Related Research Articles

The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is a family of single-seat, single-engine, all-weather stealth multirole fighters. The fifth-generation combat aircraft is designed to perform ground-attack and air-superiority missions. It has three main models: the F-35A conventional takeoff and landing (CTOL) variant, the F-35B short take-off and vertical-landing (STOVL) variant, and the F-35C carrier-based catapult-assisted take-off but arrested recovery (CATOBAR) variant. The F-35 descends from the Lockheed Martin X-35, the winning design of the Joint Strike Fighter (JSF) program. It is built by Lockheed and many subcontractors, including Northrop Grumman, Pratt & Whitney, and BAE Systems.

The Trident missile is a submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) equipped with multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRV). Originally developed by Lockheed Missiles and Space Corporation, the missile is armed with thermonuclear warheads and is launched from nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs). Trident missiles are carried by fourteen US Navy Ohio-class submarines, with American warheads, and four Royal Navy Vanguard-class submarines, with British warheads. The missile is named after the mythological trident of Neptune.

The MGM-140 Army Tactical Missile System (ATacMS) is a surface-to-surface missile (SSM) manufactured by the American company Lockheed Martin. It has a range of over 100 miles (160 km), with solid propellant, and is 13 feet (4.0 m) high and 24 inches (610 mm) in diameter.
The GBU-10 Paveway II is an American Paveway-series laser-guided bomb, based on the Mk 84 general-purpose bomb, but with laser seeker and wings for guidance. Introduced into service c. 1976. Used by USAF, US Navy, US Marine Corps, Royal Australian Air Force and various NATO air forces.

Paveway is a series of laser-guided bombs (LGBs).

The People's Republic of China has developed and possesses weapons of mass destruction, including chemical and nuclear weapons. The first of China's nuclear weapons tests took place in 1964, and its first hydrogen bomb test occurred in 1967. Tests continued until 1996, when China signed the Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty (CTBT). China has acceded to the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention (BWC) in 1984 and ratified the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC) in 1997.
The Lockheed Martin FB-22 was a proposed bomber aircraft intended to enter service with the United States Air Force. Its design was derived from the F-22 Raptor. The FB-22 was canceled following the 2006 Quadrennial Defense Review.

The M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System is an armored, self-propelled, multiple rocket launcher; a type of rocket artillery.

The Lockheed Martin Sniper is a targeting pod for military aircraft that provides positive target identification, autonomous tracking, GPS coordinate generation, and precise weapons guidance from extended standoff ranges.
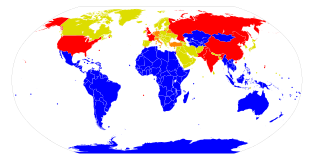
Nuclear sharing is a concept in NATO's policy of nuclear deterrence, which involves member countries without nuclear weapons of their own in the planning for the use of nuclear weapons by NATO. In particular, it provides for the armed forces of those countries to be involved in delivering nuclear weapons in the event of their use.

The GBU-57A/BMassive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP) is a precision-guided, 30,000-pound (14,000 kg) "bunker buster" bomb used by the United States Air Force. This is substantially larger than the deepest penetrating bunker busters previously available, the 5,000-pound (2,300 kg) GBU-28 and GBU-37.

The AGM-158 JASSM is a low observable standoff air-launched cruise missile developed in the United States. It is a large, stealthy long-range weapon with a 1,000 pound armor piercing warhead, but a number of problems during testing delayed its introduction into service until 2009. As of 2014, the JASSM has entered foreign service in Australia, Finland, and Poland. An extended range version of the missile, the AGM-158B JASSM-ER, entered service in 2014. By September 2016, Lockheed Martin had delivered 2,000 total JASSMs comprising both variants to the USAF.

The FGM-172 SRAW, also known as the Predator SRAW, was a lightweight, close range missile system produced by Lockheed Martin, developed by Lockheed Martin and Israel Military Industries. It was designed to complement the Javelin anti-tank missile. The Predator had a longer range and was more powerful than the AT4 that it is designed to replace, but had a shorter range than the Javelin.

The Non-Line of Sight Launch System (NLOS-LS) was a self-contained missile launcher system that was under development by NETFIRES LLC, a partnership between Lockheed Martin and Raytheon. Each Container Launch Unit (CLU) holds 15 missiles, and a self-locating networked communications system. CLUs can be linked for coordinated launching, with the missiles fired and controlled remotely via autonomous vertical launch. The weapon is roughly 2 metres tall.

The Low Cost Autonomous Attack System (LOCAAS). In 1998 the U.S. Air Force and U.S. Army Lockheed Martin began to examine the feasibility of a small, affordable cruise missile weapon for use against armoured and unarmoured vehicles, materiel and personnel, and if so develop a demonstration program. The program has cost approx. $150,000,000 so far; the cost per unit is calculated to be $30,000 based on a production of 12,000 units.

A precision-guided munition is a guided munition intended to precisely hit a specific target, to minimize collateral damage and increase lethality against intended targets.
The GBU-53/B StormBreaker, previously known as the Small Diameter Bomb II, is an American air-launched, precision-guided glide bomb.

The AGM-158C LRASM is a stealthy anti-ship cruise missile under development for the United States Air Force and United States Navy by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). The LRASM was intended to pioneer more sophisticated autonomous targeting capabilities than the U.S. Navy's current Harpoon anti-ship missile, which has been in service since 1977.

The GBU-39/B Small Diameter Bomb (SDB) is a 250 lb (110 kg) precision-guided glide bomb that is intended to provide aircraft with the ability to carry a higher number of more accurate bombs. Most US Air Force aircraft will be able to carry a pack of four SDBs in place of a single 2,000 lb (907 kg) bomb.
The Long Range Stand Off Weapon (LRSO) is a nuclear-tipped air-launched cruise missile under development that will replace AGM-86 ALCM. As of August 24, 2017, Raytheon and Lockheed Martin received separate $900 million contracts from the Department of Defense and US Air Force and are developing their own versions. Contracts will end in 2022, when the Department of Defense will select one design to continue further developments.
References
- 1 2 Warrick, Joby; Finn, Peter (April 26, 2010). "Amid outrage over civilian deaths in Pakistan, CIA turns to smaller missiles". The Washington Post . Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ↑ "Scorpion Small Smart Weapon" (PDF). National Defense Industrial Association . Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ↑ Lockheed Martin Develops a Lightweight Precision Weapon for Tactical UAVs - Defense-Update.com, 1 May 2012