
The Noctilucales are an order of marine dinoflagellates. They differ from most others in that the mature cell is diploid and its nucleus does not show a dinokaryotic organization. They show gametic meiosis.

Dinokaryota is a main grouping of dinoflagellates. They include all species where the nucleus remains a dinokaryon throughout the entire cell cycle, which is typically dominated by the haploid stage. All the "typical" dinoflagellates, such as Peridinium and Gymnodinium, belong here. Others are more unusual, including some that are colonial, amoeboid, or parasitic. Symbiodinium contains the symbiotic zooxanthellae.

The Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument is a national monument located in Teller County, Colorado. The location is famous for the abundant and exceptionally preserved insect and plant fossils that are found in the mudstones and shales of the Florissant Formation. Based on argon radiometric dating, the formation is Eocene in age and has been interpreted as a lake environment. The fossils have been preserved because of the interaction of the volcanic ash from the nearby Thirtynine Mile volcanic field with diatoms in the lake, causing an diatom bloom. As the diatoms fell to the bottom of the lake, any plants or animals that had recently died were preserved by the diatom falls. Fine layers of clays and muds interspersed with layers of ash form "paper shales" holding beautifully-preserved fossils.

Noctiluca scintillans, commonly known as the sea sparkle, and also published as Noctiluca miliaris, is a free-living, marine-dwelling species of dinoflagellate that exhibits bioluminescence when disturbed. Its bioluminescence is produced throughout the cytoplasm of this single-celled protist, by a luciferin-luciferase reaction in thousands of spherically shaped organelles, called scintillons.
The Syndiniales are an order of early branching dinoflagellates, found as parasites of crustaceans, fish, algae, cnidarians, and protists. The trophic form is often multinucleate, and ultimately divides to form motile spores, which have two flagella in typical dinoflagellate arrangement. They lack a theca and chloroplasts, and unlike all other orders, the nucleus is never a dinokaryon. A well-studied example is Amoebophrya, which is a parasite of other dinoflagellates and may play a part in ending red tides. Several MALV groups have been assigned to Syndiniales; recent studies, however, show paraphyly of MALVs suggesting that only those groups that branch as sister to dinokaryotes belong to Syndiniales.
Pelagic sediment or pelagite is a fine-grained sediment that accumulates as the result of the settling of particles to the floor of the open ocean, far from land. These particles consist primarily of either the microscopic, calcareous or siliceous shells of phytoplankton or zooplankton; clay-size siliciclastic sediment; or some mixture of these. Trace amounts of meteoric dust and variable amounts of volcanic ash also occur within pelagic sediments. Based upon the composition of the ooze, there are three main types of pelagic sediments: siliceous oozes, calcareous oozes, and red clays.
Driftwood Canyon Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. Driftwood Canyon Provincial Park covers 23 ha of the Bulkley River Valley, on the east side of Driftwood Creek, a tributary of the Bulkley River, 10 km northeast of the town of Smithers. The park is accessible from Driftwood Road from Provincial Highway 16. It was created in 1967 by the donation of the land by the late Gordon Harvey (1913–1976) to protect fossil beds on the east side of Driftwood Creek. The beds were discovered around the beginning of the 20th century. The park lands are part of the asserted traditional territory of the Wet'suwet'en First Nation.
Dinocysts or dinoflagellate cysts are typically 15 to 100 µm in diameter and produced by around 15–20% of living dinoflagellates as a dormant, zygotic stage of their lifecycle, which can accumulate in the sediments as microfossils. Organic-walled dinocysts are often resistant and made out of dinosporin. There are also calcareous dinoflagellate cysts and siliceous dinoflagellate cysts. Many books provide overviews on dinocysts.
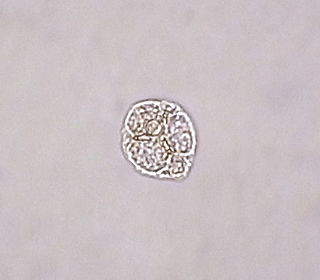
The Ebridea is a group of phagotrophic flagellate eukaryotes present in marine coastal plankton communities worldwide. Ebria tripartita is one of two described extant species in the Ebridea.
Members of this group are named for their idiosyncratic method of movement.

