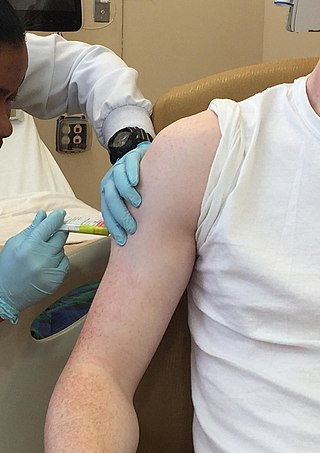
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted.

Human subject research is systematic, scientific investigation that can be either interventional or observational and involves human beings as research subjects, commonly known as test subjects. Human subject research can be either medical (clinical) research or non-medical research. Systematic investigation incorporates both the collection and analysis of data in order to answer a specific question. Medical human subject research often involves analysis of biological specimens, epidemiological and behavioral studies and medical chart review studies. On the other hand, human subject research in the social sciences often involves surveys which consist of questions to a particular group of people. Survey methodology includes questionnaires, interviews, and focus groups.
An institutional review board (IRB), also known as an independent ethics committee (IEC), ethical review board (ERB), or research ethics board (REB), is a committee at an institution that applies research ethics by reviewing the methods proposed for research involving human subjects, to ensure that the projects are ethical. The main goal of IRB reviews is to ensure that study participants are not harmed. Such boards are formally designated to approve, monitor, and review biomedical and behavioral research involving humans, and they are legally required in some countries under certain specified circumstances. Most countries use some form of IRB to safeguard ethical conduct of research so that it complies with national and international norms, regulations or codes.
In the life sciences, a contract research organization (CRO) is a company that provides support to the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries in the form of research services outsourced on a contract basis. A CRO may provide such services as biopharmaceutical development, biological assay development, commercialization, clinical development, clinical trials management, pharmacovigilance, outcomes research, and real world evidence.
Clinical monitoring is the oversight and administrative efforts that monitor a participant's health and efficacy of the treatment during a clinical trial. Both independent and government-run grant-funding agencies, such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the World Health Organization (WHO), require data and safety monitoring protocols for Phase I and II clinical trials conforming to their standards.
In pharmaceuticals, an adverse event (AE) is any untoward medical occurrence in a patient or clinical investigation subject administered a pharmaceutical product and which does not necessarily have a causal relationship with this treatment. An adverse event can therefore be any unfavourable and unintended symptom or sign or disease temporally associated with the use of a medicinal (investigational) product, whether or not related to the medicinal (investigational) product.
An academic clinical trial is a clinical trial not funded by pharmaceutical or biotechnology company for commercial ends but by public-good agencies to advance medicine. These trials are a valuable component of the health care system; they benefit patients and help determine the safety and efficacy of drugs and devices, and play an important role in the checks and balances that regular commercially oriented clinical trials.
In drug development and production, good clinical practice (GCP) is an international quality standard, which governments can then transpose into regulations for clinical trials involving human subjects. GCP follows the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH), and enforces tight guidelines on ethical aspects of clinical research.
A data clarification form (DCF) or data query form is a questionnaire specifically used in clinical research. The DCF is the primary data clarification tool from the trial sponsor or contract research organization (CRO) towards the investigator to clarify discrepancies and ask the investigator for clarification. The DCF is part of the data validation process in a clinical trial.
The ethics committee, according to Directive 2001/20/EC, is an independent body in a member state of the European Union, consisting of healthcare professionals and non-medical members, whose responsibility is to protect the rights, safety and well being of human subjects involved in a clinical trial and to provide public assurance of that protection, by, among other things, expressing an opinion on the clinical trial protocol, the suitability of the investigators involved in the trial and the adequacy of facilities, and on the methods and documents to be used to inform trial subjects and obtain their informed consent.
A Clinical Research Coordinator (CRC) is a person responsible for conducting clinical trials using good clinical practice (GCP) under the auspices of a Principal Investigator (PI).

Public Responsibility in Medicine and Research (PRIM&R) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization based in Boston, Massachusetts. The organization was formed in 1974 by a group of researchers who sought to ensure that the concerns and experiences of those working in biomedical research would be reflected in the growing body of federal regulations governing the field.

In health care, a clinical trial is a comparison test of a medication or other medical treatment, versus a placebo, other medications or devices, or the standard medical treatment for a patient's condition.
The Office for Human Research Protections (OHRP) is a small office within the United States Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS), specifically the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health in the Office of the Secretary of DHHS, that deals with ethical oversights in clinical research conducted by the department, mostly through the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
A glossary of terms used in clinical research.
Patient recruitment is the process of finding and enrolling suitable participants for clinical trials. It is a crucial aspect of drug development and medical research, as it affects the validity, reliability, and generalizability of the results. Patient recruitment can also be challenging, time-consuming, and costly, involving various ethical, regulatory, and logistical issues.
A clinical trial portal is a web portal or enterprise portal that primarily serves sponsors and investigators in a clinical trial. Clinical portals can be developed for a particular study, however study-specific portals may be part of larger, clinical sponsor or Contract Research Organization (CRO) portals that cover multiple trials. A clinical portal is typically developed by a sponsor or CRO to facilitate centralized access to relevant information, documentation and online applications by investigational sites participating in a trial, as well as for the monitors, study managers, data managers, medical, safety and regulatory staff that help plan, conduct, manage and review the trial.
The term informed assent describes the process whereby minors may agree to participate in clinical trials. It is similar to the process of informed consent in adults, however there remains some overlap between the terms.
An independent safety officer (ISO) is a clinician or researcher who is independent of the clinical study team and helps to monitor a clinical trial for research participant (patient) safety, adverse events, trial progress, and data quality. An ISO has relevant experience with clinical trials as well as with the patient population and intervention being studied. Clinical trials using an ISO are usually smaller, single-site trials with a moderate to minimal risk intervention.
A platform trial is a type of prospective, disease-focused, adaptive, randomized clinical trial (RCT) that compares multiple, simultaneous and possibly differently-timed interventions against a single, constant control group. As a disease-focused trial design, platform trials attempt to answer the question "which therapy will best treat this disease". Platform trials are unique in their utilization of both: a common control group and their opportunity to alter the therapies it investigates during its active enrollment phase. Platform trials commonly take advantage of Bayesian statistics, but may incorporate elements of frequentist statistics and/or machine learning.



