
Orhan Ghazi was the second sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1323/4 to 1362. He was born in Söğüt, as the son of Osman I.

Year 727 (DCCXXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 727 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 1119 (MXCVII) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar.

Nicaea, also known as Nikaia, was an ancient Greek city in the north-western Anatolian region of Bithynia that is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea, the Nicene Creed, and as the capital city of the Empire of Nicaea following the Fourth Crusade in 1204, until the recapture of Constantinople by the Byzantines in 1261. Nicaea was also the capital of the Ottomans from 1331 to 1335.

The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantine Empire as the Western-recognized Roman Empire in the east, with a Catholic emperor enthroned in place of the Eastern Orthodox Roman emperors. The main objective of the Latin Empire was planned by Venice, which promoted the creation of this state for their self-benefit.
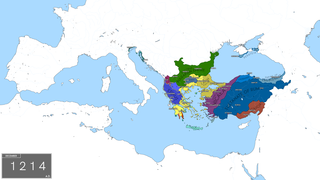
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire was the largest of the three Byzantine Greek rump states founded by the aristocracy of the Byzantine Empire that fled when Constantinople was occupied by Western European and Venetian armed forces during the Fourth Crusade, a military event known as the Sack of Constantinople. Like the other Byzantine rump states that formed due to the 1204 fracturing of the empire, such as the Empire of Trebizond and the Despotate of Epirus, it was a continuation of the eastern half of the Roman Empire that survived well into the medieval period. A fourth state, known in historiography as the Latin Empire, was established by an army of Crusaders and the Republic of Venice after the capture of Constantinople and the surrounding environs.

The siege of Nicaea was the first major battle of the First Crusade, taking place from 14 May to 19 June 1097. The city was under the control of the Seljuk Turks who opted to surrender to the Byzantines in fear of the crusaders breaking into the city. The siege was followed by the Battle of Dorylaeum and the Siege of Antioch, all taking place in modern Turkey.

The military history of Greece is the history of the wars and battles that took place in Greece, the Balkans, and the Greek colonies in the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea, respectively, since classical antiquity.

The siege of Nicaea by the forces of Orhan I from 1328 to 1331, resulted in the conquest of a key Byzantine Greek city by the Ottoman Turks. It played an important role in the expansion of the Ottoman Empire.
After its foundation by Osman I in about 1299, the Ottoman Empire expanded across Bithynia in north-west Anatolia by capturing territory from the Byzantine Empire. Osman was succeeded by his son Orhan in about 1324 and, following long sieges, he took the important cities of Bursa (1326) and Nicaea (1331). Next, Orhan besieged Nicomedia from 1333 to 1337. The Byzantine garrison surrendered due to lack of food and resources. Orhan's victory sealed Ottoman control of Bithynia.

The Byzantine–Ottoman wars were a series of decisive conflicts between the Byzantine Greeks and Ottoman Turks and their allies that led to the final destruction of the Byzantine Empire and the rise of the Ottoman Empire. The Byzantines, already having been in a weak state even before the partitioning of their Empire following the 4th Crusade, failed to recover fully under the rule of the Palaiologos dynasty. Thus, the Byzantines faced increasingly disastrous defeats at the hands of the Ottomans. Ultimately, they lost Constantinople in 1453, formally ending the conflicts.
The siege of Nicaea of 1113 occurred in the course of the Byzantine-Seljuk wars.

A Byzantine-Mongol Alliance occurred during the end of the 13th and the beginning of the 14th century between the Byzantine Empire and the Mongol Empire. Byzantium attempted to maintain friendly relations with both the Golden Horde and the Ilkhanate realms, who were often at war with each other. The alliance involved numerous exchanges of presents, military collaboration and marital links, but dissolved in the middle of the 14th century.
Battle of Thessalonica, Siege of Thessalonica, or Sack of Thessalonica may refer to:

The siege of Constantinople (1235) was a joint Bulgarian–Nicaean siege on the capital of the Latin Empire. Latin emperor John of Brienne was besieged by the Nicaean emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes and Tsar Ivan Asen II of Bulgaria.

The Treaty of Nymphaeum was a trade and defense pact signed between the Empire of Nicaea and the Republic of Genoa in Nymphaion in March 1261. This treaty would have a major impact on both the restored Byzantine Empire and the Republic of Genoa that would later dictate their histories for several centuries to come.
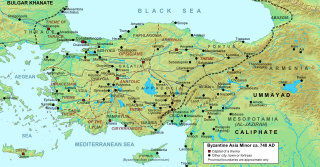
The siege of Nicaea of 727 was an unsuccessful attempt by the Umayyad Caliphate to capture the Byzantine city of Nicaea, the capital of the Opsician Theme. Ever since its failure to capture the Byzantine Empire's capital, Constantinople, in 717–718, the Caliphate had launched a series of raids into Byzantine Asia Minor. In 727, the Arab army, led by one of the Caliph's sons, penetrated deep into Asia Minor, sacked two Byzantine fortresses and in late July arrived before Nicaea. Despite constant attacks for 40 days, the city held firm and the Arabs withdrew and returned to the Caliphate. The successful repulsion of the attack was a major boost for Byzantine emperor Leo III the Isaurian's recently initiated campaign to abolish the veneration of icons in the Empire; Leo claimed it as evidence of divine favour for his policy. The siege of Nicaea marks also the high point of the Umayyad raids, as new threats and defeats on their far-flung frontiers decreased Umayyad strength elsewhere, while Byzantine power strengthened afterwards.

The siege of Sinope in 1214 was a successful siege and capture of Sinope by the Sultanate of Rum under their Sultan, Kaykaus I. Sinope was an important port city on the Black Sea coast of modern Turkey, at the time held by the Empire of Trebizond, one of the Byzantine Greek successor states formed after the Fourth Crusade. The siege is described in some detail by the near-contemporary Seljuq chronicler Ibn Bibi. The Trapezuntine emperor Alexios I led an army to break the siege, but he was defeated and captured, and the city surrendered on 1 November.













