
The Duchy of Guelders is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.
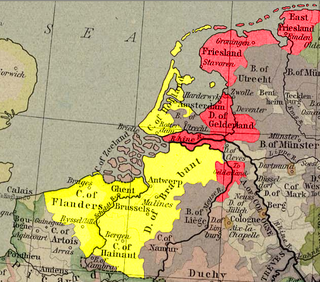
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord and Pas-de-Calais (Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy.

Venlo ( ) is a city and municipality in the southeastern Netherlands, close to the border with Germany. It is situated in the province of Limburg. The municipality of Venlo counted 101,578 inhabitants as of January 2019.
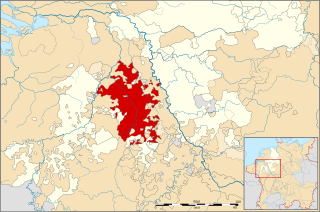
The Duchy of Jülich comprised a state within the Holy Roman Empire from the 11th to the 18th centuries. The duchy lay west of the Rhine river and was bordered by the Electorate of Cologne to the east and the Duchy of Limburg to the west. It had territories on both sides of the river Rur, around its capital Jülich – the former Roman Iuliacum – in the lower Rhineland. The duchy amalgamated with the County of Berg beyond the Rhine in 1423, and from then on also became known as Jülich-Berg. Later it became part of the United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg.

Geldern is a city in the federal German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is part of the district of Kleve, which is part of the Düsseldorf administrative region.

John II was a Franco-Dutch nobleman who ruled lands in both France and the Holy Roman Empire. He was the count of Blois and Dunois from 1372 until 1381, the lord of Avesnes, Schoonhoven, Gouda, Beaumont, Chimay and Waarde from 1356 until 1381 and the stadtholder of Holland and Zeeland in 1359–1360 and 1362–1363 during the absences of Count Albert of Bavaria. He was also a claimant jure uxoris to the Duchy of Guelders from 1372 until 1379.

William of Jülich-Cleves-Berge was a Duke of Jülich-Cleves-Berg (1539–1592). William was born in and died in Düsseldorf. He was the only son of John III, Duke of Jülich-Cleves-Berg, and Maria, Duchess of Jülich-Berg. William took over rule of his father's estates upon his death in 1539. Despite his mother having lived until 1543, William also became the Duke of Berg and Jülich and the Count of Ravensberg.
The Guelders Wars were a series of conflicts in the Low Countries between the Duke of Burgundy, who controlled Holland, Flanders, Brabant, and Hainaut on the one side, and Charles, Duke of Guelders, who controlled Guelders, Groningen, and Frisia on the other side.

The First War of the Guelderian Succession was a battle for the throne of the Duchy of Guelders that raged between 1371 and 1379.

The Treaty of Venlo of 7 September 1543 concluded the Guelders Wars (1502–1543), and the definitive acquisition of the Duchy of Guelders and the adjoining County of Zutphen by the House of Habsburg, adding them to the Habsburg Netherlands. William V, Duke of the United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg had to relinquish his claims to Guelders and Zutphen in favour of the Holy Roman Emperor and King of Spain, Charles V of Habsburg.
Guelders is a historical duchy, previously county, of the Holy Roman Empire, located in the Low Countries.

Maarten van Rossum was a military tactician of the duchy of Guelders who became field marshal in the service of Charles, Duke of Guelders. He was greatly feared outside his home country for the ruthless manner in which he waged war. In a long career, he often put his motto ""Blaken en branden is het sieraad van de oorlog" into practice. His way of waging war was quite similar to that of his Italian colleagues, the condottieri, and was characterized by guerrilla-like tactics, in which the civilian population was spared even less than was usual in his time.

Reginald II of Guelders, called "the Black", was Count of Guelders, and from 1339 onwards Duke of Guelders, and Zutphen, in the Low Countries, from 1326 to 1343. He was the son of Reginald I of Guelders and Marguerite of Flanders.
Reginald III was Duke of Guelders and Count of Zutphen from 1343 to 1361, and again in 1371. He was the son of Reginald II of Guelders and of Eleanor of Woodstock, daughter of Edward II of England.

William was Duke of Guelders, as William I, from 1377 and Duke of Jülich, as William III, from 1393. William was known for his military activities, participating in the Prussian crusade five times and battling with neighbors in France and Brabant throughout his rule. His allies included Holy Roman Emperors, Charles IV and Wenceslaus, Richard II of England, and Conrad Zöllner von Rothenstein, the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights. During his reign the duchies of Guelders and Jülich were temporarily unified.

Hendrik van den Bergh, 1573 to 22 May 1638, was a Flemish noble and professional soldier. Hereditary lord of Stevensweert, from 1618 to 1637 he was also stadtholder of Upper Guelders, the only part of Guelders to remain loyal to Habsburg Spain during the Eighty Years War. Known as a brave and resourceful cavalry commander, he spent most of his career with the Spanish Army of Flanders and became its Maestre de campo in 1628. Accused of treachery after the loss of Den Bosch in 1629, he defected to the Dutch Republic following the 1632 Conspiracy of Nobles.

Upper Guelders or Spanish Guelders was one of the four quarters in the Imperial Duchy of Guelders. In the Dutch Revolt, it was the only quarter that did not secede from the Habsburg monarchy to become part of the Seven United Netherlands, but remained under Spanish rule during the Eighty Years' War.

The Utrecht war of 1481–83 was a diocesan feud in the Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht between 1481 and 1483, influenced by the ongoing Hook and Cod wars in the neighbouring County of Holland. It was also a battle for control over Utrecht between the Dukes of Burgundy in the person of ruling Bishop David of Burgundy, and the Duchy of Cleves, which sought to replace him with Engelbert of Cleves.

















