Political parties
- Social Credit Party, multiple parties
Social credit may refer to:
The New Democratic Party of British Columbia is a provincial political party in British Columbia, Canada. The party espouses social democracy and sits on the centre-left of the political spectrum. The NDP is one of the two major parties in British Columbia (BC); since the 1990s, its rival is the centre-right BC United. The BC NDP is formally affiliated with the federal New Democratic Party and serves as its provincial branch.
Social credit is a distributive philosophy of political economy developed by C. H. Douglas. Douglas attributed economic downturns to discrepancies between the cost of goods and the compensation of the workers who made them. To combat what he saw as a chronic deficiency of purchasing power in the economy, Douglas prescribed government intervention in the form of the issuance of debt-free money directly to consumers or producers in order to combat such discrepancy.

Ernest Charles Manning was a Canadian politician and the eighth premier of Alberta between 1943 and 1968 for the Social Credit Party of Alberta. He served longer than any other premier in the province's history and was the second longest-serving provincial premier in Canadian history.

The British Columbia Social Credit Party, whose members are known as Socreds, was the governing provincial political party of British Columbia, Canada, for all but three years between the 1952 provincial election and the 1991 election. For four decades, the party dominated the British Columbian political scene, with the only break occurring between the 1972 and 1975 elections when the British Columbia New Democratic Party governed.
The name Social Credit Party has been used by a number of political parties.

The 1972 Canadian federal election was held on October 30, 1972, to elect members of the House of Commons of Canada of the 29th Parliament of Canada. It resulted in a slim victory for the governing Liberal Party led by Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau, which won 109 seats, compared to 107 seats for the opposition Progressive Conservatives led by Robert Stanfield. Trudeau's Liberals experienced a decline in support as a result of rising unemployment.

The New Zealand Social Credit Party was a political party that was New Zealand's third party from the 1950s to the 1980s. It won representation in the New Zealand House of Representatives, holding one seat at times between 1966 and 1981, and two seats from 1981 to 1987. While Social Credit once had significant support, particularly as a protest vote, it was disadvantaged by first-past-the-post voting as it had no geographically concentrated vote. Its most identifiable leaders were Vernon Cracknell (1963-70), who served just one term in parliament, and the household name Bruce Beetham, who rebuilt the party into a significant political force. At its zenith under Beetham in 1981, Social Credit achieved an unprecedented 20.7% of the vote.

The 1984 Canadian federal election was held on September 4, 1984, to elect members to the House of Commons of the 33rd Parliament of Canada.

Alberta Social Credit was a provincial political party in Alberta, Canada, that was founded on social credit monetary policy put forward by Clifford Hugh Douglas and on conservative Christian social values. The Canadian social credit movement was largely an out-growth of Alberta Social Credit. The Social Credit Party of Canada was strongest in Alberta, before developing a base in Quebec when Réal Caouette agreed to merge his Ralliement créditiste movement into the federal party. The British Columbia Social Credit Party formed the government for many years in neighbouring British Columbia, although this was effectively a coalition of centre-right forces in the province that had no interest in social credit monetary policies.

The Social Credit Party of Canada, colloquially known as the Socreds, was a populist political party in Canada that promoted social credit theories of monetary reform. It was the federal wing of the Canadian social credit movement.
The Abolitionist Party of Canada was a Canadian political party founded by perennial candidate John Turmel. The party ran on a platform of monetary reform, including the abolition of interest rates and the income tax; the use of the local employment trading system of banking; and introducing a form of Social Credit with monthly dividends being paid out to each Canadian.
Historically in Quebec, Canada, there were a number of political parties that were part of the Canadian social credit movement. There were various parties at different times with different names at the provincial level, all broadly following the social credit philosophy; at various times they had varying degrees of affiliation with the Social Credit Party of Canada at the federal level.

John C. Turmel is a perennial candidate for election in Canada, and according to the Guinness World Records holds the records for the most elections contested and for the most elections lost, having contested 110 elections and lost 109. The other contest was a by-election that was pre-empted by a general election call.

The 1958 Canadian federal election was held to elect members of the House of Commons of Canada of the 24th Parliament of Canada on March 31, 1958, just nine months after the 23rd election. It transformed Prime Minister John Diefenbaker's minority into the largest majority government in Canadian history and the second-largest percentage of the popular vote. Although the Tories would surpass their 1958 seat total in the 1984 election, the 1958 result remains unmatched both in terms of percentage of seats (78.5%) and the size of the government majority over all opposition parties. Voter turnout was 79.4%.
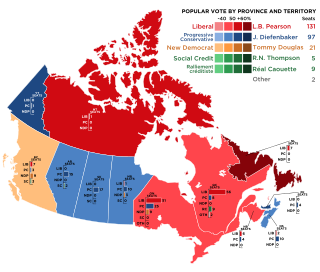
The 1965 Canadian federal election was held on November 8, 1965 to elect members of the House of Commons of Canada of the 27th Parliament of Canada. The Liberal Party of Prime Minister Lester B. Pearson was re-elected with a larger number of seats in the House. Although the Liberals lost a small share of the popular vote, they were able to win more seats, falling just short of a majority.
CDS, CDs, Cds, etc. may refer to:
The Social Credit Party of Saskatchewan was a political party in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan that promoted social credit economic theories from the mid-1930s to the mid-1970s.
Conservatism in Canada is generally considered a movement which is primarily represented by the modern-day Conservative Party of Canada in federal party politics, as well as various centre-right and right-wing parties at the provincial level. Far-right politics have never been a prominent force in Canadian society. The first party which called itself "Conservative" in what would become Canada was elected in the Province of Canada election of 1854.
The Politics of British Columbia involve not only the governance of British Columbia, Canada, and the various political factions that have held or vied for legislative power, but also a number of experiments or attempts at political and electoral reform.
Populism in Canada has been part of the country's political culture through its history and across the political spectrum. Populist parties and movements have included the Canadian social credit movement which achieved electoral strengths in Western Canada and to some extent in Quebec in the early to mid 20th century, and the Reform Party of Canada which became the largest conservative party in Parliament from a base in Western Canada in the 1990s.