
Oviraptor is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. The first remains were collected from the Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia in 1923 during a paleontological expedition led by Roy Chapman Andrews, and in the following year the genus and type species Oviraptor philoceratops were named by Henry Fairfield Osborn. The genus name refers to the initial thought of egg-stealing habits, and the specific name was intended to reinforce this view indicating a preference over ceratopsian eggs. Despite the fact that numerous specimens have been referred to the genus, Oviraptor is only known from a single partial skeleton regarded as the holotype, as well as a nest of about fifteen eggs and several small fragments from a juvenile.
The Disciples of Apocalypse (DOA) were a biker-themed professional wrestling stable in the World Wrestling Federation (WWF) in the late 1990s. The group came together from the firing of Crush and Savio Vega from the Nation of Domination stable in June 1997 and consisted of four main members: Crush, Chainz, Skull and 8-Ball.

The lying triceps extension, also known as skull crusher and French extension or French press, is a strength exercise used in many different forms of strength training. It is one of the most stimulating exercises to the entire triceps muscle group in the upper arm, and works the triceps from the elbow all the way to the latissimus dorsi. Due to its full use of the triceps muscle group, the lying triceps extensions are used by many as part of their training regimen.

A skull fracture is a break in one or more of the eight bones that form the cranial portion of the skull, usually occurring as a result of blunt force trauma. If the force of the impact is excessive, the bone may fracture at or near the site of the impact and cause damage to the underlying structures within the skull such as the membranes, blood vessels, and brain.

A basilar skull fracture is a break of a bone in the base of the skull. Symptoms may include bruising behind the ears, bruising around the eyes, or blood behind the ear drum. A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak occurs in about 20% of cases and may result in fluid leaking from the nose or ear. Meningitis occurs in about 14% of cases. Other complications include injuries to the cranial nerves or blood vessels.

Bernissartia is an extinct genus of neosuchian crocodyliform that lived in the Early Cretaceous, around 130 million years ago.

Mighty Max was a series of toys that were manufactured by Bluebird Toys PLC in the UK in 1992. The toys were similar to the earlier Polly Pocket toyline, but these toys were marketed primarily towards young boys. In Canada and the United States, they were distributed by Irwin Toy Limited and Mattel Inc. respectively. The original toyline consisted mainly of "Doom Zones" and "Horror Heads". "Doom Zones" were small playsets with a horror theme and featured miniature figurines of menacing creatures and the hero Max, a young boy with blond hair, jeans, a white t-shirt with a red "M" on it, and a baseball cap which also always had an "M" on it. The "Horror Heads" were smaller-sized playsets, also shaped like the heads of creatures and contained miniature figures. It was later adapted into a TV series, as well as a tie-in video game The Adventures of Mighty Max produced by Ocean Software for the Super NES and Mega Drive/Genesis.

Teshik-Tash 1 is a Neanderthal skeleton discovered in 1938 in Teshik-Tash Cave, in the Bajsuntau mountain range, Uzbek SSR (Uzbekistan), Central Asia.

Psephoderma is a genus of placodonts very similar to the related genera Placochelys and Cyamodus. Psephoderma had a flattened skull and a narrow, straight rostrum, much narrower than that of its relatives. Inside this skull, embedded in the jaws, were rounded teeth specialized for crushing the shellfish it ate. Unlike henodontid placodonts, Psephoderma's carapace was divided into two pieces, one on the shoulders and back, and another on the ventral end. Psephoderma grew to 180 centimetres (5.9 ft) long, larger than many of its relatives, and lived in the Late Triassic, about 210 million years ago. It was one of the last placodonts to live. Fossils of Psephoderma have been found in the Rhaetian deposits in the Alps and in England, hence the specific names.
"Dough" is the fourth episode of the third series of British television sitcom, Bottom. It was first broadcast on 27 January 1995.
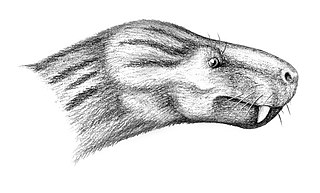
Charassognathus is an extinct genus of Late Permian cynodonts. Described in 2007 from a locality near Fraserburg, South Africa, Charassognathus is one of the earliest and most basal cynodonts. It is known only from the holotype, which dates from the Late Permian Period. The type and only species is C. gracilis. The holotype, found in the Tropidostoma Assemblage Zone of the Teekloof Formation, is made up of a crushed skull, partial lower jaw and one leg.

