Related Research Articles

The economy of Azerbaijan is highly dependent on oil and gas exports, in particular since the completion of the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan Pipeline. The transition to oil production in the late 1990s led to rapid economic growth over the period 1995–2014. Since 2014, GDP growth has slowed down substantially.

A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin valva, the moving part of a door, in turn from volvere, to turn, roll.

An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may be termed a gas well. Wells are created by drilling down into an oil or gas reserve and if necessary equipped with extraction devices such as pumpjacks. Creating the wells can be an expensive process, costing at least hundreds of thousands of dollars, and costing much more when in difficult-to-access locations, e.g., offshore. The process of modern drilling for wells first started in the 19th century but was made more efficient with advances to oil drilling rigs and technology during the 20th century.

The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation, and marketing of petroleum products. The largest volume products of the industry are fuel oil and gasoline (petrol). Petroleum is also the raw material for many chemical products, including pharmaceuticals, solvents, fertilizers, pesticides, synthetic fragrances, and plastics. The industry is usually divided into three major components: upstream, midstream, and downstream. Upstream regards exploration and extraction of crude oil, midstream encompasses transportation and storage of crude, and downstream concerns refining crude oil into various end products.

In petroleum and natural gas extraction, a Christmas tree, or tree, is an assembly of valves, casing spools, and fittings used to regulate the flow of pipes in an oil well, gas well, water injection well, water disposal well, gas injection well, condensate well, and other types of well.

A crankcase ventilation system (CVS) removes unwanted gases from the crankcase of an internal combustion engine. The system usually consists of a tube, a one-way valve and a vacuum source.

A blowout is the uncontrolled release of crude oil and/or natural gas from an oil well or gas well after pressure control systems have failed. Modern wells have blowout preventers intended to prevent such an occurrence. An accidental spark during a blowout can lead to a catastrophic oil or gas fire.
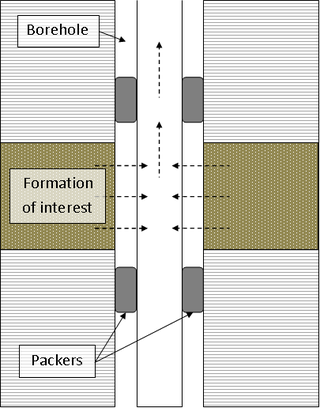
A drill stem test (DST) is a procedure for isolating and testing the pressure, permeability and productive capacity of a geological formation during the drilling of a well. The test is an important measurement of pressure behaviour at the drill stem and is a valuable way of obtaining information on the formation fluid and establishing whether a well has found a commercial hydrocarbon reservoir.

The petroleum industry in Azerbaijan produced about 33 million tonnes of oil and 35 billion cubic meters of gas in 2022. Azerbaijan is one of the birthplaces of the oil industry.
Artificial lift is the use of artificial means to increase the flow of liquids, such as crude oil or water, from a production well. Generally this is achieved by the use of a mechanical device inside the well or by decreasing the weight of the hydrostatic column by injecting gas into the liquid some distance down the well. A newer method called Continuous Belt Transportation (CBT) uses an oil absorbing belt to extract from marginal and idle wells. Artificial lift is needed in wells when there is insufficient pressure in the reservoir to lift the produced fluids to the surface, but often used in naturally flowing wells to increase the flow rate above what would flow naturally. The produced fluid can be oil, water or a mix of oil and water, typically mixed with some amount of gas.

Petroleum is a fossil fuel that can be drawn from beneath the Earth's surface. Reservoirs of petroleum are formed through the mixture of plants, algae, and sediments in shallow seas under high pressure. Petroleum is mostly recovered from oil drilling. Seismic surveys and other methods are used to locate oil reservoirs. Oil rigs and oil platforms are used to drill long holes into the earth to create an oil well and extract petroleum. After extraction, oil is refined to make gasoline and other products such as tires and refrigerators. Extraction of petroleum can be dangerous and have led to oil spills.
A multiphase flow meter is a device used to measure the individual phase flow rates of constituent phases in a given flow where oil, water and gas mixtures are initially co-mingled together during the oil production processes.
The term separator in oilfield terminology designates a pressure vessel used for separating well fluids produced from oil and gas wells into gaseous and liquid components. A separator for petroleum production is a large vessel designed to separate production fluids into their constituent components of oil, gas and water. A separating vessel may be referred to in the following ways: Oil and gas separator, Separator, Stage separator, Trap, Knockout vessel, Flash chamber, Expansion separator or expansion vessel, Scrubber, Filter. These separating vessels are normally used on a producing lease or platform near the wellhead, manifold, or tank battery to separate fluids produced from oil and gas wells into oil and gas or liquid and gas. An oil and gas separator generally includes the following essential components and features:
- A vessel that includes (a) primary separation device and/or section, (b) secondary "gravity" settling (separating) section, (c) mist extractor to remove small liquid particles from the gas, (d) gas outlet, (e) liquid settling (separating) section to remove gas or vapor from oil, (f) oil outlet, and (g) water outlet.
- Adequate volumetric liquid capacity to handle liquid surges (slugs) from the wells and/or flowlines.
- Adequate vessel diameter and height or length to allow most of the liquid to separate from the gas so that the mist extractor will not be flooded.
- A means of controlling an oil level in the separator, which usually includes a liquid-level controller and a diaphragm motor valve on the oil outlet.
- A back pressure valve on the gas outlet to maintain a steady pressure in the vessel.
- Pressure relief devices.

The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake and sometimes referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau. It covers a surface area of 371,000 km2 (143,000 sq mi), an area approximately equal to that of Japan, with a volume of 78,200 km3 (19,000 cu mi). It has a salinity of approximately 1.2%, about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast.

Instrumentation is used to monitor and control the process plant in the oil, gas and petrochemical industries. Instrumentation ensures that the plant operates within defined parameters to produce materials of consistent quality and within the required specifications. It also ensures that the plant is operated safely and acts to correct out of tolerance operation and to automatically shut down the plant to prevent hazardous conditions from occurring. Instrumentation comprises sensor elements, signal transmitters, controllers, indicators and alarms, actuated valves, logic circuits and operator interfaces.
Relief wells are used both in the natural gas and petroleum industry and in flood control.

Cameron International Corporation (formerly Cooper Cameron Corporation (CCC) and Cooper Oil Tool, Cameron Iron Works) though now operating under Schlumberger, is a global provider of pressure control, production, processing, and flow control systems as well as project management and aftermarket services for the oil and gas and process industries. Cameron was acquired by Schlumberger (SLB) in 2016, and now operates as 'Cameron, an SLB Company.' At the start of the SLB acquisition in 2015, Cameron employed approximately 23,000 people and delivered $9.8 billion in revenue.

Nobel Energy is a group of companies concentrated in the energy industry providing integrated engineering, construction, procurement and supply chain management, and drilling services. Nobel Energy is a part of NEQSOL Holding, an international group of companies, acting in energy, telecommunications, high-technology, and construction industries in the UK, the USA, Turkey, Azerbaijan, Ukraine, Georgia, Kazakhstan, and the UAE.
The main areas of machine building are the preparation of machine tools, equipment of tractors and automobiles, shipbuilding, aircraft building, Agricultural Machine Building, Electrical Engineering, Radio Engineering and automation equipment.
References
- Neft Dashlary
- NEFTEKHIMAVTOMAT Seminars on Applications of radioisotope devices and methods in the industry of Azerbaidjan [ permanent dead link ]
- Flow control valve for oil and gas wells