Established in 1989, the Stonerose Interpretive Center and Fossil Site is an Eocene Epoch fossil site and accompanying interpretive center, located in Republic, Washington, part of the Okanagan Highland. The fossils are from organisms that lived in the area nearly 50 million years ago when the area that is now the city of Republic was part of an ancient lake. The old lake's bottom layers are now volcanic ash hardened into sedimentary rock, becoming fine-grained tuffaceous shale. The fossils include various, and some extinct, insects, fish, leaves and twigs, as well as bird feathers. The Republic upland lacustrine fossil beds are significant as they represent the earliest known records of the Rosaceae and Aceraceae.

Allognathosuchus is an extinct genus of alligatorine crocodylian with a complicated taxonomic history.
Karlodinium is a genus of dinoflagellates.
Dinodnavirus is a genus of viruses that infect dinoflagellates. This genus belongs to the clade of nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses. The name is derived from 'dino' (dinoflagellate) and DNA.
A small number of dinoflagellates contain an internal skeleton. One of the best known species is perhaps Actiniscus pentasterias, in which each cell contains a pair of siliceous five-armed stars surrounding the nucleus. This species was originally described by Ehrenberg. Although the description is incomplete and without illustrations, Ehrenberg described the skeletal elements but mentioned that the living cell was colorless and non-motile. Ehrenberg subsequently diagrammed the silicified skeletal elements (pentasters) from geological deposits in various parts of the world.These can be found as microfossils. Pentasters were studied from the Cenozoic South Pacific by Dumitrică http://deepseadrilling.org/21/volume/dsdp21_25.pdf Tappan gave a survey of dinoflagellates with internal skeletons. This included the first detailed description of the pentasters in Actiniscus pentasterias, based on scanning electron microscopy.
The Castle Hayne Limestone is a geologic formation in North Carolina. It consists of cobble to pebble sized clasts, usually rounded, coated with phosphate and glauconite in a limestone matrix. The Castle Hayne Limestone is known for containing fossils dating back to the Paleogene period. It preserves many of North Carolina's renowned Eocene fossils. It is named after the locality of Castle Hayne in New Hanover county, though the formation itself stretches over several counties.
The Golden Valley Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Late Paleocene to Early Eocene age in the Williston Basin of North Dakota. It is present in western North Dakota and was named for the city of Golden Valley by W.E. Benson and W.M. Laird in 1947. It preserves significant assemblages of fossil plants and vertebrates, as well as mollusk and insect fossils.

A nematocyst is a subcellular structure or organelle containing extrusive filaments found in two families of athecate dinoflagellates, the Warnowiaceae and Polykrikaceae. It is distinct from the similar subcellular structures found in the cnidocyte cells of cnidarians, a group of multicellular organisms including jellyfish and corals; such structures are also often called nematocysts, and cnidocytes are sometimes referred to as nematocytes. It is unclear whether the relationship between dinoflagellate and cnidarian nematocysts is a case of convergent evolution or common descent, although molecular evidence has been interpreted as supporting an endosymbiotic origin for cnidarian nematocysts.
The geology of Barbados includes exposures of reef-related carbonate rocks spanning 85 percent of the island's surface. This Coral Rock Formation is 70 meters thick and dates to the Pleistocene. Unlike neighboring islands in the Lesser Antilles volcanic arc, Barbados is unusual because it is not a volcanic island. Instead, the island of Barbados is the exposed part of the Barbados Ridge Accretionary Prism, left as deep ocean sediments "scraped" to the surface as the Atlantic oceanic crust subducted beneath the Caribbean Plate.









