
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow tinged skin. The virus persists in the liver, becoming chronic, in about 70% of those initially infected. Early on, chronic infection typically has no symptoms. Over many years however, it often leads to liver disease and occasionally cirrhosis. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will develop serious complications such as liver failure, liver cancer, or dilated blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach.

Gilead Sciences, Inc. is an American biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Foster City, California that focuses on researching and developing antiviral drugs used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, influenza, and COVID-19, including ledipasvir/sofosbuvir and sofosbuvir. Gilead is a member of the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index and the S&P 500.

Boceprevir is a protease inhibitor used to treat hepatitis caused by hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1. It binds to the HCV nonstructural protein 3 active site.

Nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) is a zinc-binding and proline-rich hydrophilic phosphoprotein that plays a key role in Hepatitis C virus RNA replication. It appears to be a dimeric form without trans-membrane helices.

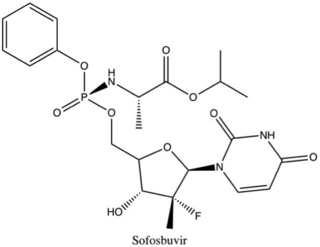
Sofosbuvir, sold under the brand name Sovaldi among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is taken by mouth.
Daclatasvir, sold under the brand name Daklinza, is an antiviral medication used in combination with other medications to treat hepatitis C (HCV). The other medications used in combination include sofosbuvir, ribavirin, and interferon, vary depending on the virus type and whether the person has cirrhosis. It is taken by mouth.

Simeprevir, sold under the brand name Olysio among others, is a medication used in combination with other medications for the treatment of hepatitis C. It is specifically used for hepatitis C genotype 1 and 4. Medications it is used with include sofosbuvir or ribavirin and peginterferon-alfa. Cure rates are in 80s to 90s percent. It may be used in those who also have HIV/AIDS. It is taken by mouth once daily for typically 12 weeks.

John Charles Martin was an American billionaire businessman, and the former executive chairman (2016–2018) and CEO (1996–2016) of the American biotechnology company Gilead Sciences. He joined Gilead Sciences in 1990 as vice president for research and development. Gilead is known for developing drugs such as Atripla and commercializing Sovaldi (sofosbuvir) for the treatment of the liver virus hepatitis C. Martin is the recipient of a number of awards, including the Biotechnology Heritage Award (2017).
Ledipasvir is a drug for the treatment of hepatitis C that was developed by Gilead Sciences. After completing Phase III clinical trials, on February 10, 2014, Gilead filed for U.S. approval of a ledipasvir/sofosbuvir fixed-dose combination tablet for genotype 1 hepatitis C. The ledipasvir/sofosbuvir combination is a direct-acting antiviral agent that interferes with HCV replication and can be used to treat patients with genotypes 1a or 1b without PEG-interferon or ribavirin.

Dasabuvir, sold under the brand name Exviera, is an antiviral medication for the treatment of hepatitis C. It is often used together with the combination medication ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir specifically for hepatitis C virus (HCV) type 1. Ribavirin may also additionally be used. These combinations result in a cure in more than 90% of people. It is taken by mouth.
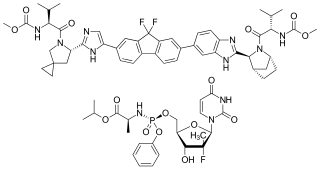
Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir, sold under the trade name Harvoni among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is a fixed-dose combination of ledipasvir and sofosbuvir. Cure rates are 94% to 99% in people infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1. Some evidence also supports use in HCV genotype 3 and 4. It is taken daily by mouth for 8–24 weeks.
Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, sold under the brand name Technivie among others, is a medication used to treat hepatitis C. It is a fixed-dose combination of ombitasvir, paritaprevir, and ritonavir. Specifically it is used together with dasabuvir or ribavirin for cases caused by hepatitis C virus genotype 1 or 4. Cure rates are around 95%. It is taken by mouth.
Elbasvir/grazoprevir, sold under the brand name Zepatier, is a fixed-dose combination for the treatment of hepatitis C, containing elbasvir and grazoprevir. It is used to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes 1 or 4 infection in both treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced patients.
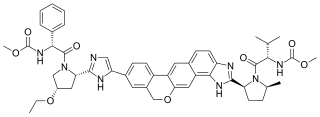
Velpatasvir is an NS5A inhibitor which is used together with sofosbuvir in the treatment of hepatitis C infection of all six major genotypes.

Daclatasvir/sofosbuvir is a two-drug combination for the treatment of hepatitis C. It is given as a single daily pill containing daclatasvir, a viral NS5A inhibitor, and sofosbuvir, a nucleotide inhibitor of the viral RNA polymerase NS5B.

Voxilaprevir is a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural (NS) protein 3/4A protease inhibitor that is used in combination with sofosbuvir and velpatasvir. The combination has the trade name Vosevi and received a positive opinion from the European Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use in June 2017.
Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir, sold under the brand name Epclusa among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication for the treatment of hepatitis C in adults. It combines sofosbuvir and velpatasvir. It is more than 90% effective for hepatitis C genotypes one through six. It also works for hepatitis C in those who also have cirrhosis or HIV/AIDS. It is taken by mouth.
Glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (G/P), sold under the brand names Mavyret and Maviret, is a fixed-dose combination medication used to treat hepatitis C. It contains glecaprevir and pibrentasvir. It works against all six types of hepatitis C. At twelve weeks following treatment between 81% and 100% of people have no evidence of hepatitis C. It is taken once a day by mouth with food.
Non-structural protein 5B (NS5B) inhibitors are a class of direct-acting antivirals widely used in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Depending on site of action and chemical composition, NS5B inhibitors may be categorized into three classes—nucleoside active site inhibitors (NIs), non-nucleoside allosteric inhibitors, and pyrophosphate analogues. Subsequently, all three classes are then subclassified. All inhibit RNA synthesis by NS5B but at different stages/sites resulting in inability of viral RNA replication. Expression of direct-acting NS5B inhibitors does not take place in cells that are not infected by hepatitis C virus, which seems to be beneficial for this class of drugs.
The term Direct-acting antivirals (DAA) has long been associated with the combination of antiviral drugs used to treat hepatitis C infections. These are the more effective than older treatments such as ribavirin and interferon. The DAA drugs against hepatitis C are taken orally, as tablets, for 8 to 12 weeks. The treatment depends on the type or types (genotypes) of hepatitis C virus that are causing the infection. Both during and at the end of treatment, blood tests are used to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and subsequent cure.