The Bitch Is Back is a studio album by American heavy metal band Bitch, released in 1987 on Metal Blade Records. It gets its name from the cover version of the Elton John song "The Bitch Is Back". AllMusic's Alex Henderson gave the records 4.5 stars, calling it a reminder of "how brutally fun real metal can be".

Boii is an extinct genus of microsaur within the family Tuditanidae. It was found in Carboniferous coal from mines near the community of Kounov in the Czech Republic. The only remains of the genus consist of a crushed skull, shoulder girdle bones, and scales, which were similar to microsaurian elements originally referred to Asaphestera. Boii can be characterized by its heavily sculptured skull, thin ventral plate of the clavicles, and a larger number of fangs on the roof of the mouth. For many years the type and only known species, Boii crassidens, was considered to be a species of Sparodus, until 1966 when Robert Carroll assigned it to its own genus.
Seed of the woman or offspring of the woman is a phrase from the Book of Genesis: as a result of the serpent's temptation of Eve, which resulted in the fall of man, God announces that he will put an enmity between the seed of the serpent and the seed of the woman. In Christianity, this verse is known as the protoevangelium, and is interpreted as a prophecy of the coming of Jesus. In Judaism, the "seed of the woman" is taken as a collective reference to humankind in general.

Helen Ballentine, known professionally as Skullcrusher, is an American indie folk singer-songwriter and musician.

Caiman wannlangstoni is an extinct species of caiman that lived in what is now the Amazon Basin and surrounding areas during the Middle and Late Miocene. Fossils of C. wannlangstoni have been found in the Pebas Formation near Iquitos in Peru and include partial skulls and isolated skull bones. Other fossils were uncovered from the Urumaco Formation in Venezuela and the Laventan Honda Group of Colombia. The species was first described in 2015. Features that in combination distinguish C. wannlangstoni from other caimans include a deep snout, a wavy upper jaw margin, a large and upward-directed narial opening, and blunt teeth at the back of the jaws. Based on the sizes of the skulls, its estimated body length is about 211 to 227 centimetres.

Kuttanacaiman is a monotypic genus of extinct caiman represented by the type species Kuttanacaiman iquitosensis. Kuttanacaiman lived in what is now the Amazon basin during the Middle Miocene, approximately 13 million years ago (Ma). The species was named in 2015 on the basis of one nearly complete skull and a second partial skull from the Pebas Formation near Iquitos, Peru. K. iquitosensis is characterized by a short, rounded snout and blunt teeth at the back of its jaws that were likely adapted to crushing freshwater bivalves. Its estimated total body length is 171.2 to 189.1 centimetres.

Aurelio Herrera was an American professional boxer in the featherweight and lightweight divisions.
Caiman brevirostris is an extinct species of caiman that lived during the Late Miocene, around 11.6 million years ago, to the end of the Miocene 5.3 million years ago in Acre and Amazonas, Brazil as well as Urumaco, Venezuela. Several specimens have been referred to the species, but only 3 of them are confidently placed in the species. C. brevirostris was originally named in 1987 on the basis of a single, incomplete rostrum with an associated mandibular ramus that had been found in Acre, Brazil. C. brevirostris is very distinct among Caiman species and caimaninae overall in that it preserves a characteristically short and robust skull that bears blunt posterior teeth that were built to break down harder foods. This was an adaption for durophagy, likely to crush shells of mollusks and clams which were common in the wetlands that C. brevirostris resided in.














