transport, the weight of the cargo, and the distance to the delivery destination. Many shipping services, especially air carriers, use dimensional weight for calculating the price, which takes into account both weight and volume of the cargo.

"Face of the Enemy" is the 140th episode of the American science fiction television series Star Trek: The Next Generation, and the 14th episode of the sixth season.
"Emergence" is an episode of the American science fiction television series Star Trek: The Next Generation. It is the 175th episode of the series, and the 23rd episode of the seventh season. Set in the 24th century, the series follows the adventures of the Starfleet crew of the Federation starship Enterprise-D. The crew has a bizarre experience on the holodeck and trouble with the Enterprise. The episode explores the relationship between technology and its creators.

A heavy-lift ship is a vessel designed to move very large loads that cannot be transported by normal ships. They are of two types:
A shipping agency, shipping agent, or ship agency is the term used to refer to the appointed companies that handle operational and procedural (legal) requirements for a commercial vessel's call at a port for the purposes of cargo handling (loading/discharging), emergency calls, repairs, crew changes, or ship demolition, and protect the general interests of their principals on behalf of ship owners, disponent owners, or charterers in an objective manner.
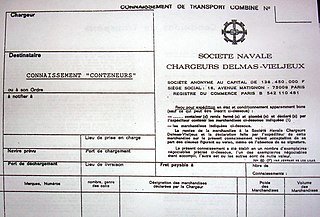
A bill of lading is a document issued by a carrier to acknowledge receipt of cargo for shipment. Although the term is historically related only to carriage by sea, a bill of lading may today be used for any type of carriage of goods. Bills of lading are one of three crucial documents used in international trade to ensure that exporters receive payment and importers receive the merchandise. The other two documents are a policy of insurance and an invoice. Whereas a bill of lading is negotiable, both a policy and an invoice are assignable. In international trade outside the United States, bills of lading are distinct from waybills in that the latter are not transferable and do not confer title. Nevertheless, the UK Carriage of Goods by Sea Act 1992 grants "all rights of suit under the contract of carriage" to the lawful holder of a bill of lading, or to the consignee under a sea waybill or a ship's delivery order.